
The First Serbian Uprising was an uprising of Serbs in Orašac against the Ottoman Empire from 14 February 1804, to 7 October 1813. The uprising began as a local revolt against the Dahije, who had seized power in a coup d'état. It later evolved into a war for independence, known as the Serbian Revolution, after more than three centuries of Ottoman Empire rule and brief Austrian occupations.

A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in the late 13th century before entering Europe in the mid-14th century with the Bulgarian–Ottoman wars. The mid-15th century saw the Serbian–Ottoman wars and the Albanian-Ottoman wars. Much of this period was characterized by the Ottoman expansion into the Balkans. The Ottoman Empire made further inroads into Central Europe in the 15th and 16th centuries, culminating in the peak of Ottoman territorial claims in Europe.

The Russo-Turkish War of 1735–1739 between Russia and the Ottoman Empire was caused by the Ottoman Empire's war with Persia and the continuing raids by the Crimean Tatars. The war also represented Russia's ongoing struggle for access to the Black Sea. In 1737, the Habsburg monarchy joined the war on Russia's side, known in historiography as the Austro-Turkish War of 1737–1739.

The Great Turkish War or The Last Crusade, also called in Ottoman sources The Disaster Years, was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Poland-Lithuania, Venice, Russia, and the Kingdom of Hungary. Intensive fighting began in 1683 and ended with the signing of the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The war was a resounding defeat for the Ottoman Empire, which for the first time lost substantial territory, in Hungary and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as well as in part of the western Balkans. The war was significant also for being the first instance of Russia joining an alliance with Western Europe. Historians have labeled the war as the Fourteenth Crusade launched against the Turks by the papacy.

The Siege of Adrianople, was fought during the First Balkan War. The siege began on 3 November 1912 and ended on 26 March 1913 with the capture of Edirne (Adrianople) by the Bulgarian 2nd Army and the Serbian 2nd Army.

The Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718) was fought between Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz was not an acceptable permanent agreement for the Ottoman Empire. Twelve years after Karlowitz, it began the long-term prospect of taking revenge for its defeat at the Battle of Vienna in 1683. First, the army of Turkish Grand Vizier Baltacı Mehmet defeated Peter the Great's Russian Army in the Russo-Turkish War (1710–1711). Then, during the Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718), Ottoman Grand Vizier Damat Ali reconquered the Morea from the Venetians. As the guarantor of the Treaty of Karlowitz, the Austrians threatened the Ottoman Empire, which caused it to declare war in April 1716.

The Battle of Zenta, also known as the Battle of Senta, was fought on 11 September 1697, near Zenta, Kingdom of Hungary, between Ottoman and Holy League armies during the Great Turkish War. The battle was the most decisive engagement of the war, and it saw the Ottomans suffer an overwhelming defeat by an Imperial force half as large sent by Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor.

Ottoman Serbia refers to the Ottoman period in the history of Serbia. Various regions of medieval Serbia came under Ottoman rule already at the end of the 14th century, while the Serbian Despotate fell in 1459. Northern regions of what is now the Republic of Serbia were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire during later conquests, from 1521 to 1552. Since the Habsburg expansion towards those northern regions, in 1699 and 1718, Ottoman rule was gradually reduced to Serbian territories south of the Sava and Danube rivers (1739). From 1804 to 1830, the Principality of Serbia was gradually restored, as a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. It gained independence in 1878, and expanded into southern regions, thus reducing Ottoman control to the historical region of the Old Serbia, that was liberated in 1912, thus ending Ottoman rule in Serbian lands.

The Sanjak of Smederevo, also known in historiography as the Pashalik of Belgrade, was an Ottoman administrative unit (sanjak) centered on Smederevo, that existed between the 15th and the outset of the 19th centuries. It was located in the territory of present-day Central Serbia.
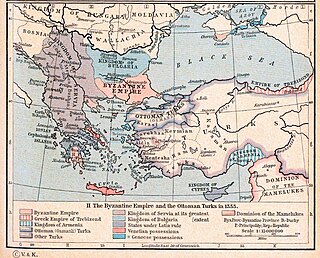
The Great Migrations of the Serbs, also known as the Great Exoduses of the Serbs, were two migrations of Serbs from various territories under the rule of the Ottoman Empire to the Kingdom of Hungary under the Habsburg monarchy.
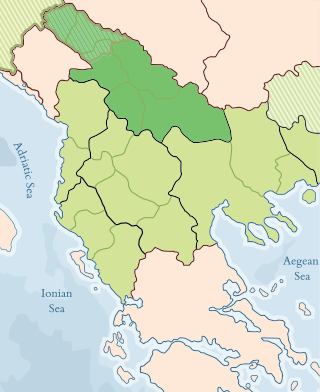
Kosovo was part of the Ottoman Empire from 1455 to 1913, originally as part of the eyalet of Rumelia, and from 1864 as a separate Kosovo vilayet.

The Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th to the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy, which was at times supported by the Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, The Holy Roman Empire, and Habsburg Spain. The wars were dominated by land campaigns in Hungary, including Transylvania and Vojvodina, Croatia, and central Serbia.

The Seventh Ottoman–Venetian War was fought between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire between 1714 and 1718. It was the last conflict between the two powers, and ended with an Ottoman victory and the loss of Venice's major possession in the Greek peninsula, the Peloponnese (Morea). Venice was saved from a greater defeat by the intervention of Austria in 1716. The Austrian victories led to the signing of the Treaty of Passarowitz in 1718, which ended the war.

The siege of Scutari, also referred to as the siege of Shkodër, known in Turkish as İşkodra Müdafaası(in Turkish) or İşkodra Savunması, took place from 28 October 1912 to 23 April 1913 when the army of the Kingdom of Montenegro defeated the forces of the Ottoman Empire and invaded Shkodër.

The siege of Belgrade was a successful attempt by Habsburg troops under the command of the Elector of Bavaria Maximilian II Emanuel to capture the city of Belgrade from the Ottoman Empire. Part of the Great Turkish War (1683–1699), the siege lasted a month and culminated in the capture of the city on 6 September 1688. By conquering Belgrade, Habsburg forces gained an important strategic outpost, as the city had been the Ottoman's chief fortress in Europe for more than a century and a half. The Ottomans recaptured the city two years later, in October 1690. In 1693, Habsburg forces attempted to capture the city again, but failed.

In the siege of Belgrade a Habsburg Austrian army led by Feldmarschall Ernst Gideon von Laudon besieged an Ottoman Turkish force under Osman Pasha in the fortress of Belgrade. After a three-week leaguer, the Austrians forced the surrender of the fortress. During the campaign which was part of the Austro-Turkish War, the Austrian army was greatly hampered by illness. Austria held the city until 1791 when it handed Belgrade back to the Ottomans according to the terms of the peace treaty. Several Austrian soldiers who distinguished themselves during the siege later held important commands in the subsequent French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Belgrade is the capital of modern Serbia.

The siege of Belgrade was a successful attempt by Habsburg forces under the command of Prince Eugene of Savoy to capture the strategically important city of Belgrade from the Ottoman Empire. It took place during the Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718), barely a year after the Habsburg victory at the Battle of Petrovaradin (Peterwardein). The Imperial Army routed the Ottoman relief army under Grand Vizier Hacı Halil Pasha on 16 August. As a consequence, the Belgrade garrison, deprived of relief, surrendered to Habsburg forces on 21 August. The Ottoman Sultan Ahmed III sued for peace, resulting in the Treaty of Passarowitz a year later, which completed the transfer of the remainder of Hungary, the Banat of Temeswar with lower Syrmia, and the city of Belgrade with central Serbia into Habsburg hands.

The capture of Belgrade was the recapture of Belgrade by the Ottoman Empire in 1739.

The siege of Belgrade in 1521 is an event that followed as a result of the third major Ottoman attack on this Hungarian stronghold in the Ottoman–Hungarian wars at the time of the greatest expansion of the Ottoman Empire to the west. Ottoman Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent launched his army in mid-May 1521. The Hungarian state was almost in disarray and unable to effectively counter the Ottoman army.

Habsburg-occupied Serbia refers to the period between 1686 and 1699 of the Great Turkish War, during which various regions of present-day Serbia were occupied by the Habsburg monarchy. In those regions, Habsburg authorities have established various forms of provisional military administration, including the newly organized Serbian Militia. By the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699, some of those regions remained under the permanent Habsburg rule, while others were returned to the Ottoman Empire.




















