An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid is dispersed in the other. Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working.

Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent, coined c. 1950. As they consist of a water-repellent and a water-attracting part, they enable water and oil to mix; they can form foam and facilitate the detachment of dirt.
In chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
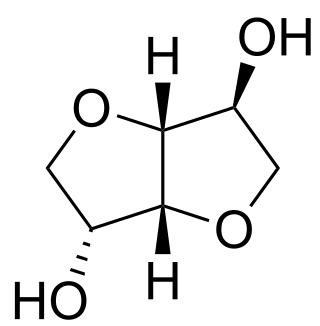
Isosorbide is a bicyclic chemical compound from the group of diols and the oxygen-containing heterocycles, containing two fused furan rings. The starting material for isosorbide is D-sorbitol, which is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of D-glucose, which is in turn produced by hydrolysis of starch. Isosorbide is discussed as a plant-based platform chemical from which biodegradable derivatives of various functionality can be obtained.

Polysorbates are a class of emulsifiers used in some pharmaceuticals and food preparation. They are commonly used in oral and topical pharmaceutical dosage forms. They are also often used in cosmetics to solubilize essential oils into water-based products. Polysorbates are oily liquids derived from ethoxylated sorbitan esterified with fatty acids. Common brand names for polysorbates include Kolliphor, Scattics, Alkest, Canarcel, Tween, and Kotilen.

Monoglycerides are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol.
Emulsifying wax is a cosmetic emulsifying ingredient. The ingredient name is often followed by the initials NF, indicating that it conforms to the specifications of the National Formulary.

Polysorbate 80 is a nonionic surfactant and emulsifier often used in pharmaceuticals, foods, and cosmetics. This synthetic compound is a viscous, water-soluble yellow liquid.
Polysorbate 20 is a polysorbate-type nonionic surfactant formed by the ethoxylation of sorbitan monolaurate. Its stability and relative nontoxicity allows it to be used as a detergent and emulsifier in a number of domestic, scientific, and pharmacological applications. As the name implies, the ethoxylation process leaves the molecule with 20 repeat units of polyethylene glycol; in practice these are distributed across 4 different chains, leading to a commercial product containing a range of chemical species.
Sorbitan monostearate is an ester of sorbitan and stearic acid and is sometimes referred to as a synthetic wax.
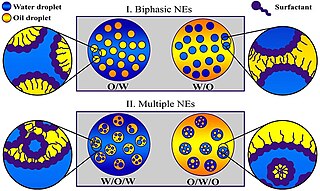
A miniemulsion is a particular type of emulsion. A miniemulsion is obtained by ultrasonicating a mixture comprising two immiscible liquid phases, one or more surfactants and, possibly, one or more co-surfactants. They usually have nanodroplets with uniform size distribution (20–500 nm) and are also known as sub-micron, mini-, and ultra-fine grain emulsions.

Sorbitan tristearate is a nonionic surfactant. It is variously used as a dispersing agent, emulsifier, and stabilizer, in food and in aerosol sprays. As a food additive, it has the E number E492. Brand names for polysorbates include Alkest, Canarcel, and Span. The consistency of sorbitan tristearate is waxy; its color is light cream to tan.

The ouzo effect, also known as the louche effect and spontaneous emulsification, is the phenomenon of formation of a milky oil-in-water emulsion when water is added to ouzo and other anise-flavored liqueurs and spirits, such as pastis, rakı, arak, sambuca and absinthe. Such emulsions occur with only minimal mixing and are highly stable.
Emulsified Fuels are emulsions composed of water and a combustible liquid, either oil or a fuel. Emulsions are a particular example of a dispersion comprising a continuous and a dispersed phase. The most commonly used emulsion fuel is water-in-diesel emulsion. In the case of emulsions, both phases are the immiscible liquids, oil and water. Emulsion fuels can be either a microemulsion or an ordinary emulsion. The essential differences between the two are stability and particle size distribution. Microemulsions are isotropic whereas macroemulsions are prone to settling and changes in particle size over time. Both use surfactants and can be either water-in-oil, or oil-in-water or bicontinuous.
Lactylates are organic compounds that are FDA approved for use as food additives and cosmetic ingredients, e.g. as food-grade emulsifiers. These additives are non-toxic, biodegradable, and typically manufactured using biorenewable feedstocks. Owing to their safety and versatile functionality, lactylates are used in a wide variety of food and non-food applications. In the United States, the Food Chemicals Codex specifies the labeling requirements for food ingredients including lactylates. In the European Union, lactylates must be labelled in accordance with the requirements of the applicable EU regulation. Lactylates may be labelled as calcium stearoyl lactylate (CSL), sodium stearoyl lactylate (SSL), or lactylic esters of fatty acids (LEFA).

Sucrose esters or sucrose fatty acid esters are a group of non-naturally occurring surfactants chemically synthesized from the esterification of sucrose and fatty acids. This group of substances is remarkable for the wide range of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) that it covers. The polar sucrose moiety serves as a hydrophilic end of the molecule, while the long fatty acid chain serves as a lipophilic end of the molecule. Due to this amphipathic property, sucrose esters act as emulsifiers; i.e., they have the ability to bind both water and oil simultaneously. Depending on the HLB value, some can be used as water-in-oil emulsifiers, and some as oil-in-water emulsifiers. Sucrose esters are used in cosmetics, food preservatives, food additives, and other products. A class of sucrose esters with highly substituted hydroxyl groups, olestra, is also used as a fat replacer in food.
Sorbitan monopalmitate (SMP) is a food additive, permitted by the EU. It is entry E495 in the E number list of permitted food additives. It is also known under the trade name Span 40.
Edible oil refining is a set of processes or treatments necessary to turn vegetable raw oil into edible oil.














