
Spirulina is the dried biomass of cyanobacteria that can be consumed by humans and animals. The three species are Arthrospira platensis, A. fusiformis, and A. maxima.

Oscillatoria is a genus of filamentous cyanobacteria. It is often found in freshwater environments. Its name refers to the oscillating motion of its filaments as they slide against each other to position the colony to face a light source. Oscillatoria uses photosynthesis to survive and reproduce. Each filament of Oscillatoria consists of a row of cells called a trichome. The tip of the trichome oscillates like a pendulum.

Porphyra is a genus of coldwater seaweeds that grow in cold, shallow seawater. More specifically, it belongs to red algae phylum of laver species, comprising approximately 70 species. It grows in the intertidal zone, typically between the upper intertidal zone and the splash zone in cold waters of temperate oceans. In East Asia, it is used to produce the sea vegetable products nori and gim. There are considered to be 60–70 species of Porphyra worldwide and seven around Britain and Ireland, where it has been traditionally used to produce edible sea vegetables on the Irish Sea coast. The species Porphyra purpurea has one of the largest plastid genomes known, with 251 genes.

Syringodium is a genus in the family Cymodoceaceae described as a genus in 1860. It is found along shorelines of tropical and subtropical marine environments.

Arthrospira is a genus of free-floating filamentous cyanobacteria characterized by cylindrical, multicellular trichomes in an open left-hand helix. A dietary supplement is made from A. platensis and A. maxima, known as spirulina. The A. maxima and A. platensis species were once classified in the genus Spirulina. Although the introduction of the two separate genera Arthrospira and Spirulina is now generally accepted, there has been much dispute in the past and the resulting taxonomical confusion is tremendous.

Scytonema is a genus of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that contains over 100 species. It grows in filaments that form dark mats. Many species are aquatic and are either free-floating or grow attached to a submerged substrate, while others species grow on terrestrial rocks, wood, soil, or plants. Scytonema is a nitrogen fixer, and can provide fixed nitrogen to the leaves of plants on which it is growing. Some species of Scytonema form a symbiotic relationship with fungi to produce a lichen.

Oscillatoria brevis is a species of the genus Oscillatoria first identified in 1892. It is a blue-green filamentous cyanobacterium, which can be found in brackish and fresh waterways. O. brevis can also be isolated from soil.

Maurice-Augustin Gomont was a French phycologist.

Fischerella is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Hapalosiphonaceae.
Kamptonema is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Microcoleaceae.
Kamptonema chlorinum is a species of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Microcoleaceae.
Jaaginema is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Pseudanabaenaceae.
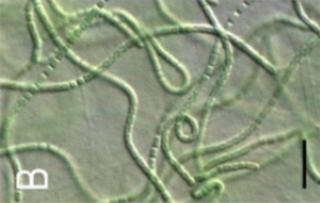
Leptolyngbya is a genus of cyanobacteria in the family Leptolyngbyaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution.

Phormidium is a genus of cyanobacteria in the family Oscillatoriaceae.










