
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

Citrus is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus Citrus is native to South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. Various citrus species have been used and domesticated by indigenous cultures in these areas since ancient times. From there its cultivation spread into Micronesia and Polynesia by the Austronesian expansion ; and to the Middle East and the Mediterranean via the incense trade route, and onwards to Europe and the Americas.

The mandarin orange, also known as mandarin or mandarine, is a small, rounded citrus tree fruit. Treated as a distinct species of orange, it is usually eaten plain or in fruit salads. Tangerines are a group of orange-coloured citrus fruit consisting of hybrids of mandarin orange with some pomelo contribution.

Stephania is a dark background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 32 km (20 mi) in diameter. It was discovered on 19 May 1881, by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at the Vienna Observatory. The C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 18.2 hours. It was named after Princess Stéphanie of Belgium.

Annona reticulata is a small deciduous or semi-evergreen tree in the plant family Annonaceae. It is best known for its fruit, called custard apple, a common name shared with fruits of several other species in the same genus: A. cherimola and A. squamosa. Other English common names include ox heart and bullock's heart. The fruit is sweet and useful in preparation of desserts, but is generally less popular for eating than that of A. cherimola.

Menispermaceae is a family of flowering plants. The alkaloid tubocurarine, a neuromuscular blocker and the active ingredient in the 'tube curare' form of the dart poison curare, is derived from the South American liana Chondrodendron tomentosum. Several other South American genera belonging to the family have been used to prepare the 'pot' and 'calabash' forms of curare. The family contains 78 genera with some 440 species, which are distributed throughout low-lying tropical areas with some species present in temperate and arid regions.
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons.

Grass jelly, also known as leaf jelly or herb jelly, is a jelly-like dessert originating from China. It is commonly consumed in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is created by using Chinese mesona and has a mild, slightly bitter taste. Grass jelly was invented by the Hakka people who historically used the food to alleviate heat stroke after long days working in the field. The dish was introduced to Southeast Asia by the Chinese diaspora. It is served chilled, with other toppings such as fruit, or in bubble tea or other drinks. Outside Asia, it is sold in Asian supermarkets.

Stephania is a genus of flowering plants in the family Menispermaceae, native to eastern and southern Asia and Australia. They are herbaceous perennial vines, growing to around four metres tall, with a large tuber. The leaves are arranged spirally on the stem and are peltate, with the leaf petiole attached near the centre of the leaf. The name Stephania comes from the Greek, "a crown". This refers to the anthers being arranged in a crown-like manner.

Stephania tetrandra is a herbaceous perennial vine of the family Menispermaceae native to China and Taiwan. It grows from a short, woody caudex, climbing to a height of around three meters. The leaves are arranged spirally on the stem, and are peltate, i.e. with the leaf petiole attached near the centre of the leaf. Its root is used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).

Princess Anna Maria Maximiliane Stephania Karoline Johanna Luisa Xaveria Nepomucena Aloysia Benedicta of Saxony, Duchess of Saxony was the seventh child and fourth eldest daughter of John of Saxony and his wife Amalie Auguste of Bavaria and a younger sister of Albert of Saxony and George of Saxony. Through her marriage to Archduke Ferdinand, Grand Prince of Tuscany, Anna was a member of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine and an Archduchess and Princess of Austria and Princess of Hungary, Croatia, Bohemia, and Tuscany. Ann died shortly before her husband succeeded his father as Grand Duke of Tuscany.

The guppy, also known as millionfish or the rainbow fish, is one of the world's most widely distributed tropical fish and one of the most popular freshwater aquarium fish species. It is a member of the family Poeciliidae and, like almost all American members of the family, is live-bearing. Guppies originate from northeast South America, but have been introduced to many environments and are now found all over the world. They are highly adaptable and thrive in many different environmental and ecological conditions. Male guppies, which are smaller than females, have ornamental caudal and dorsal fins. Wild guppies generally feed on a variety of food sources, including benthic algae and aquatic insect larvae. Guppies are used as a model organism in the fields of ecology, evolution, and behavioural studies.
Stephania Bell is an American physical therapist who has become an author, as well as both on-air and online sports commentator at ESPN where she serves as an American football injury analyst.
S. reticulata may refer to:
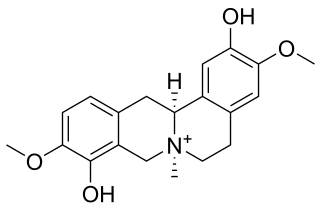
Cyclanoline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Stephania venosa tuber.

Cycleanine is a selective vascular calcium antagonist isolated from Stephania.
Stephania crebra is a herbaceous perennial vine in the genus Stephania of the family Menispermaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia and was first described in Thailand in 1988 by L. L. Forman. It is one of 15 Stephania found only in northern Thailand, specifically in the province of Chiang Mai. It has leaves 12–17 cm (4.7–6.7 in) long and 9–16 cm (3.5–6.3 in) wide. It resembles Stephania reticulata but S. crebra has larger flowers but smaller drupes and endocarps.

The reticulated giraffe is a species/subspecies of giraffe native to the Horn of Africa. It is differentiated from other types of giraffe by its coat, which consists of large, polygonal, block-like spots, which extend onto the lower legs, tail and face. These prominent liver-red spots also show much less white between them, when compared to other giraffe species. While the reticulated giraffe may yet still be found in parts of its historic range, such as areas of Somalia and Ethiopia, its population stronghold is primarily within Kenya. There are approximately 8,500 individuals living in the wild.
Stephania Haralabidis was born in Athens, Greece. Haralabidis is a Greek American water polo player who played at USC and currently playing for Ethnikos and the U.S. national team. Haralabidis also has two sisters, her twin Ioanna and older sister Anastaia. Ioanna was also on the USC women's water polo team.

Orobanche reticulata is a species of broomrape known by the common name thistle broomrape. It is a parasitic plant whose host is normally the creeping thistle. It is native to the lowlands of Western Europe and Central Asia, but in the United Kingdom it is a rare and protected plant, growing only in Yorkshire, on grassland sites such as Quarry Moor.














