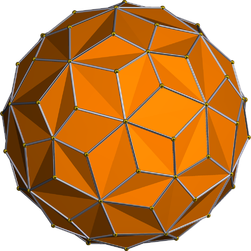
In geometry, the snub dodecahedron, or snub icosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.

In geometry, the triakis icosahedron is an Archimedean dual solid, or a Catalan solid. Its dual is the truncated dodecahedron.

In geometry, a pentakis dodecahedron or kisdodecahedron is the polyhedron created by attaching a pentagonal pyramid to each face of a regular dodecahedron; that is, it is the Kleetope of the dodecahedron. It is a Catalan solid, meaning that it is a dual of an Archimedean solid, in this case, the truncated icosahedron.

In geometry, the deltoidal icositetrahedron is a Catalan solid. Its 24 faces are congruent kites. The deltoidal icositetrahedron, whose dual is the (uniform) rhombicuboctahedron, is tightly related to the pseudo-deltoidal icositetrahedron, whose dual is the pseudorhombicuboctahedron; but the actual and pseudo-d.i. are not to be confused with each other.

In geometry, a disdyakis dodecahedron,, is a Catalan solid with 48 faces and the dual to the Archimedean truncated cuboctahedron. As such it is face-transitive but with irregular face polygons. It resembles an augmented rhombic dodecahedron. Replacing each face of the rhombic dodecahedron with a flat pyramid creates a polyhedron that looks almost like the disdyakis dodecahedron, and is topologically equivalent to it. More formally, the disdyakis dodecahedron is the Kleetope of the rhombic dodecahedron. The net of the rhombic dodecahedral pyramid also shares the same topology.
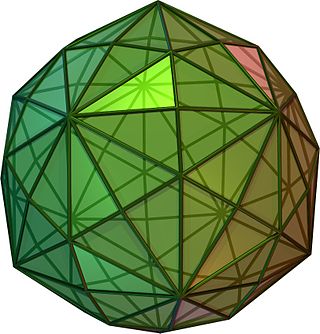
In geometry, a disdyakis triacontahedron, hexakis icosahedron, decakis dodecahedron or kisrhombic triacontahedron is a Catalan solid with 120 faces and the dual to the Archimedean truncated icosidodecahedron. As such it is face-uniform but with irregular face polygons. It slightly resembles an inflated rhombic triacontahedron: if one replaces each face of the rhombic triacontahedron with a single vertex and four triangles in a regular fashion, one ends up with a disdyakis triacontahedron. That is, the disdyakis triacontahedron is the Kleetope of the rhombic triacontahedron. It also has the most faces among the Archimedean and Catalan solids, with the snub dodecahedron, with 92 faces, in second place.

In geometry, a pentagonal hexecontahedron is a Catalan solid, dual of the snub dodecahedron. It has two distinct forms, which are mirror images of each other. It has 92 vertices that span 60 pentagonal faces. It is the Catalan solid with the most vertices. Among the Catalan and Archimedean solids, it has the second largest number of vertices, after the truncated icosidodecahedron, which has 120 vertices.

In geometry, the small dodecicosidodecahedron (or small dodekicosidodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U33. It has 44 faces (20 triangles, 12 pentagons, and 12 decagons), 120 edges, and 60 vertices. Its vertex figure is a crossed quadrilateral.

In geometry, the great snub icosidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U57. It has 92 faces (80 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It can be represented by a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄2,3}, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram .
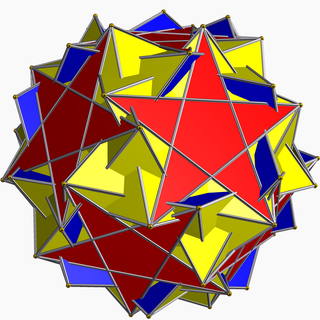
In geometry, the inverted snub dodecadodecahedron (or vertisnub dodecadodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U60. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5/3,5}.

In geometry, the great inverted snub icosidodecahedron (or great vertisnub icosidodecahedron) is a uniform star polyhedron, indexed as U69. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄3,3}, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram . In the book Polyhedron Models by Magnus Wenninger, the polyhedron is misnamed great snub icosidodecahedron, and vice versa.

In geometry, the small triambic icosahedron is a star polyhedron composed of 20 intersecting non-regular hexagon faces. It has 60 edges and 32 vertices, and Euler characteristic of −8. It is an isohedron, meaning that all of its faces are symmetric to each other. Branko Grünbaum has conjectured that it is the only Euclidean isohedron with convex faces of six or more sides, but the small hexagonal hexecontahedron is another example.

In geometry, the medial rhombic triacontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is a stellation of the rhombic triacontahedron, and can also be called small stellated triacontahedron. Its dual is the dodecadodecahedron.

In geometry, the great rhombic triacontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral, isotoxal polyhedron. It is the dual of the great icosidodecahedron (U54). Like the convex rhombic triacontahedron it has 30 rhombic faces, 60 edges and 32 vertices.

In geometry, the great rhombihexacron (or great dipteral disdodecahedron) is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform great rhombihexahedron (U21). It has 24 identical bow-tie-shaped faces, 18 vertices, and 48 edges.

In geometry, the medial pentagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the snub dodecadodecahedron. It has 60 intersecting irregular pentagonal faces.

In geometry, the great pentagrammic hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the great retrosnub icosidodecahedron. Its 60 faces are irregular pentagrams.

In geometry, the small hexagrammic hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the small retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron. It is partially degenerate, having coincident vertices, as its dual has coplanar triangular faces.

In geometry, the great hexagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform great snub dodecicosidodecahedron. It is partially degenerate, having coincident vertices, as its dual has coplanar pentagrammic faces.
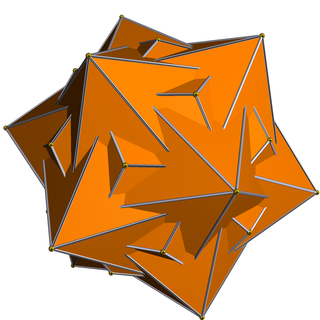
In geometry, the medial hexagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform snub icosidodecadodecahedron.