The United States Navy, United States Coast Guard, and United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use a hull classification symbol to identify their ships by type and by individual ship within a type. The system is analogous to the pennant number system that the Royal Navy and other European and Commonwealth navies use.

A naval ship is a military ship that is used by a navy. Naval ships are differentiated from civilian ships by construction and purpose. Generally, naval ships are damage resilient and armed with weapon systems, though armament on troop transports is light or non-existent.

A warship or combatant ship is a ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are typically faster and more maneuverable than merchant ships. Unlike a merchant ship, which carries cargo, a warship typically carries only weapons, ammunition and supplies for its crew.

A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are regarded by some as the first aircraft carriers and appeared just before the First World War.

A submarine tender, in British English a submarine depot ship, is a type of depot ship that supplies and supports submarines.

A troopship is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable to land troops directly on shore, typically loading and unloading at a seaport or onto smaller vessels, either tenders or barges.
J. Samuel White was a British shipbuilding firm based in Cowes, taking its name from John Samuel White (1838–1915).

SS Nomadic is a former tender of the White Star Line, launched on 25 April 1911 at Belfast, that is now on display in Belfast's Titanic Quarter. She was built to transfer passengers and mail to and from the ocean liners RMS Olympic and RMS Titanic. She is the only surviving vessel designed by Thomas Andrews, who also helped design those two ocean liners, and the last White Star Line vessel in existence today.

The Baltic Sea campaigns were conducted by Axis and Allied naval forces in the Baltic Sea, the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the connected lakes Ladoga and Onega on the Eastern Front of World War II. After early fighting between Polish and German forces, the main combatants were the Kriegsmarine and the Soviet Navy, with Finland supporting the Germans until 1944 and the Soviets thereafter. The Swedish Navy and merchant fleet played important roles, and the British Royal Navy planned Operation Catherine for control of the Baltic Sea and its exit choke point into the North Sea.

An auxiliary ship is a naval ship designed to support combatant ships and other naval operations. Auxiliary ships are not primary combatant vessels, though they may have some limited combat capacity, usually for purposes of self-defense.

A destroyer tender or destroyer depot ship is a type of depot ship: an auxiliary ship designed to provide maintenance support to a flotilla of destroyers or other small warships. The use of this class has faded from its peak in the first half of the 20th century as the roles and weaponry of small combatants have evolved.

USS Bridgeport (AD-10/ID-3009) was a destroyer tender in the United States Navy during World War I and the years after. She was a twin-screw, steel-hulled passenger and cargo steamship built in 1901 at Vegesack, Germany as SS Breslau of the North German Lloyd line. Breslau was one of the seven ships of the Köln class of ships built for the Bremen to Baltimore and Galveston route.

United States Navy operations during World War I began on April 6, 1917, after the formal declaration of war on the German Empire. The United States Navy focused on countering enemy U-boats in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea while convoying men and supplies to France and Italy. Because of United States's late entry into the war, her capital ships never engaged the German fleet and few decisive submarine actions occurred.

Heian Maru (平安丸) was a Japanese ocean liner launched in 1930 and operated primarily on the NYK line's trans-Pacific service between Yokohama and Seattle. Shortly before the outbreak of the Pacific War, it was requisitioned by the Imperial Japanese Navy and converted to use as an auxiliary submarine tender. In 1944 it was sunk by American aircraft at Chuuk Lagoon during Operation Hailstone. Its submerged hulk – the largest of Chuuk's "Ghost Fleet" – remains a popular scuba diving destination.
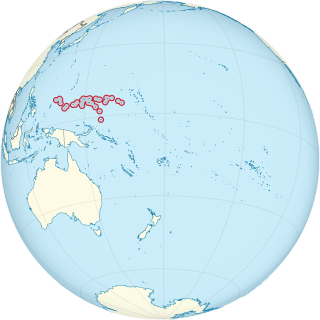
Naval Base Ulithi was a major United States Navy base at the Ulithi Atoll in the Caroline Islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea during World War II. The base was built to support the island-hopping Pacific War efforts of the Allied nations fighting the Empire of Japan. In terms of the number of ships at one base, Naval Base Ulithi was the largest naval base in the world in 1944 and 1945, with over 600 ships at times.
This glossary defines the various types of ships and accessory watercraft that have been used in service of the United States. Such service is mainly defined as military vessels used in the United States Navy and United States Coast Guard, as well as the defunct, incorporated, or renamed institutions such as the United States Revenue Cutter Service. Service of the United States can also be defined in this context as special government missions in the form of expeditions, such as the Wilkes Expedition or the North Pacific Exploring and Surveying Expedition. The scope of the glossary encompasses both the "Old Navy" of the United States, from its beginnings as the "Continental Navy", through the "New Navy" and up to modern day. The watercraft included in the glossary are derived from United States ships with logbooks published by the National Archives and Records Administration.

Naval Base Kossol Roads also called Naval Base Kossol Passage was a major United States Navy base at Kossol Roads in northern Palau in the western Caroline Islands in the western Pacific Ocean during World War II. Kossol Roads lagoon is surrounded by fringing coral reef. The base was built to support the island hopping Pacific War efforts of the allied nations fighting the Empire of Japan. In terms of the number of ships at one base, Naval Base Kossol Roads was one of the largest Naval Base in the world in 1944 and 1945. Naval Base Kossol Roads was unique, as it was the only large US Naval base to have no shore facilities. Kossol Roads was part of US Naval Base Carolines.


















