
King George Island is the largest of the South Shetland Islands, lying 120 km off the coast of Antarctica in the Southern Ocean. The island was named after King George III.

Hope Bay on Trinity Peninsula, is five kilometres long and three kilometres wide, indenting the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and opening on Antarctic Sound. It is the site of the Argentinian Antarctic settlement Esperanza Base, established in 1952.
This is a list of extreme points in Antarctica.

Tower Island is an Antarctic island 9 kilometres (5 nmi) long and 305 m (1,001 ft) high. It marks the north-east extent of Palmer Archipelago. It lies 37 kilometres (20 nmi) north-east of Trinity Island, separated by Gilbert Strait. Both islands are separated from the Davis Coast to the south by Orléans Strait, running northeast–southwest. The Pearl Rocks lie off the West Coast of Tower Island.
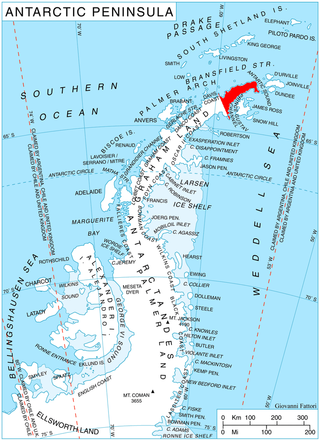
Trinity Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Antarctic Peninsula. It extends northeastward for about 130 km (80 mi) to Cape Dubouzet from an imaginary line connecting Cape Kater on the north-west coast and Cape Longing on the south-east coast. Prime Head is the northernmost point of this peninsula. Some 20 kilometers southeast of Prime Head is Hope Bay with the year-round Argentinian Esperanza Base.

Palmer Archipelago, also known as Antarctic Archipelago, Archipiélago Palmer, Antarktiske Arkipel or Palmer Inseln, is a group of islands off the northwestern coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It extends from Tower Island in the north to Anvers Island in the south. It is separated by the Gerlache and Bismarck straits from the Antarctic Peninsula and Wilhelm Archipelago, respectively.
Trinity Island or Île de la Trinité or Isla Trinidad is an island 24 km (15 mi) long and 10 km (6 mi) wide in the northern part of the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It lies 37 km (23 mi) east of Hoseason Island, 72.6 km (45 mi) south of Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands, and 10.3 km (6 mi) north-northwest of Cape Andreas on the Antarctic Peninsula. The island was named by Otto Nordenskiöld, leader of the 1901-1904 Swedish Antarctic Expedition (SAE) in commemoration of Edward Bransfield's "Trinity Land" of 1820.

Bellingshausen Station is a Russian Antarctic station at Collins Harbour, on King George Island of the South Shetland Islands. It was one of the first research stations founded by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition in 1968. It is also the location of Trinity Church, the only permanently staffed Eastern Orthodox church in Antarctica.

The Willis Islands are a small archipelago to the west of South Georgia Island in the South Georgia Islands. They are 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Bird Island, separated by the Stewart Strait. They were discovered on 14 January 1775 by Captain James Cook and named for Cook's midshipman Thomas Willis, the crew member who first sighted them. The Willis Islands were charted in greater detail and individually named by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel between 1926-1930.

Vice-Admiral of England Sir Thomas Spert was a mariner who reached the rank of vice admiral in service to King Henry VIII of England. He was sailing master of the flagships Mary Rose and Henry Grace a Dieu. He served as the first Master of Trinity House, the private corporation for maritime affairs in London. Spert Island off the coast of Antarctica is named for him.

Religion in Antarctica is largely dominated by Christianity, with Christian buildings being the only religious buildings on the continent. Although used regularly for Christian worship, the Chapel of the Snows has also been used for Buddhist and Baháʼí Faith ceremonies. Some of the early religious buildings are now protected as important historical monuments.
Astudillo Glacier is a small glacier flowing into Paradise Harbor between Leith Cove and Skontorp Cove on the Danco Coast of Graham Land. The glacier was surveyed by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition of 1950–51, which applied the name, probably after an expedition member.
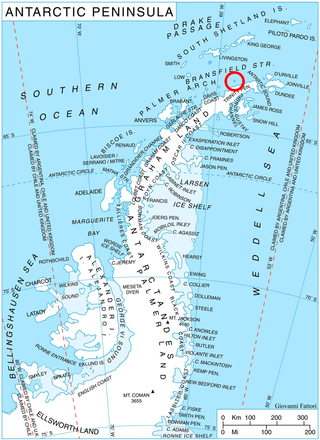
Astrolabe Island, located at 63°17′S58°40′W, is an island 5 km (3 mi) long, lying in the Bransfield Strait 23 km (14 mi) northwest of Cape Ducorps, Trinity Peninsula in Antarctica. It was discovered by the French expedition, 1837–40, under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville, and named by him for his chief expedition ship, the Astrolabe. The island was photographed from the air and triangulated by FIDASE, 1956–57.

Pastra Glacier is a 4.8 km long and 2 km wide glacier in the central part of Trinity Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. Draining northwards to flow into Milburn Bay.

Andrew Glacier is a glacier 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, flowing northeast into Ognen Cove in Charcot Bay immediately west of the Webster Peaks on Trinity Peninsula, northern Graham Land.

Lister Glacier is a glacier 5 nautical miles (9 km) long and 1 nautical mile (2 km) wide, draining the northeast slopes of Stribog Mountains and flowing into Bouquet Bay just south of Duclaux Point on the northeast side of Brabant Island, in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica.

Chayka Passage is the 1 km long in south-north direction and 110 m wide passage between Spert Island and the southwest coast of Trinity Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. Its south entrance is situated just west of Bulnes Point. The vertical cliffs of Symplegades rise either side of the feature.
Zikoniya Island is the 140 m long in west–east direction and 120 m wide rocky island lying off Spert Island on the southwest side of Trinity Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It is “named after the ocean fishing trawler Zikoniya of the Bulgarian company Ocean Fisheries – Burgas whose ships operated in the waters of South Georgia, Kerguelen, the South Orkney Islands, South Shetland Islands and Antarctic Peninsula from 1970 to the early 1990s. The Bulgarian fishermen, along with those of the Soviet Union, Poland and East Germany are the pioneers of modern Antarctic fishing industry.”
Melanita Island is the 780 m long in southwest-northeast direction and 400 m wide rocky island lying off Spert Island on the southwest side of Trinity Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It is “named after the ocean fishing trawler Melanita of the Bulgarian company Ocean Fisheries – Burgas whose ships operated in the waters of South Georgia, Kerguelen, the South Orkney Islands, South Shetland Islands and Antarctic Peninsula from 1970 to the early 1990s. The Bulgarian fishermen, along with those of the Soviet Union, Poland and East Germany are the pioneers of modern Antarctic fishing industry.”
Feniks Island is the 230 m long in west–east direction and 170 m wide in south–north direction rocky island lying off Spert Island on the southwest side of Trinity Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It is “named after the ocean fishing trawler Feniks of the Bulgarian company Ocean Fisheries – Burgas whose ships operated in the waters of South Georgia, Kerguelen, the South Orkney Islands, South Shetland Islands and Antarctic Peninsula from 1970 to the early 1990s. The Bulgarian fishermen, along with those of the Soviet Union, Poland and East Germany are the pioneers of modern Antarctic fishing industry.”











