Related Research Articles

The New York City Transit Authority is a public-benefit corporation in the U.S. state of New York that operates public transportation in New York City. Part of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, the busiest and largest transit system in North America, the NYCTA has a daily ridership of 8 million trips.

The Franklin Avenue Shuttle is a New York City Subway shuttle service operating in Brooklyn. The shuttle service uses the BMT Franklin Avenue Line exclusively. The north terminus is Franklin Avenue, with a transfer available to the IND Fulton Street Line. The south terminus is Prospect Park, with a transfer available to the BMT Brighton Line. NYCT Rapid Transit Operations refer to it internally as the S or FS. Like the other two shuttles, the 42nd Street Shuttle in Manhattan and the Rockaway Park Shuttle in Queens, its route bullet is colored dark gray on route signs, station signs, rolling stock, and the official subway map.

The MetroCard is a magnetic stripe card used for fare payment on transportation in the New York City area. It is the primary payment method for the New York City Subway, New York City Transit buses and MTA buses. The MetroCard is also accepted by several partner agencies: Nassau Inter-County Express (NICE), the PATH train system, the Roosevelt Island Tramway, AirTrain JFK, and Westchester County's Bee-Line Bus System.

The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is a public benefit corporation responsible for public transportation in the New York City metropolitan area of the U.S. state of New York. The MTA is the largest public transit authority in the United States, serving 12 counties in Downstate New York, along with two counties in southwestern Connecticut under contract to the Connecticut Department of Transportation, carrying over 11 million passengers on an average weekday systemwide, and over 850,000 vehicles on its seven toll bridges and two tunnels per weekday.
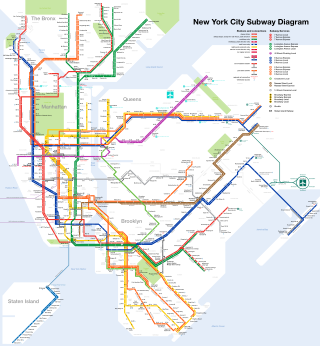
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system that serves four of the five boroughs of New York City, New York: the Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, and Queens. Its operator is the New York City Transit Authority, which is itself controlled by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority of New York. In 2015, an average of 5.65 million passengers used the system daily, making it the busiest rapid transit system in the United States and the 11th busiest in the world.
York Region Transit (YRT) is the public transit operator in York Region, Ontario, Canada. Its headquarters are in Richmond Hill, at 50 High Tech Road.
Straphanger may mean:

The 23rd Street Crosstown is a surface transit line on 23rd Street in Manhattan, New York City. It currently hosts the M23 SBS bus route of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA)'s Regional Bus Operations. The M23 runs between Chelsea Piers, along the West Side Highway near 22nd Street, via 23rd Street, to Avenue C and 20th Street in Stuyvesant Town–Peter Cooper Village.

The transportation system of New York City is a network of complex infrastructural systems. New York City, being the most populous city in the United States, has a transportation system which includes one of the largest subway systems in the world; the world's first mechanically ventilated vehicular tunnel; and an aerial tramway. New York City is also home to an extensive bus system in each of the five boroughs; citywide and Staten Island ferry systems; and numerous yellow taxis and boro taxis throughout the city. Private cars are less used compared to other cities in the rest of the United States.

Viva is the bus rapid transit operations of York Region Transit in York Region, Ontario, Canada. Viva service forms the spine for YRT's local bus service, providing seamless transit service across York Region with connections to northern Toronto.
Gene Russianoff is staff attorney and chief spokesman for the Straphangers Campaign, a New York City-based public transport advocacy group that focuses primarily on subway and bus services run by New York City Transit. At the same time, Russianoff has also served as a government reform advocate for NYPIRG.

The fares for services operated under the brands of MTA Regional Bus, New York City Subway, Staten Island Railway (SIR), PATH, Roosevelt Island Tramway, AirTrain JFK, NYC Ferry, and the suburban bus operators Nassau Inter-County Express (NICE) and Westchester County Bee-Line System (Bee-Line) are listed below.

Select Bus Service is a brand used by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA)'s Regional Bus Operations for limited-stop bus routes with some bus rapid transit features in New York City. The first SBS route was implemented in 2008 in order to improve speed and reliability on long, busy corridors.

MTA Regional Bus Operations (RBO) is the surface transit division of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). It was created in 2008 to consolidate all bus operations in New York City operated by the MTA. As of February 2018, MTA Regional Bus Operations runs 234 local routes, 71 express routes, and 20 Select Bus Service routes. Its fleet of 5,725 buses is the largest municipal bus fleet in the United States and operates 24/7. In 2021, the system had a ridership of 496,239,500, or about 1,811,600 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2022.
The Tri-State Transportation Campaign (TSTC) is a non-profit advocacy and policy organization dedicated to reducing car and truck dependency and promoting a "more balanced, environmentally sound and equitable transportation network" in downstate New York, New Jersey and Connecticut. TSTC's methods include political and media advocacy including a self-published blog, original research and analysis, litigation, and community organizing.

MTA Bus Time, stylized as BusTime, is a Service Interface for Real Time Information, automatic vehicle location (AVL), and passenger information system provided by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) of New York City for customers of its bus operations under the New York City Bus and MTA Bus Company brands. First tested in late 2010 and officially launched in early 2011, MTA Bus Time was installed in all MTA bus routes in New York City by 2014.

In 2017, New York Governor Andrew Cuomo declared a state of emergency for the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) due to ongoing reliability and crowding problems with mass transit in New York City. This order applied particularly to the New York City Subway, which was the most severely affected by dilapidated infrastructure, causing overcrowding and delays. With many parts of the system approaching or exceeding 100 years of age, general deterioration could be seen in many subway stations. By 2017, only 65% of weekday trains reached their destinations on time, the lowest rate since a transit crisis in the 1970s. To a lesser extent, New York City buses operated by the MTA were also affected. Both the subway and the buses are run by the New York City Transit Authority (NYCTA), a subsidiary of the MTA. A separate crisis at Penn Station affected the routes of the three railroad agencies that provided service into the station. Media outlets deemed these crises "the summer of hell".
OMNY is a contactless fare payment system, currently being implemented for use on public transit in the New York metropolitan area. OMNY can currently be used to pay fares at all New York City Subway and Staten Island Railway stations and on all MTA buses; when completely rolled out, it will replace the MetroCard on PATH trains, Bee-Line buses, NICE buses, and AirTrain JFK. OMNY will also expand beyond the current scope of the MetroCard to include the Long Island Rail Road and Metro-North Railroad.
References
- ↑ Gootman (2010)
- ↑ Chan, Sewell (03-13-2009), "MTA warns of dire fiscal picture," New York Times City Room blog.
- ↑ Haughney (2011)