
The capybara is a giant cavy rodent native to South America. It is the largest living rodent in the world. Also called capivara, capiguara, chigüire, chigüiro, or fercho, carpincho and ronsoco, it is a member of the genus Hydrochoerus, of which the only other extant member is the lesser capybara. Its close relatives include guinea pigs and rock cavies, and it is more distantly related to the agouti, the chinchilla, and the coypu. The capybara inhabits savannas and dense forests and lives near bodies of water. It is a highly social species and can be found in groups as large as 100 individuals, but usually lives in groups of 10–20 individuals. The capybara is not a threatened species, but it is hunted for its meat and hide and also for grease from its thick fatty skin.

Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of 916,445 km2, and the population of Venezuela was estimated at 28 million in 2019. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas.

The Bromeliaceae is a family of monocot flowering plants of 75 genera and around 3590 known species native mainly to the tropical Americas, with a few species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, Pitcairnia feliciana.

The Orinoco is one of the longest rivers in South America at 2,250 kilometres (1,400 mi). Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers 880,000 km2 (340,000 sq mi), with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the world by discharge volume of water. The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the Llanos of Colombia. The environment and wildlife in the Orinoco's basin are extremely diverse.

A tepui, or tepuy, is a table-top mountain or mesa found in the Guiana Highlands of South America, especially in Venezuela and western Guyana. The word tepui means "house of the gods" in the native tongue of the Pemon, the indigenous people who inhabit the Gran Sabana.
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 5,131 km2 (1,981 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.
The Federal Dependencies of Venezuela encompass most of Venezuela's offshore islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Venezuela, excluding those islands that form the State of Nueva Esparta and some Caribbean coastal islands that are integrated with nearby states. These islands, with a total area of 342 square kilometres, are sparsely populated – according to the preliminary results of the 2011 Census only 2,155 people live there permanently, with another hundred from Margarita Island who live there seasonally to engage in fishing. Local government is officially under the authority of Central government in Caracas, although de facto power is often held in the heads of the sparse and somewhat isolated communities that decorate the territories.

Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus is a mosquito-borne viral pathogen that causes Venezuelan equine encephalitis or encephalomyelitis (VEE). VEE can affect all equine species, such as horses, donkeys, and zebras. After infection, equines may suddenly die or show progressive central nervous system disorders. Humans also can contract this disease. Healthy adults who become infected by the virus may experience flu-like symptoms, such as high fevers and headaches. People with weakened immune systems and the young and the elderly can become severely ill or die from this disease.

The fauna of Venezuela consists of a huge variety of animals. Venezuela's diverse wildlife includes manatees, Amazon river dolphins, and Orinoco crocodiles, which have been reported to reach up to 6.6 metres (22 ft) in length. Some 23% of reptilian and 50% of amphibian species that inhabit the country are endemic to Venezuela. Overall, around 8,000 species are endemic to the country.

Oryzomys gorgasi, also known as Gorgas's oryzomys or Gorgas's rice rat, is a rodent in the genus Oryzomys of family Cricetidae. First recorded in 1967, it is known from only a few localities, including a freshwater swamp in the lowlands of northwestern Colombia and a mangrove islet in northwestern Venezuela. It reportedly formerly occurred on the island of Curaçao off northwestern Venezuela; this extinct population has been described as a separate species, Oryzomys curasoae, but does not differ morphologically from mainland populations.

The plushcap is a species of bird in the tanager family Thraupidae and it is the only member of the genus Catamblyrhynchus.

Roupala is a Neotropical genus of woody shrubs and trees in the plant family Proteaceae. Its 34 species are generally found in forests from sea level to 4000 m altitude from Mexico to Argentina.

Guyana, officially the Co‑operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America and the capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With 215,000 square kilometres (83,000 sq mi), Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname; it is also the second-least populous sovereign state in South America after Suriname.

Ilex, or holly, is a genus of about 480 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. The species are evergreen or deciduous trees, shrubs, and climbers from tropics to temperate zones worldwide. The type species is Ilex aquifolium, the common European holly used in Christmas decorations and cards.
Meruidae is a recently described family of aquatic beetles in the suborder Adephaga, with only one genus and species, Meru phyllisae. This beetle species was first found in the early 1980s. At 0.8 mm, it is one of the smallest adephagan beetles in the world. A recent survey of aquatic beetles of Venezuela prove that Meru is most common during the wet season, when larger areas of granitic rock surface are covered with water film, which the adult beetles as well as the larvae inhabit.
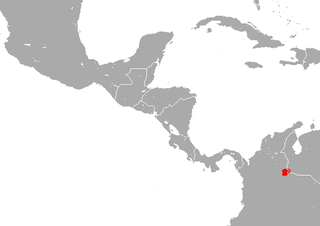
The Tamá small-eared shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is known from the Cordillera Oriental of Colombia and the Páramo de Tamá of western Venezuela, where it has been found primarily in cloud forest at elevations between 2380 and 3330 m. Its range includes Venezuela's El Tamá National Park. The closest relatives of the species are C. meridensis and C. thomasi.
Steyerbromelia discolor is a plant species in the genus Steyerbromelia. This species is endemic to Venezuela.
Steyerbromelia ramosa is a plant species in the genus Steyerbromelia. This species is endemic to Venezuela.
Steyerbromelia thomasii is a plant species in the genus Steyerbromelia. This species is endemic to Venezuela.

Roupala montana is a species of shrub or tree in the family Proteaceae which is native to much of the Neotropics. It is a morphologically variable species with four recognised varieties. The species is used medicinally in Venezuela, and as an aphrodisiac in Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela.















