
The number e, also known as Euler's number, is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828 that can be characterized in many ways. It is the base of natural logarithms. It is the limit of (1 + 1/n)n as n approaches infinity, an expression that arises in the study of compound interest. It can also be calculated as the sum of the infinite series

In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn . The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors start the sequence from 1 and 1 or sometimes from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the first few values in the sequence are:

In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities and with ,
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is en, plural ens.
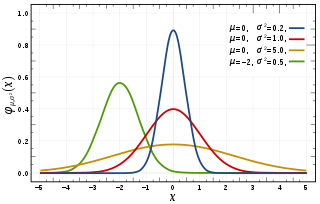
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
The number π is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number π appears in many formulae across mathematics and physics. It is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such as are commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an equation involving only finite sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of π implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of π appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found.
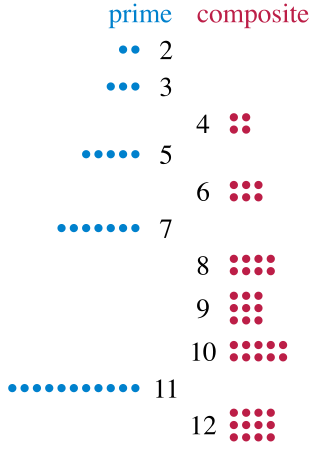
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.
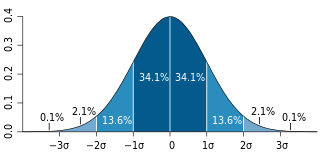
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range.

In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the mid-18th century.

In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. It is the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by , , , , or .
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures.

Guns N' Roses is an American hard rock band from Los Angeles, California, formed in March 1985 when local bands Hollywood Rose and L.A. Guns merged. When they signed to Geffen Records in 1986, the band's "classic lineup" consisted of vocalist Axl Rose, lead guitarist Slash, rhythm guitarist Izzy Stradlin, bassist Duff McKagan, and drummer Steven Adler. The current lineup consists of Rose, Slash, McKagan, guitarist Richard Fortus, drummer Frank Ferrer and keyboardists Dizzy Reed and Melissa Reese.
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has garnered attention throughout history in part because distal extremities in humans typically contain five digits.

Trogiomorpha is one of the three major suborders of barklice, booklice, and parasitic lice in the order Psocodea, alongside Troctomorpha and Psocomorpha. There are about 8 families and more than 430 described species in Trogiomorpha. Trogiomorpha is widely agreed to be the earliest diverging of the three suborders, and retains the most primitive characteristics.

Psocodea is a taxonomic group of insects comprising the bark lice, book lice and parasitic lice. It was formerly considered a superorder, but is now generally considered by entomologists as an order. Despite the greatly differing appearance of parasitic lice (Phthiraptera), they are believed to have evolved from within the former order Psocoptera, which contained the bark lice and book lice, now found to be paraphyletic. They are often regarded as the most primitive of the hemipteroids. Psocodea contains around 11,000 species, divided among four suborders and more than 70 families. They range in size from 1–10 millimetres (0.04–0.4 in) in length.

Neotrogla is a genus of barklice noted for its reversed sex roles and organs, traits shared by all species of the genus.
Afrotrogla is an African genus of large-winged psocids in the family Prionoglarididae, discovered and described by Charles Lienhard. There are three described species in Afrotrogla, all found in certain caves of Namibia.
Sensitibilla is an African genus of large-winged psocids in the family Prionoglarididae, discovered and described by Charles Lienhard. It contains four species.
Speleopsocus is a genus of psocids (booklice) in the family Prionoglarididae from the Tepui of Venezuela. It is monotypic, containing only one species, Speleopsocus chimanta.
Palaeosiamoglaris is a genus of fossil psocids in the family Prionoglarididae, found in mesozoic amber.











