
Montenegro–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, and of the NATO. Also Montenegro is an EU candidate and Spain is an EU member. Montenegro has an embassy in Madrid. Spain is accredited to Montenegro from its embassy in Belgrade, Serbia.

North Macedonia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. North Macedonia has an embassy in Madrid and three consulates in Barcelona, Madrid and Valencia. Spain has an embassy in Skopje. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe, and NATO. Also North Macedonia is an EU candidate and Spain is an EU member.

Fiji–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Spain has an embassy office in Suva which reports directly to the Spanish embassy in Wellington, New Zealand. Fiji maintains relations with Spain through its embassy in Belgium.

Kiribati and Spain have had bilateral diplomatic relations since 2011. The embassy of Spain in Wellington, New Zealand, is accredited for Kiribati.

Marshall Islands–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. The Spanish embassy in Manila, Philippines, is accredited for the Marshall Islands, plus Spain has an honorary consulate in Majuro. The Marshall Islands have an embassy in Madrid and a consulate in Barcelona.

Nauru–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. The embassy of Spain in Canberra, Australia is accredited for Nauru as a non-resident embassy. The Spanish consulate general in Sydney is also accredited in his duties to Nauru.
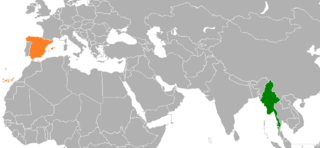
Myanmar–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Myanmar is accredited to Spain from its embassy in Paris, France. Spain has an embassy in Yangon.

Singapore–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Singapore is accredited to Spain through its embassy in Paris, France and has two honorary consulates in Barcelona and Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Singapore.

Central African Republic–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between the Central African Republic (CAR) and Spain. The Central African Republic does not have embassy in Spain, however, its embassy in Paris is accredited to Spain, and maintains an honorary consulate in Madrid. Spain also does not have an embassy in the Central African Republic but its embassy in Cameroon is accredited to CAR.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. The Democratic Republic of the Congo has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Kinshasa.

Djibouti–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Djibouti does not have embassy in Spain but his embassy in Paris is accredited to this country. Spain also has no embassy in Djibouti, but its embassy in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia is accredited to this country.
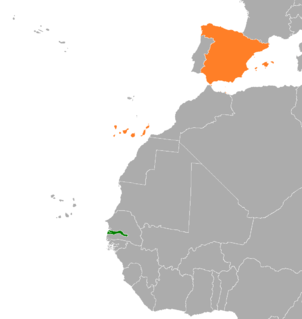
Gambia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Gambia has an embassy in Madrid and honorary consulates in Almería, Barcelona, Gerona, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Madrid and Zaragoza. Spain has an embassy office in Banjul.
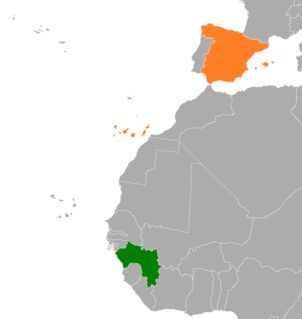
Guinea–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Guinea has an embassy in Madrid and honorary consulate in Barcelona, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Valencia. Spain has an embassy in Conakry
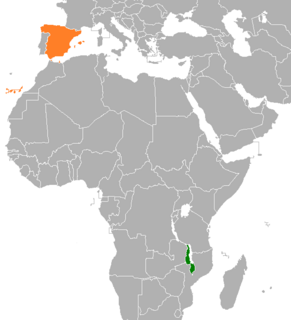
Malawi–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Malawi has an embassy in Madrid and a consulate in Barcelona. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Spain does not have representation in Lilongwe. The Spanish Embassy in Harare (Zimbabwe) is accredited to Malawi.

Mozambique–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Mozambique has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Maputo.

Namibia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Namibia is accredited to Spain from its embassy in Paris, France. Spain has an embassy in Windhoek.

Rwanda–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Rwanda does not have an embassy in Spain, however its embassy in Paris, France, is accredited to Spain and maintains an honorary consulate in Madrid. Spain does not have an embassy in Rwanda, however, its embassy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, is accredited to Rwanda and maintains an honorary consulate in Kigali.

Spain–Tanzania relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Tanzania does not have embassy in Spain, but his embassy in Paris is accredited to this country. Spain has an embassy in Dar es Salaam and an honorary consulate in Zanzibar.

Spain–Togo relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Togo does not have an embassy in Madrid but their embassy in Paris is accredited for Spain, but they have a consulate in Barcelona. Spain also does not have an embassy in Togo but its embassy in Accra, Ghana is accredited to this country, also has a consulate in Lomé.

Spain–Uganda relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Uganda does not have an embassy in Madrid but its embassy in Paris, France is accredited to Spain, it does have a consulate in Barcelona. Spain also does not have an embassy in Uganda but its embassy in Nairobi, Kenya is accredited for Uganda, but has an honorary consulate in Kampala.






















