
Ching-Te is a small lunar impact crater located in a mountainous area to the east of the Mare Serenitatis. It is a circular, bowl-shaped formation with no distinguishing features.

Al-Marrakushi is a small, relatively isolated lunar impact crater in the eastern Mare Fecunditatis. It is a circular, symmetrical formation, with inner walls that slope down to the midpoint. To the northeast is the prominent crater Langrenus. The mare near Al-Marrakushi is marked by ray material from its larger neighbor.
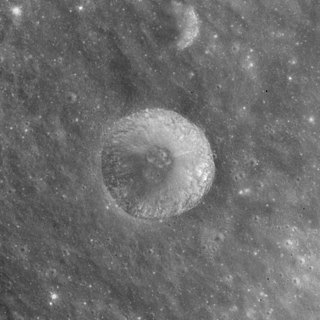
Acosta is a small lunar impact crater located just to the north of the prominent crater Langrenus, near the east edge of Mare Fecunditatis. To the west are the trio of Atwood, Naonobu, and Bilharz. Acosta is named after the Portuguese naturalist Cristóvão da Costa.
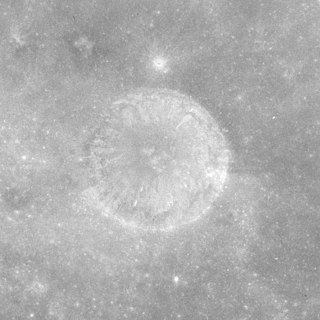
Avery is a small lunar impact crater located near the eastern limb of the Moon. This is a circular, bowl-shaped formation with a small interior floor. It lies near the western edge of Mare Smythii. To the east is the crater Haldane, and to the southwest is Carrillo. Gilbert lies to the southwest.

Born is a small lunar impact crater located near the eastern edge of the Moon, to the northeast of the prominent crater Langrenus. It was previously designated Maclaurin Y before being named by the IAU in 1979. Maclaurin itself lies to the north.

Crile is a tiny lunar impact crater. It is roughly circular and cup-shaped, with interior walls that slope down to the midpoint. The crater lies in the Palus Somni, between the Mare Crisium to the east and Mare Tranquillitatis to the west.

Curtis is a very small lunar impact crater that lies in the western Mare Crisium, to the east of the crater Picard. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation that is otherwise undistinguished. It was named after American astronomer Heber D. Curtis in 1973. In the past it was designated Picard Z.

Bohnenberger is a lunar impact crater that lies near the east edge of the Mare Nectaris, in the foothills of the Montes Pyrenaeus mountain range that forms the perimeter of the mare. To the east beyond the mountains is the larger crater Colombo. The crater has a low rim along the north wall, and the floor is somewhat irregular with a ridge crossing the floor. There is a small crater along the western inner wall.

Artamonov is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. Its eroded outer rim does not have the circular shape of most lunar craters, but the overall shape of three or four merged craters. The largest is in the south, with smaller circular bulges to the north and east.

Atwood is a small earth moon impact crater that is located on the Mare Fecunditatis, to the northwest of the prominent crater Langrenus. It forms a triple-crater formation with Naonobu attached to the north rim and Bilharz near the west rim.

Back is a small lunar impact crater that is located near the eastern limb of the Moon. It lies on the northwest edge of the Mare Smythii, and the northeast rim is adjacent to the crater Schubert. To the west is Jenkins, and to the southwest is the Weierstrass–Van Vleck crater pair.

Becquerel is a lunar impact crater that lies in the northern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. This is an ancient and heavily worn formation that is now little more than an irregular buri in the surface. The outer rim has been worn and reshaped until it forms a rugged, mountainous region around the flatter interior.

Barkla is a lunar impact crater that lies near the eastern limb of the Moon. It is located to the east of the prominent crater Langrenus, and was formerly designated Langrenus A before being renamed by the IAU in 1979. Due east of Barkla is Kapteyn, a formation only slightly larger with a similar size. Southwest of Barkla is the crater Lamé.

Cusanus is a lunar impact crater that is located near the northeastern limb of the Moon. In this location the crater appears very foreshortened when observed from the Earth, and its visibility is affected by libration. The northern rim of Cusanus is nearly joined to the south-southeastern rim of the larger crater Petermann. To the west is Baillaud and to the southeast is Hayn.

Dollond is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the central region of the Moon, to the north of the crater Abulfeda. It was named after British optician John Dollond. Due west of Dollond is Anděl. Dollond is circular and cone shaped, with a tiny floor at the midpoint of the sloping interior walls.

Eckert is a tiny, isolated lunar impact crater in the northern part of the Mare Crisium. This crater forms a circular pit in the dark surface of the surrounding lunar mare. Just to the west is a wrinkle ridge in the mare surface, a feature that is prominent only under oblique lighting from the Sun. The nearest craters of note are Peirce to the west-northwest, and Picard to the southwest. Both of these craters lie in the Mare Crisium basin.

Bondarenko is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the northeast of the large, dark-floored crater Tsiolkovskiy, and south of the crater Chauvenet. This is a worn crater formation with an irregular floor, similar to other craters in the area, which are covered by ejecta from Tsiolkovskiy.

Florensky is a lunar impact crater that is attached to the northeastern rim of the larger crater Vernadskiy. It is located on the far side of the Moon and cannot be directly seen from the Earth. The rim of this crater has been heavily eroded and it forms an irregular ring about the uneven interior. This crater was previously identified as Vernadskiy B before being assigned a name by the IAU in 1985.
Fibiger is a lunar impact crater located on the lunar near side near the northern pole. The nearest major feature is the Byrd crater. The crater was adopted and named after Danish pathologist Johannes Andreas Grib Fibiger in 2009 by the IAU. Located just north of Fibiger are craters Erlanger and Peary, which are 9.9 km and 73 km in diameter, respectively.

Cai Lun is a lunar impact crater located on the lunar far side near the northern pole. The crater is located in between the prominent craters Haskin and Nansen. Cai Lun was adopted and named after Chinese inventor Cai Lun by the IAU in August, 2010.



















