
Martinus Willem Beijerinck was a Dutch microbiologist and botanist who was one of the founders of virology and environmental microbiology. He is credited with the discovery of viruses, which he called Contagium vivum fluidum.
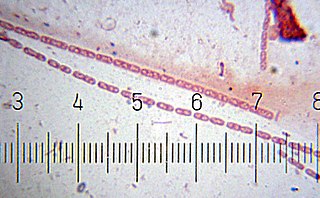
Streptobacillus is a genus of fastidious microaerophilic gram-negative bacteria, which grow in culture as rods in chains.

The Nitrosomonadales are an order of the class Betaproteobacteria in the phylum "Proteobacteria". Like all members of their class, they are Gram-negative.
Rat-bite fever is an acute, febrile human illness caused by bacteria transmitted by rodents, in most cases, which is passed from rodent to human by the rodent's urine or mucous secretions. Alternative names for rat-bite fever include streptobacillary fever, streptobacillosis, spirillary fever, bogger, and epidemic arthritic erythema. It is a rare disease spread by infected rodents and can be caused by two specific types of bacteria. Most cases occur in Japan, but specific strains of the disease are present in the United States, Europe, Australia, and Africa. Some cases are diagnosed after patients were exposed to the urine or bodily secretions of an infected animal. These secretions can come from the mouth, nose, or eyes of the rodent. The majority of cases are due to the animal's bite. It can also be transmitted through food or water contaminated with rat feces or urine. Other animals can be infected with this disease, including weasels, gerbils, and squirrels. Household pets such as dogs or cats exposed to these animals can also carry the disease and infect humans. If a person is bitten by a rodent, it is important to quickly wash and cleanse the wound area thoroughly with antiseptic solution to reduce the risk of infection.
Sodoku (鼠毒) is a bacterial zoonotic disease. It is caused by the Gram-negative rod Spirillum minus. It is a form of rat-bite fever (RBF).
The genus Selenomonas constitutes a group of motile crescent-shaped bacteria within the Veillonellaceae family and includes species living in the gastrointestinal tracts of animals, in particular the ruminants. A number of smaller forms discovered with the light microscope are now in culture but many, especially the large selenomonads are not, owing to their fastidious and incompletely known growth requirements.
Relapsing fever is a vector-borne disease caused by infection with certain bacteria in the genus Borrelia, which is transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks.

Spirillum is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria in the family Spirillaceae of the Nitrosomonadales of the Betaproteobacteria. There are two species of Spirillum with validly or effectively published names - Spirillum winogradskyi and Spirillum volutans.
Spirillum minus is an organism associated with rat-bite fever that has never been fully identified and was assigned to the genus Spirillum in 1887 based on morphology, although it is not a validly published name. As Spirillum species generally obligately microaerophiles and are not found in mammals, this organism may be misclassified. Sequencing data should help to resolve this question.

Henry Vandyke Carter was an English anatomist, surgeon, and anatomical artist most notable for his illustrations of the book Gray's Anatomy.

Spirillaceae is a family in the order Nitrosomonadales in the class Betaproteobacteria of the bacteria.

Lesueurillidae is an extinct family of paleozoic molluscs (gastropods?) with anisostrophically coiled shells of uncertain position (Gastropoda?).
Janua is a genus of polychaetes, containing the following subgenera and species:
Frederick George Novy was an American bacteriologist, organic chemist, and instructor.
Spirillum winogradskyi is a gram-negative, bacterium from the genus of Spirillum which was isolated from the sulfidic sludge of a municipal wastewater treatment plant.
Spiral bacteria, bacteria of spiral (helical) shape, form the third major morphological category of prokaryotes along with the rod-shaped bacilli and round cocci. Spiral bacteria can be subclassified by the number of twists per cell, cell thickness, cell flexibility, and motility. The two types of spiral cells are spirillum and spirochete, with spirillum being rigid with external flagella, and spirochetes being flexible with internal flagella.
Penicillium spirillum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium.
Aquaspirillum (ak'wă-spī-ril'ŭm) is a genus of aerobic bacteria in the family Neisseriaceae that lives in freshwater.
Azospirillum is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, non-fermentative and nitrogen-fixing bacterial genus from the family of Rhodospirillaceae. Azospirillum bacteria can promote plant growth.




