
A diatom is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion tonnes of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.

Bolidophyceae is a class of photosynthetic heterokont picophytoplankton, and consist of less than 20 known species. They are distinguished by the angle of flagellar insertion and swimming patterns as well as recent molecular analyses. Bolidophyceae is the sister taxon to the diatoms (Bacillariophyceae). They lack the characteristic theca of the diatoms, and have been proposed as an intermediate group between the diatoms and all other heterokonts.

Bacteriastrum is a genus of diatoms in family Chaetocerotaceae. There are more than 30 described species in genus Bacteriastrum, but many of these are not currently accepted, and new species are still added to the genus. The type species for the genus is Bacteriastrum furcatum Shadbolt.

Ochrophytes, also known as heterokontophytes or stramenochromes, are a group of algae. They are the photosynthetic stramenopiles, a group of eukaryotes, organisms with a cell nucleus, characterized by the presence of two unequal flagella, one of which has tripartite hairs called mastigonemes. In particular, they are characterized by photosynthetic organelles or plastids enclosed by four membranes, with membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids organized in piles of three, chlorophyll a and c as their photosynthetic pigments, and additional pigments such as β-carotene and xanthophylls. Ochrophytes are one of the most diverse lineages of eukaryotes, containing ecologically important algae such as brown algae and diatoms. They are classified either as phylum Ochrophyta or Heterokontophyta, or as subphylum Ochrophytina within phylum Gyrista. Their plastids are of red algal origin.
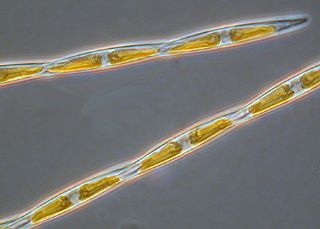
Pseudo-nitzschia is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produce DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of Pseudo-nitzschia occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health.

Ditylum brightwellii is a species of cosmopolitan marine centric diatoms. It is a unicellular photosynthetic autotroph that has the ability to divide rapidly and contribute to spring phytoplankton blooms.
Skeletonema grethae is a species of diatom. Together with S. pseudocostatum, S. tropicum, and S. japonicum, it possesses external processes of its fultoportulae that have narrow tips which connect with those of sibling cells via fork-, knot-, or knuckle-like unions.
Skeletonema japonicum is a diatom. Together with S. pseudocostatum, S. tropicum, and S. grethae, it possesses external processes of its fultoportulae that have narrow tips which connect with those of sibling cells via fork-, knot-, or knuckle-like unions.
Skeletonema marinoi is a diatom. Together with S. dohrnii, this species has flattened extremities of the processes of the fultoportulae, which interlock with those of succeeding valves without forming knuckles.
Navicula australoshetlandica is an algae species in the genus Navicula, known from inland waters of the Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic regions.
Navicula dobrinatemniskovae is an algal species in the genus Navicula, known from inland waters of the Antarctic region. The species was named after Prof. Dsc Dobrina Temniskova from the University of Sofia
Navicula cremeri is an algae in the genus Navicula, known from inland waters of the Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic regions.
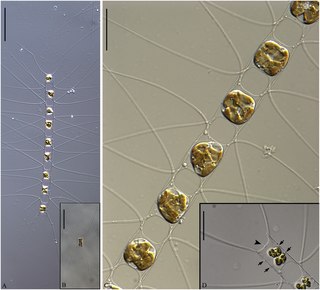
Chaetoceros elegans is a species of diatom in the family Chaetocerotaceae. According to Li, 2017, the type locality is Dapeng Bay, Guangdong Province, P. R. China.

Eucampia zodiacus is a common marine centric diatom species. It is known to be cosmopolitan except in polar regions. E. zodiacus is a harmful diatom that has become known as the predominant organisms causing the bleaching of aqua-cultured nori seaweed.

Turritopsis rubra, commonly referred to as the Crimson Jelly, is a hydrozoan within the family Oceaniidae. The species is native to New Zealand and southern Australia, typically appearing near shorelines in the summer months. The species follows a distribution pattern across the southern Pacific Ocean and can frequently be found in shallow coastal waters.
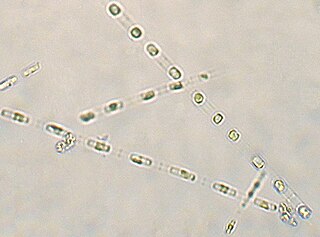
Skeletonema is a genus of diatoms in the family Skeletonemataceae. It is the type genus of its family. The genus Skeletonema was established by R. K. Greville in 1865 for a single species, S. barbadense, found in the Barbados deposit [Jung 2009]. These diatoms are photosynthetic organisms, meaning they obtain carbon dioxide from their surrounding environment and produce oxygen along with other byproducts. Reproduce sexually and asexually [Guiry 2011]. Skeletonema belong to the morphological category referred to as centric diatoms. These are classified by having valves with radial symmetry and the cells lack significant motility [Horner 2002]. Skeletonema are cylindrical shaped with a silica frustule. Cells are joined by long marginal processes to form a filament [Horner 2002]. Their length ranges from 2-61 micrometers, with a diameter ranging from 2-21 micrometers [Hasle 1997]. They are found typically in the neritic zone of the ocean and are highly populous in coastal systems [Jung 2009]. The genus is considered cosmopolitan, showing a wide range of tolerance for salinity and temperature [Hasle 1973]. For example, they have been found in various aquatic environments such as brackish or freshwater. Skeletonema are found worldwide excluding Antarctic waters [Hevia-Orube 2016]. Some harmful effects these diatoms may have on an ecosystem are attributed to large blooming events which may cause hypoxic events in coastal systems. Additionally, they are known to cause water discoloration [Kraberg 2010].

Diatoms belong to a large group called the heterokonts, which include both autotrophs such as golden algae and kelp; and heterotrophs such as water moulds. The classification of heterokonts is still unsettled: they may be designated a division, phylum, kingdom, or something intermediate to those. Consequently, diatoms are ranked anywhere from a class, usually called Diatomophyceae or Bacillariophyceae, to a division (=phylum), usually called Bacillariophyta, with corresponding changes in the ranks of their subgroups.
Chaetoceros coarctatus is a marine, unicellular species of planktonic diatom in the genus Chaetoceros, first described by Lauder in January 1864 using samples from the Hong Kong harbor. Like many diatoms, it is preyed upon by ctenophores. During warming periods of the Mediterranean Sea, this non-native species, first introduced through the Suez Canal, expands its range. Cell chains showcase pairs of posterior and anterior terminal setae, as well as intercalary setae, for anti-predatory mechanical protection and floating benefits. These silica appendages have spines, curved tips, and are longer those on other members of the Chaetoceros genus for higher survival benefits.
Linda Karen Medlin is a molecular biologist known for her work on diatoms. She is an elected member of the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters.

Skeletonema costatum is a cosmopolitan centric diatom that belongs to the genus Skeletonema. It was first described by R. K. Greville, who originally named it Melosira costata, in 1866. It was later renamed by Cleve in 1873 and was more narrowly defined by Zingone et al. and Sarno et al. Skeletonemacostatum is the most well known species of the genus Skeletonema and is often one of the dominant species responsible for red tide events.










