Herne Hill railway station is in the London Borough of Lambeth, South London, England, on the boundary between London fare zones 2 and 3. Train services are provided by Thameslink to London Blackfriars, Farringdon, St Pancras International and St Albans on the Thameslink route and by Southeastern to London Victoria and Orpington on the Chatham Main Line. It is 3 miles 76 chains (6.4 km) down the line from Victoria.

Sevenoaks railway station is a stop on the South Eastern Main Line, serving the town of Sevenoaks, in Kent, England. It is 22 miles 9 chains (35.6 km) down the line from London Charing Cross and is situated between Dunton Green and Hildenborough stations. Trains calling at the station are operated by Southeastern and Thameslink.

Ramsgate railway station serves the town of Ramsgate in Thanet in Kent, England. The station lies on the Chatham Main Line, 79 miles 21 chains (127.6 km) down the line from London Victoria, the Kent Coast Line, and the Ashford to Ramsgate line. The station is managed by Southeastern, which operates all trains serving it.
The Southern Region was a region of British Railways from 1948 until 1992 when railways were re-privatised. The region ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s. The region covered south London, southern England and the south coast, including the busy commuter belt areas of Kent, Sussex and Surrey. The region was largely based upon the former Southern Railway area.

St Blazey engine shed is located in Par, Cornwall, United Kingdom, although it is named after the adjacent village of St Blazey. It was built in 1874 as the headquarters of the Cornwall Minerals Railway but for many years was a depot of the Great Western Railway. The current depot operator is DB Cargo and the depot TOPS code is BZ.

Bescot TMD is a locomotive traction maintenance depot in Bescot, an area of Walsall in the West Midlands, England. Situated adjacent to Bescot Stadium railway station, the depot with code BS is currently operated by DB Schenker Rail (UK). Bescot Yard is to the south-east of the depot. This entire complex of track is clearly visible from the northern end of the M6 and M5 motorway junction. The Depot is located on the Chase Line and the Walsall-Wolverhampton Line.

Laira Traction and Rolling Stock Maintenance Depot is a railway traction maintenance depot situated in Plymouth, Devon, England. The depot is operated by Great Western Railway (GWR) and is where their fleet of Class 802 InterCity Express Trains and remaining Castle Class trains are overhauled. Other trains visit for daily servicing including some operated by CrossCountry.

Penzance TMD, also known as Long Rock TMD, is a railway traction maintenance depot situated in the village of Long Rock east of Penzance, Cornwall, England, and is the most westerly and southerly rail depot in the country. The depot operator is Great Western Railway. The depot code is PZ.
The area around Hornsey railway station in Hornsey has been the site of several railway maintenance facilities from the mid-19th century onwards.

Heaton TMD is a railway traction maintenance depot situated in the Heaton area of Newcastle upon Tyne, England, it is located next to the East Coast Main Line, around 2 miles (3 km) east of Newcastle Central station. Heaton was a sub-shed of Gateshead between 1963 and 1967.

Thornaby TMD was a railway traction maintenance depot situated in Thornaby, England, latterly operated by DB Schenker. The depot was situated to the east of Thornaby, on the northern side of the line to Middlesbrough.

Hither Green (London) Traction Maintenance Depot or Hither Green (London) TMD is a railway depot used for the maintenance and servicing of freight trains adjacent to the Hither Green marshalling yard. The depot is a hub for moving freight around south-east England; it is owned and operated by DBS. The official depot code is HG; in steam days, the shed code was 73C.

The Widened Lines is a double-track railway line forming part of the Thameslink route between St Pancras and Farringdon within Central London.

Longhedge Railway Works was a locomotive and carriage works built by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway in the borough of Battersea, South London to serve their new London terminus at Victoria. The facility existed between 1862 until the mid-1950s.

Ryde Traincare Depot is a railway traction maintenance depot, situated in Ryde, Isle of Wight, to the east of Ryde St John's Road railway station. The depot is operated by Island Line, is allocated the Island Line fleet of the British Rail Class 484s. The depot code is RY.

Reading Southern railway station is a former railway station in Reading, Berkshire, England, located to the south of Reading General station on the Great Western main line.
William Martley was the locomotive superintendent of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) in England from 1860 until his death.
The LCDR M1 class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR), very similar to the earlier M class but with steel frames, larger tenders and other detailed differences. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1880.

The LCDR C class or Europa Class was a class of 2-4-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR). The class was designed by William Martley and introduced in 1873, intended for the heaviest express services between London and Dover.

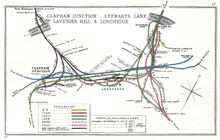
Stewarts Lane was the name of two separate railway stations in Battersea, South London.