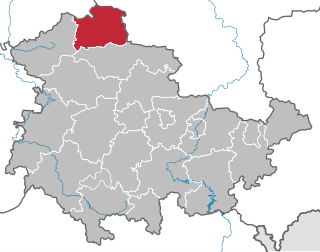
The South Harz Nature Park (German : Naturpark Südharz) is located in the county of Nordhausen in north Thuringia, Germany. The act designating this nature park in the Harz Mountains came into force on 31 December 2010 [1] [2] and thus founded the fifth nature park in Thuringia. It has an area of 267 km² [2] . The park is managed by the South Harz Tourist Association (Südharzer Tourismusverband e.V.) in conjunction with the Kyffhäuser Nature Park.

German is a West Germanic language that is mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, South Tyrol (Italy), the German-speaking Community of Belgium, and Liechtenstein. It is also one of the three official languages of Luxembourg and a co-official language in the Opole Voivodeship in Poland. The languages which are most similar to German are the other members of the West Germanic language branch: Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German/Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, and Yiddish. There are also strong similarities in vocabulary with Danish, Norwegian and Swedish, although those belong to the North Germanic group. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language, after English.

Thuringia, officially the Free State of Thuringia, is a state of Germany.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central and Western Europe, lying between the Baltic and North Seas to the north, and the Alps to the south. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France to the southwest, and Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands to the west.
Contents
The nature park covers parts of the southern foothills of the Lower Harz, the gypsum karst landscape of the adjacent Zechstein belt and the transition region with the North Thuringian bunter sandstone country. In the south, the park is bounded by the valley of the River Helme; on the other sides by the state border of Thuringia. Its western boundary is part of the German Green Belt. To the east is the South Harz Karst Landscape Biosphere Reserve (in Saxony-Anhalt), to the north, the Harz/Saxony-Anhalt Nature Park and to the northwest, the Harz Nature Park (in Lower Saxony). The entire Harz is a so-called major nature reserve (Großschutzgebiet) in which the Harz National Park is also located.
The Zechstein is a unit of sedimentary rock layers of Middle to Late Permian age located in the European Permian Basin which stretches from the east coast of England to northern Poland. The name Zechstein was formerly also used as a unit of time in the geologic timescale, but nowadays it is only used for the corresponding sedimentary deposits in Europe.

The German Green Belt is a project of Bund Naturschutz (BUND), one of Germany's largest environmental groups. The project began in 1989 facing a forbidding, 870-mile (1,400 km) network of fences and guard towers once ran the length of Germany, separating East and West. Now, one of the world's most unusual nature reserves is being created along the old "Death Strip," turning a monument to repression into a symbol of renewal.

The Harz/Saxony-Anhalt Nature Park is situated n the districts of Harz and Mansfeld-Südharz in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. The nature park which lies in the Harz Mountains was founded in 2003 and has an area of around 1,660 km². It is looked after by the Harz Regional Association.
Within the nature park there are ponors, karst springs, subsidence lakes and dolines as well as steep gypsum cliffs. Thanks to the many caves, numerous species of bat - including the barbastelle - live in the beech woods, where they find suitable places to roost. It is also home to the wildcat and lynx. Areas of dry grassland with orchids are the remnants of old meadows and pastures on the karst surfaces.

A ponor is a natural surface opening that may be found in landscapes where the geology and the geomorphology is characterized by some kind of karst, the international geological term for larger karst-induced surface water inlets.

A karst spring is a spring that is part of a karst system. That includes the underground drainage of a much larger area, which means that karst springs often have a very large discharge. Because of their often conical or bowl shape, such water sources are also known in German-speaking lands as a Topf ("pot") which is reflected in names such as Aachtopf or Blautopf.

Subsidence is either the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground's surface with little or no horizontal motion. The definition of subsidence is not restricted by either rate, magnitude, or area involved in the downward movement. Subsidence may be caused by either natural processes or human activitites. Natural proceses include various karst phenomena, thawing of permafrost, consolidation, oxidation of organic soils, slow crustal warping, normal faulting, caldera subsidence, or withdrawal of fluid lava from beneath a solid crust. Human activities such as subsurface mining or the extraction of underground fluids, e.g. petroleum, natural gas, or groundwater. Ground subsidence is of concern to geologists, geotechnical engineers, surveyors, engineers, urban planners, landowners, and the public in general. Subsidence is a global problem.
The highest point in the South Harz Nature Park is the Großer Ehrenberg (635.5 m above sea level (NN) ).

The Großer Ehrenberg is a mountain, 635.5 m above sea level (NN), and the highest peak in the Thuringian part of the Harz mountains. It is also the highest point of the county of Nordhausen in Germany.

Normalnull or Normal-Null is an outdated official vertical datum used in Germany. Elevations using this reference system were to be marked "Meter über Normal-Null". Normalnull has been replaced by Normalhöhennull.