
The economy of the Philippines is an emerging market, and considered as a newly industrialized country in the Asia-Pacific region. In 2024, the Philippine economy is estimated to be at ₱26.55 trillion, making it the world's 32nd largest by nominal GDP and 13th largest in Asia according to the International Monetary Fund.

Transportation in the Philippines covers the transportation methods within this archipelagic nation of over 7,500 islands. From a previously underdeveloped state of transportation, the government of the Philippines has been improving transportation through various direct infrastructure projects, and these include an increase in air, sea, road, and rail transportation and transport hubs.

Metropolitan Manila, commonly shortened to Metro Manila and formally the National Capital Region, is the capital region and largest metropolitan area of the Philippines. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay, the region lies between the Central Luzon and Calabarzon regions. Encompassing an area of 619.57 km2 (239.22 sq mi) and with a population of 13,484,462 as of 2020, it is composed of sixteen highly urbanized cities: the capital city, Manila, Caloocan, Las Piñas, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Navotas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, Quezon City, San Juan, Taguig, and Valenzuela, along with one independent municipality, Pateros. As the second most populous and the most densely populated region in the Philippines, it ranks as the 9th most populous metropolitan area in Asia and the 6th most populous urban area in the world.

Bulacan, officially the Province of Bulacan ,(Kapampangan: Lalawigan ning Bulacan), is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is the city of Malolos. Bulacan was established on August 15, 1578, and part of the Metro Luzon Urban Beltway Super Region.

General Santos, officially the City of General Santos, and abbreviated as GenSan, is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Soccsksargen, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 697,315 people.

San Miguel Corporation, abbreviated as SMC, is a Philippine multinational conglomerate headquartered in Mandaluyong, Metro Manila. The company is one of the largest and most diversified conglomerates in the Philippines. Originally founded in 1890, San Miguel has ventured beyond its core business, with investments in various sectors such as food and drink, finance, infrastructure, oil and energy, transportation, and real estate.

Sergio Osmeña Sr. was a Filipino lawyer and politician who served as the fourth President of the Philippines from 1944 to 1946. He was Vice President under Manuel L. Quezon. Upon Quezon's sudden death in 1944, Osmeña succeeded him at age 65, becoming the oldest person to assume the Philippine presidency until Rodrigo Duterte took office in 2016 at age 71. A founder of the Nacionalista Party, Osmeña was also the first Visayan to become president.

Samal, officially the Municipality of Samal, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Bataan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 38,302 people.

Rail transportation in the Philippines is currently used mostly to transport passengers within Metro Manila and provinces of Laguna and Quezon, as well as a commuter service in the Bicol Region. Freight transport services once operated in the country, but these services were halted. However, there are plans to restore old freight services and build new lines. From a peak of 1,100 kilometers (680 mi), the country currently has a railway footprint of 533.14 kilometers (331.28 mi), of which only 129.85 kilometers (80.69 mi) are operational as of 2024, including all the urban rail lines. World War II, natural calamities, underspending, and neglect have all contributed to the decline of the Philippine railway network. In the 2019 Global Competitiveness Report, the Philippines has the lowest efficiency score among other Asian countries in terms of efficiency of train services, receiving a score of 2.4, and ranking 86th out of 101 countries globally. The government is currently expanding the railway network up to 1,900 kilometers (1,200 mi) by 2022 through numerous projects.

Metropolitan Cebu, or simply Metro Cebu,, is the main urban center of the province of Cebu in the Philippines. Metro Cebu is located along the central eastern portion of the island including the nearby island of Mactan. It accounts for 19.9 percent of the land area and 61.5 percent of the population of the entire province of Cebu.
Roberto "Obet" Mamangon Pagdanganan is a Filipino politician and lawyer who served as the 29th Governor of Bulacan from 1988 to 1998 and subsequently as Secretary of Tourism and Secretary of Agrarian Reform.

Coffee is an important agricultural product in the Philippines, and is one of the Philippines' most important export products aside from being in high demand in the country's local consumer market.

Metro Pacific Investments Corporation (MPIC) is a Philippine-based unit investment holding company of First Pacific Company Limited through Metro Pacific Holdings, Inc. MPIC through its subsidiaries, provides water, sanitation, and sewerage services and also operates in real estate, and infrastructure projects. It also invests in some hospitals in the Philippines.

As of 2005, the Philippines was the ninth largest sugar producer in the world and second largest sugar producer among the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries, after Thailand, according to Food and Agriculture Organization. At least seventeen provinces of the Philippines have grown sugarcane, of which the two on Negros Island account for half of the nation's total production, and sugar is one of the Philippines' most important agricultural exports. As of crop year 2009–2010, 29 sugar mills are operational divided as follows: thirteen mills on Negros, six mills on Luzon, four mills on Panay, three mills in Eastern Visayas and three mills on Mindanao.
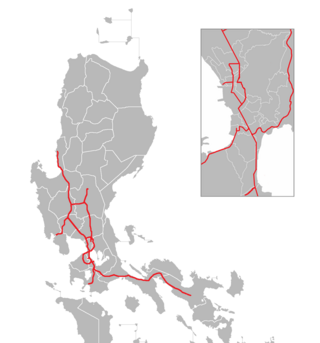
The Philippine expressway network, also known as the High Standard Highway Network, is a controlled-access highway network managed by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) which consists of all expressways and regional high standard highways in the Philippines.
The chocolate industry in the Philippines developed after introducing the cocoa tree into Philippine agriculture. The growing of cacao or cocoa boasts a long history stretching from the colonial times. Originating from Mesoamerican forests, cacao was first introduced by the Spanish colonizers four centuries ago. Since then the Philippine cocoa industry has been the primary producer of cocoa beans in Southeast Asia. There are many areas of production of cacao in the Philippines, owing to soil and climate. The chocolate industry is currently on a small to medium scale.
Lemery Works, also known as Batangas Works, is a steel mill under-construction in Lemery, Batangas, Philippines. Owned by SteelAsia, it is set to become the first steel beam manufacturing plant in the Philippines upon its completion in 2023.













