
The Mississippi River is the largest river of the United States and the chief river of the second-largest drainage system on the North American continent, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. Its source is Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota and it flows generally south for 2,320 miles (3,730 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian Mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the fourth-longest and fifteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.

Baton Rouge is the capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana and its second-largest city. Located on the eastern bank of the Mississippi River, it is the parish seat of East Baton Rouge Parish.

West Feliciana Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. As of the 2010 census, the population was 15,625. The parish seat is St. Francisville. The parish was established in 1824.

West Baton Rouge Parish is one of the sixty-four parishes in the U.S. state of Louisiana. As of the 2010 census, the population was 23,788. The parish seat is Port Allen. The parish was created in 1807.

East Baton Rouge Parish is the most populous parish in the U.S. state of Louisiana. As of the 2010 census, the population was 440,171. The parish seat is Baton Rouge, Louisiana's state capital.

Hammond is the largest city in Tangipahoa Parish, Louisiana, United States, located 45 miles (72 km) east of Baton Rouge and 45 miles (72 km) northwest of New Orleans. Its population was 20,019 in the 2010 census. Hammond is home to Southeastern Louisiana University and is the principal city of the Hammond Metropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Tangipahoa Parish.

Port Allen is a city in, and the parish seat of, West Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, United States. Located on the west bank of the Mississippi River, it is bordered by Interstate 10 and US Highway 190. The population was 5,180 at the 2010 census, down from 5,278 in 2000. It is part of the Baton Rouge Metropolitan Statistical Area.

St. Francisville is a town in, and the parish seat of, West Feliciana Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 1,712 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Baton Rouge Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Barton Springs is a set of four natural water springs located at Barton Creek on the grounds of Zilker Park in Austin, Texas, resulting from water flowing through the Edwards Aquifer. The largest spring, Main Barton Spring supplies water to Barton Springs Pool, a popular recreational destination in Austin. The smaller springs are located nearby, two with man-made structures built to contain and direct their flow. The springs are the only known habitat of the Barton Springs Salamander, an endangered species.

The Cheyenne River, also written Chyone, referring to the Cheyenne people who once lived there, is a tributary of the Missouri River in the U.S. states of Wyoming and South Dakota. It is approximately 295 miles (475 km) long and drains an area of 24,240 square miles (62,800 km2). About 60% of the drainage basin is in South Dakota and almost all of the remainder is in Wyoming.
The Floridan aquifer system, composed of the Upper and Lower Floridan aquifers, is a thick sequence of Paleogene carbonate rock which spans an area of about 100,000 square miles in the southeastern United States. It underlies the entire state of Florida and parts of Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, and South Carolina.

The Atchafalaya Basin, or Atchafalaya Swamp, is the largest wetland and swamp in the United States. Located in south central Louisiana, it is a combination of wetlands and river delta area where the Atchafalaya River and the Gulf of Mexico converge. The river stretches from near Simmesport in the north through parts of eight parishes to the Morgan City southern area.
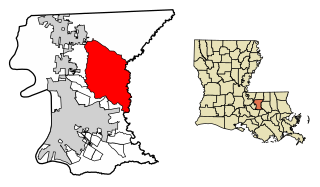
Central is the thirteenth-largest city in the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is the second largest city in East Baton Rouge Parish. Central became the state's newest city in April 2005. It is part of the Baton Rouge Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population of Central was 26,864 as of the 2010 census.
Issues that affect drinking water supply and sanitation in the United States include water scarcity, pollution, a backlog of investment, concerns about the affordability of water for the poorest, and a rapidly retiring workforce. Increased variability and intensity of rainfall as a result of climate change is expected to produce both more severe droughts and flooding, with potentially serious consequences for water supply and for pollution from combined sewer overflows. Droughts are likely to particularly affect the 66 percent of Americans whose communities depend on surface water. As for drinking water quality, there are concerns about disinfection by-products, lead, perchlorates and pharmaceutical substances, but generally drinking water quality in the U.S. is good.
Istrouma Area Council serves Scouts in both Louisiana and Mississippi, primarily in the Greater Baton Rouge Area and Florida Parishes. Specifically, the council includes Scouts from the following parishes: Ascension, East Baton Rouge, West Baton Rouge, East Feliciana, West Feliciana, Iberville, Pointe Coupee, St. Helena, St. James, St. Tammany, Washington, and Tangipahoa. Wilkinson County is the sole Mississippi county in the council.

The foundation of Baton Rouge, Louisiana, dates to 1721, at the site of a bâton rouge or "red stick" Muscogee boundary marker. It became the state capital of Louisiana in 1849.
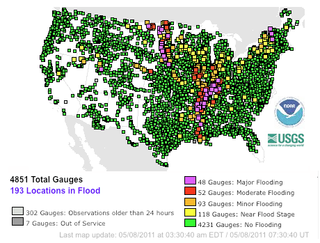
The Mississippi River floods in April and May 2011 were among the largest and most damaging recorded along the U.S. waterway in the past century, comparable in extent to the major floods of 1927 and 1993. In April 2011, two major storm systems deposited record levels of rainfall on the Mississippi River watershed. When that additional water combined with the springtime snowmelt, the river and many of its tributaries began to swell to record levels by the beginning of May. Areas along the Mississippi itself experiencing flooding included Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
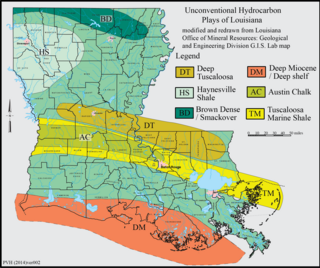
The Brown Dense limestone is an informal name used by petroleum geologists for a layer of rock that lies beneath large parts of southern Arkansas and northwest Louisiana. The Brown Dense is a 300- to 500-foot thick interval within organic-rich, fine-grained carbonate rock that comprise the Lower Member of the Smackover Formation. Within this area, the Lower Smackover Member lies at depths of 8,000 to 10,000 feet beneath the land surface.


















