
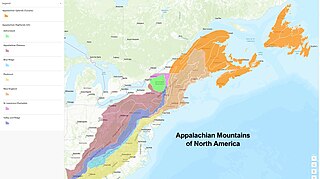
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the United States Geological Survey and the Geological Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' physiographic regions. The U.S. uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands; the Appalachian Mountains are not synonymous with the Appalachian Plateau, which is one of the provinces of the Appalachian Highlands.
The geology of the Appalachians dates back more than 1.2 billion years to the Mesoproterozoic era when two continental cratons collided to form the supercontinent Rodinia, 500 million years prior to the development of the range during the formation of Pangea. The rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveal elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks, and slivers of ancient ocean floor—strong evidences that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of Pangea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded.

The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia. The province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. To the west of the Blue Ridge, between it and the bulk of the Appalachians, lies the Great Appalachian Valley, bordered on the west by the Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian range.
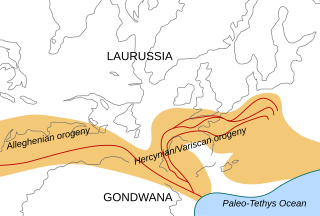
The Alleghanian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957.

The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago (Ma) and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the east coast of the United States. As the mountain chain eroded in the Silurian and Devonian periods, sediment spread throughout the present-day Appalachians and midcontinental North America.

The Hudson Highlands are mountains on both sides of the Hudson River in New York state lying primarily in Putnam County on its east bank and Orange County on its west. They continue somewhat to the south in Westchester County and Rockland County, respectively. The highlands are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains.

South Mountain is a colloquial name applied to an Appalachian Mountain range extending north and northeast along the south side of Lebanon Valley to the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. South Mountain includes the southernmost cluster of peaks that straddle Berks, Lancaster, and Lebanon counties and the northernmost end of the ridge on which Lehigh University is built, in Bethlehem in the Lehigh Valley.

The U.S. state of Georgia is commonly divided into four geologic regions that influence the location of the state's four traditional physiographic regions. The four geologic regions include the Appalachian foreland, Blue Ridge, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain. These four geologic regions commonly share names with and typically overlap the four physiographic regions of the state: the Appalachian Plateau and adjacent Valley and Ridge; the Blue Ridge; the Piedmont and the Coastal Plain.
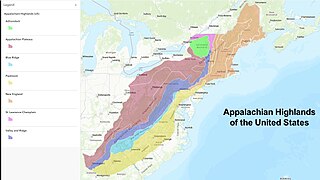
The Appalachian Highlands is one of eight government-defined physiographic divisions of the contiguous United States. It links with the Appalachian Uplands in Canada to make up the Appalachian Mountains. The Highlands includes seven physiographic provinces, which is the second level in the physiographic classification system in the United States. At the next level of physiographic classification, called section/subsection, there are 20 unique land areas with one of the provinces having no sections.

The Geology of Pennsylvania consists of six distinct physiographic provinces, three of which are subdivided into different sections. Each province has its own economic advantages and geologic hazards and plays an important role in shaping everyday life in the state. From the southeast corner to the northwest corner of the state, they include: the Atlantic Plain Province, the Piedmont Province, the New England Province, the Ridge and Valley Province, the Appalachain Province, and the Central Lowlands Province.
New Jersey is a very geologically and geographically diverse region in the United States' Middle Atlantic region, offering variety from the Appalachian Mountains and the Highlands in the state's northwest, to the Atlantic Coastal Plain region that encompasses both the Pine Barrens and the Jersey Shore. The state's geological features have impacted the course of settlement, development, commerce and industry over the past four centuries.

Pochuck Mountain is a ridge in the New York-New Jersey Highlands region of the Appalachian Mountains. Pochuck Mountain's summit and most of its peaks lie within Vernon Township, Sussex County, New Jersey, although the south-western portion of the ridge lies within Hardyston Township, and the north-eastern tip of the ridge extends over the New York state line into Orange County. The ridge marks the eastern edge of the Great Appalachian Valley, and it divides the watersheds of the Wallkill River and its tributary Pochuck Creek. The two rivers meet at Pochuck Neck, marking the terminus of the ridge.

Wawayanda Mountain is a ridge in the New York-New Jersey Highlands region of the Appalachian Mountains. The summit lies within Sussex County, New Jersey.

The Reading Prong is a physiographic subprovince of the New England Uplands section of the New England province of the Appalachian Highlands. The prong consists of mountains made up of crystalline metamorphic rock.

The Ramapo Fault zone is a system of faults between the northern Appalachian Mountains and Piedmont areas to the east. Spanning more than 185 miles (298 km) in New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, it is perhaps the best known fault zone in the Mid-Atlantic region, and some small earthquakes have been known to occur in its vicinity. Recently, public knowledge about the fault has increased, especially after the 1970s, when the fault's proximity to the Indian Point nuclear plant in New York was noted.
Cameron's Line is an Ordovician suture fault in the northeast United States which formed as part of the continental collision known as the Taconic orogeny around 450 mya. Named after Eugene N. Cameron, who first described it in the 1950s, it ties together the North American continental craton, the prehistoric Taconic Island volcanic arc, and the bottom of the ancient Iapetus Ocean.
The Hamburg Mountains are a range of the New York-New Jersey Highlands region of the Appalachian Mountains. The summit, reaching a height of 1,473 feet (449 m), lies within Sussex County, New Jersey.
The Pimple Hills are a range of the New York-New Jersey Highlands region of the Appalachian Mountains. The summit, reaching a height of 1,122 feet (342 m), lies within Sussex County, New Jersey.

The geology of the State of New York is made up of ancient Precambrian crystalline basement rock, forming the Adirondack Mountains and the bedrock of much of the state. These rocks experienced numerous deformations during mountain building events and much of the region was flooded by shallow seas depositing thick sequences of sedimentary rock during the Paleozoic. Fewer rocks have deposited since the Mesozoic as several kilometers of rock have eroded into the continental shelf and Atlantic coastal plain, although volcanic and sedimentary rocks in the Newark Basin are a prominent fossil-bearing feature near New York City from the Mesozoic rifting of the supercontinent Pangea.

The geology of North Carolina includes ancient Proterozoic rocks belonging to the Grenville Province in the Blue Ridge. The region experienced igneous activity and the addition of new terranes and orogeny mountain building events throughout the Paleozoic, followed by the rifting of the Atlantic Ocean and the deposition of thick sediments in the Coastal Plain and offshore waters.















