Related Research Articles
The Thermomicrobia is a group of thermophilic green non-sulfur bacteria. Based on species Thermomicrobium roseum and Sphaerobacter thermophilus, this bacteria class has the following description:
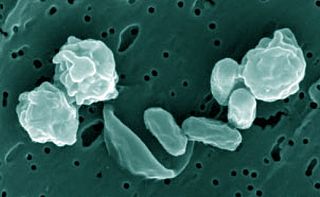
Bacillus odysseyi is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, round-spore- and endospore-forming eubacterium of the genus Bacillus. This novel species was discovered by scientist Myron T. La Duc of NASA’s Biotechnology and Planetary Protection Group, a unit whose purpose is to clean and sterilize spacecraft so as not to have microorganisms contaminate other celestial bodies or foreign microorganisms contaminate Earth, on the surface of the Mars Odyssey in a clean room at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge before the spacecraft was launched to space. La Duc named the bacterium Bacillus odysseyi sp. nov. after the Odyssey mission. It had apparently evolved to live in the sparse environment of a clean room, and its secondary spore coat makes it especially resistant to radiation.
Solibacillus is a genus of Gram positive, rod shaped, spore-forming bacteria.
Patulibacter is a genus of bacteria from the family Patulibacteraceae.
Sphaerisporangium is a Gram-positive genus of bacteria from the family of Streptosporangiaceae.
Solirubrobacter is a Gram-positive, spore-forming, aerobic, mesophilic and non-motile genus of bacteria from the family Solirubrobacteraceae.
Caldanaerovirga is a xylanolytic, anaerobic and alkalithermophilic genus of bacteria from the family of Thermosediminibacterales with one known species.
Anaerolineaceae is a family of bacteria from the order of Anaerolineales. Anaerolineaceae bacteria occur in marine sediments. There are a total of twelve genera in this family, most of which only encompass one species. All known members of the family are Gram-negative and non-motile. They also do not form bacterial spores and are either mesophilic or thermophilic obligate anaerobes. It is also known that all species in this family are chemoheterotrophs.
Solibacillus isronensis is a bacterium from the genus of Solibacillus which has been isolated from a cryogenic tube from India. It is named after ISRO, India's space agency which discovered the species.
Knoellia is a genus of Gram positive, aerobic, non-endosporeforming bacteria. Species in this genus are mesophilic and have cells that are irregular rods or coccoid.
Knoellia remsis a species of Gram positive, nonmotile, non-sporeforming bacteria. The bacteria are aerobic and mesophilic, and the cells are coccoid that group in pairs, tetrads, or clusters. It was originally isolated from an air sample from the Regenerative Enclosed Life Support Module Simulator, which was a system designed to simulate life aboard the International Space Station. The species is named after REMS, the acronym for the Regenerative Enclosed Life Support Module Simulator. The species was originally classified as Tetrasphaera remsis in 2007, but was reclassified into the genus Knoellia in 2018.
Metabacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria exhibiting Gram-positive or Gram-variable staining in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Metabacillus fastidiosus.
Neobacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria that show Gram-positive or Gram-variable staining. This genus belongs under the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species of Neobacillus is Neobacillus niacini.
Cytobacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria that stain either Gram-positive or Gram-variable in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Cytobacillus firmus.
Alteribacter is a genus of Gram-positive or Gram-variable, rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Alteribacter auranticus.
Evansella is a genus of Gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Evansella cellulosilytica.
Ferdinandcohnia is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria that generally display Gram-positive staining in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Ferdinandcohnia humi.
Gottfriedia is a genus of gram-positive or Gram-variable rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Gottfriedia luciferensis.
Heyndrickxia is a genus of gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Heyndrickxia oleronia.
Litchfieldia is a genus of Gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Litchfieldia alkalitelluris.
References
- 1 2 "Solibacillus". LPSN .
- 1 2 "Solibacillus kalamii". www.uniprot.org.
- ↑ "Details: DSM-101595". www.dsmz.de.
- ↑ Parker, Charles Thomas; Garrity, George M (7 December 2016). Parker, Charles Thomas; Garrity, George M (eds.). "Taxonomy of the species Solibacillus kalamii Sielaff et al". NamesforLife, LLC. doi:10.1601/tx.29716.
- ↑ Checinska Sielaff, Aleksandra; Kumar, Rajendran Mathan; Pal, Deepika; Mayilraj, Shanmugam; Venkateswaran, Kasthuri (1 April 2017). "Solibacillus kalamii sp. nov., isolated from a high-efficiency particulate arrestance filter system used in the International Space Station". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 67 (4): 896–901. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001706 . PMID 28475026.