
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonist/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on the estrogen receptor (ER). A characteristic that distinguishes these substances from pure ER agonists and antagonists is that their action is different in various tissues, thereby granting the possibility to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.

Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has been used for Albright syndrome. Tamoxifen is typically taken daily by mouth for five years for breast cancer.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors, which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER).

Toremifene, sold under the brand name Fareston among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women. It is taken by mouth.

Lasofoxifene, sold under the brand name Fablyn, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which is marketed by Pfizer in Lithuania and Portugal for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and for the treatment of vaginal atrophy, and the result of an exclusive research collaboration with Ligand Pharmaceuticals (LGND). It also appears to have had a statistically significant effect of reducing breast cancer in women according to a study published in The Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Hormonal therapy in oncology is hormone therapy for cancer and is one of the major modalities of medical oncology, others being cytotoxic chemotherapy and targeted therapy (biotherapeutics). It involves the manipulation of the endocrine system through exogenous or external administration of specific hormones, particularly steroid hormones, or drugs which inhibit the production or activity of such hormones. Because steroid hormones are powerful drivers of gene expression in certain cancer cells, changing the levels or activity of certain hormones can cause certain cancers to cease growing, or even undergo cell death. Surgical removal of endocrine organs, such as orchiectomy and oophorectomy can also be employed as a form of hormonal therapy.
Antiestrogens, also known as estrogen antagonists or estrogen blockers, are a class of drugs which prevent estrogens like estradiol from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the estrogen receptor (ER) and/or inhibiting or suppressing estrogen production. Antiestrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiandrogens and antiprogestogens. Antiestrogens are commonly used to stop steroid hormones, estrogen, from binding to the estrogen receptors leading to the decrease of estrogen levels. Decreased levels of estrogen can lead to complications in sexual development. Antiandrogens are sex hormone antagonists which are able to lower the production and the effects that testosterone can have on female bodies.
The estrogen receptor test (ERT) is a laboratory test to determine whether cancer cells have estrogen receptors. This information can help establish how the cancer should be treated.

Ethamoxytriphetol is a synthetic nonsteroidal antiestrogen that was studied clinically in the late 1950s and early 1960s but was never marketed. MER-25 was first reported in 1958, and was the first antiestrogen to be discovered. It has been described as "essentially devoid of estrogenic activity" and as having "very low estrogenic activity in all species tested". However, some estrogenic effects in the uterus have been observed, so it is not a pure antiestrogen but is, instead, technically a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). For all intents and purposes, it is a nearly pure antiestrogen, however.

Brilanestrant (INN) is a nonsteroidal combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was discovered by Aragon Pharmaceuticals and was under development by Genentech for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer.

Elacestrant, sold under the brand name Orserdu, is an anticancer medication which is used in the treatment of breast cancer. It is taken by mouth.

Etacstil is an orally active, nonsteroidal, combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was developed for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. It was shown to overcome antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer by altering the shape of the estrogen receptor, thus exhibiting SERD properties. Etacstil is a tamoxifen derivative and one of the first drugs to overcome tamoxifen-resistance. It is the predecessor of GW-7604, of which etacstil is a prodrug. This is analogous to the case of tamoxifen being a prodrug of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen).
A hormone-sensitive cancer, or hormone-dependent cancer, is a type of cancer that is dependent on a hormone for growth and/or survival. Examples include breast cancer, which is dependent on estrogens like estradiol, and prostate cancer, which is dependent on androgens like testosterone.

ICI-164384, also known as N-n-butyl-N-methyl-11-(3,17β-dihydroxyestra-1,3,5 -trien-7α-yl)undecanamide, is a steroidal antiestrogen and a synthetic derivative of estradiol which is closely related to fulvestrant and was never marketed. It is a silent antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) with no intrinsic estrogenic activity and hence is a pure antiestrogen, unlike selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen. The drug was under development by AstraZeneca for the treatment of breast cancer but was discontinued in favor of fulvestrant, which is very similar to ICI-164384 but is more potent in comparison.

Miproxifene (INN) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed. It is a derivative of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen) in which an additional 4-isopropyl group is present in the β-phenyl ring. The drug has been found to be 3- to 10-fold more potent than tamoxifen in inhibiting breast cancer cell growth in in vitro models. Miproxifene is the active metabolite of miproxifene phosphate (TAT-59), a phosphate ester and prodrug of miproxifene that was developed to improve its water solubility. Miproxifene phosphate was under development for the treatment of breast cancer and reached phase III clinical trials for this indication but development was discontinued.

Miproxifene phosphate is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was under development in Japan for the treatment of breast cancer but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase III clinical trials for this indication before development was discontinued. The drug is a phosphate ester and prodrug of miproxifene (DP-TAT-59) with improved water solubility that was better suited for clinical development. Miproxifene has been found to be 3- to 10-fold as potent as tamoxifen in inhibiting breast cancer cell growth in in vitro models. It is a derivative of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen) in which an additional 4-isopropyl group is present in the β-phenyl ring.
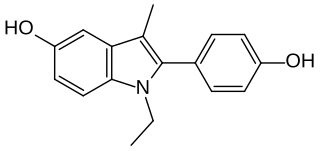
D-15414 is a nonsteroidal weak estrogen of the 2-phenylindole group which was never marketed. It is the major metabolite of the selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) zindoxifene (D-16726). D-15414 has high affinity for the estrogen receptor (ER) and inhibits the growth of ER-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells in vitro. However, contradictorily, subsequent research found that the drug produced fully estrogenic effects in vitro similarly to but less actively than estradiol, with no antiestrogenic activity observed. The reason for the discrepancy between the findings is unclear, though may be due to methodology. The unexpected estrogenic activity of D-15414 may be responsible for the failure of zindoxifene in clinical trials as a treatment for breast cancer.

ERX-11, also known as ERα coregulator-binding modulator-11, is a novel antiestrogen and experimental hormonal antineoplastic agent which is being researched for the potential treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. It is not a competitive antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) like conventional antiestrogens such as tamoxifen or fulvestrant; instead of binding to the ligand-binding site of the ER, ERX-11 interacts with a different part of the ERα and blocks protein–protein interactions of the ERα with coregulators that are necessary for the receptor to act and regulate gene expression. It was designed to bind to the coregulator binding region of the ERα and inhibit the ERα/coactivator interaction, although its precise binding site and mode of action have yet to be fully elucidated and understood. Nonetheless, it is clear that ERX-11 binds within the AF-2 domain of the ERα.
Endocrine therapy is a common treatment for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. However, resistance to this therapy can develop, leading to relapse and progression of disease. This highlights the need for new strategies to combat this resistance.













