Anastrozole, sold under the brand name Arimidex among others, is an antiestrogenic medication used in addition to other treatments for breast cancer. Specifically it is used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. It has also been used to prevent breast cancer in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth.

Toremifene, sold under the brand name Fareston among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women. It is taken by mouth.

Lasofoxifene, sold under the brand name Fablyn, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which is marketed by Pfizer in Lithuania and Portugal for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and for the treatment of vaginal atrophy, and the result of an exclusive research collaboration with Ligand Pharmaceuticals (LGND). It also appears to have had a statistically significant effect of reducing breast cancer in women according to a study published in The Journal of the National Cancer Institute.

Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are a class of drugs that selectively activate the androgen receptor in specific tissues, promoting muscle and bone growth while having less effect on male reproductive tissues like the prostate gland.

Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen. The drug is under development under the tentative brand name TamoGel as a topical gel for the treatment of hyperplasia of the breast. It has completed a phase II clinical trial for cyclical mastalgia, but further studies are required before afimoxifene can be approved for this indication and marketed.
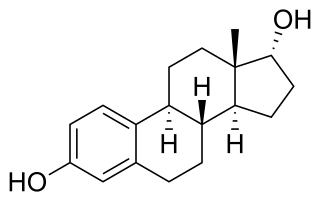
Alfatradiol, also known as 17α-estradiol and sold under the brand names Avicis, Avixis, Ell-Cranell Alpha, and Pantostin, is a weak estrogen and 5α-reductase inhibitor medication which is used topically in the treatment of pattern hair loss in men and women. It is a stereoisomer of the endogenous steroid hormone and estrogen 17β-estradiol.

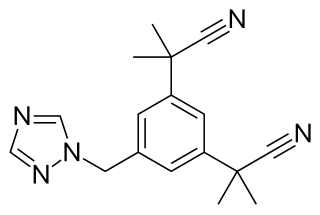
Acolbifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which, as of 2015, is in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of breast cancer.

Brilanestrant (INN) is a nonsteroidal combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was discovered by Aragon Pharmaceuticals and was under development by Genentech for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer.

Erteberel is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen which acts as a selective ERβ agonist and was under development by Eli Lilly for the treatment of schizophrenia. It was specifically under investigation for the treatment of negative symptoms and cognitive impairment associated with the condition. It managed to reach phase II clinical trials for this indication in the United States in 2015. As of 2021 development has been discontinued. Erteberel was also under investigation for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and reached phase II clinical studies for this use but failed to improve symptoms in men with the condition and development for this indication was discontinued. The drug has also been proposed as a potential novel treatment for glioblastoma.

ICI-164384, also known as N-n-butyl-N-methyl-11-(3,17β-dihydroxyestra-1,3,5 -trien-7α-yl)undecanamide, is a steroidal antiestrogen and a synthetic derivative of estradiol which is closely related to fulvestrant and was never marketed. It is a silent antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) with no intrinsic estrogenic activity and hence is a pure antiestrogen, unlike selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen. The drug was under development by AstraZeneca for the treatment of breast cancer but was discontinued in favor of fulvestrant, which is very similar to ICI-164384 but is more potent in comparison.

Droloxifene, also known as 3-hydroxytamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was developed originally in Germany and later in Japan for the treatment of breast cancer, osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women, and cardiovascular disorders but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase II and phase III clinical trials for these indications before development was discontinued in 2000. The drug was found to be significantly less effective than tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer in two phase III clinical trials.

Miproxifene (INN) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed. It is a derivative of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen) in which an additional 4-isopropyl group is present in the β-phenyl ring. The drug has been found to be 3- to 10-fold more potent than tamoxifen in inhibiting breast cancer cell growth in in vitro models. Miproxifene is the active metabolite of miproxifene phosphate (TAT-59), a phosphate ester and prodrug of miproxifene that was developed to improve its water solubility. Miproxifene phosphate was under development for the treatment of breast cancer and reached phase III clinical trials for this indication but development was discontinued.

Miproxifene phosphate is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was under development in Japan for the treatment of breast cancer but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase III clinical trials for this indication before development was discontinued. The drug is a phosphate ester and prodrug of miproxifene (DP-TAT-59) with improved water solubility that was better suited for clinical development. Miproxifene has been found to be 3- to 10-fold as potent as tamoxifen in inhibiting breast cancer cell growth in in vitro models. It is a derivative of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen) in which an additional 4-isopropyl group is present in the β-phenyl ring.
Tesmilifene, also known as N,N-diethyl-2-(4-phenylmethyl)ethanamine (DPPE), is a small-molecule antineoplastic drug and chemopotentiator that was under development by YM BioSciences for the treatment of breast cancer in the 2000s but was never marketed. It reached phase III clinical trials for advanced/metastatic breast cancer before development was discontinued.
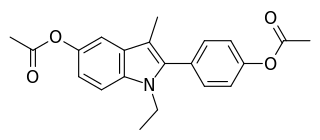
Zindoxifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that was under development in the 1980s and early 1990s for the treatment of breast cancer but was not marketed. It showed estrogenic-like activity in preclinical studies and failed to demonstrate effectiveness as a treatment for breast cancer in clinical trials. Zindoxifene was the lead compound of the distinct 2-phenylindole class of SERMs, and the marketed SERM bazedoxifene was derived from the major active metabolite of zindoxifene, D-15414. Zindoxifene was first described in 1984.
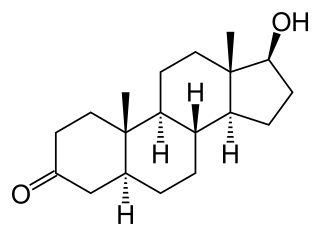
Androstanolone, or stanolone, also known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and sold under the brand name Andractim among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication and hormone which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used to treat breast development and small penis in males. Compared to testosterone, androstanolone (DHT) is less likely to aromatize into estrogen, and therefore it shows less pronounced estrogenic side effects, such as gynecomastia and water retention. On the other hand, androstanolone (DHT) show more significant androgenic side effects, such as acne, hair loss and prostate enlargement.

EM-5854 is a steroidal antiandrogen which was under development by Endoceutics, Inc. for the treatment of prostate cancer. It was first described in a patent in 2008, and was further characterized in 2012. EM-5854 reached phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of prostate cancer but development was discontinued in March 2019.

NC 45-0095 is a synthetic nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which was under development by Novo Nordisk for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis but was never marketed. It is a partial agonist of the estrogen receptor (IC50Tooltip half-maximal inhibitory concentration (for binding inhibition) = 9.5 nM; EC50Tooltip half-maximal effective concentration = 13 nM) with mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity, and shows full estrogenic activity in bone and uterus (EmaxTooltip maximal efficacy (relative to moxestrol, in Ishikawa endometrial cancer cell line) = 105%). The compound is a pyrroloindolizine derivative. Its development was discontinued by 2003.

















