
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.

7-Dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) is a zoosterol that functions in the serum as a cholesterol precursor, and is photochemically converted to vitamin D3 in the skin, therefore functioning as provitamin-D3. The presence of this compound in human skin enables humans to manufacture vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Upon exposure to ultraviolet UV-B rays in the sun light, 7-DHC is converted into vitamin D3 via previtamin D3 as an intermediate isomer. It is also found in the milk of several mammalian species. Lanolin, a waxy substance that is naturally secreted by wool-bearing mammals, contains 7-DHC which is converted into vitamin D by sunlight and then ingested during grooming as a nutrient. In insects 7-dehydrocholesterol is a precursor for the hormone ecdysone, required for reaching adulthood. 7-DHC was discovered by Nobel-laureate organic chemist Adolf Windaus.

The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin.

Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer of the skin are sometimes referred to as basal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes form a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. A number of structural proteins, enzymes, lipids, and antimicrobial peptides contribute to maintain the important barrier function of the skin. Keratinocytes differentiate from epidermal stem cells in the lower part of the epidermis and migrate towards the surface, finally becoming corneocytes and eventually being shed, which happens every 40 to 56 days in humans.
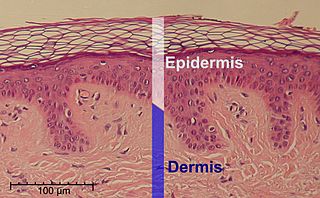
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss.

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis. Consisting of dead tissue, it protects underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress. It is composed of 15–20 layers of flattened cells with no nuclei and cell organelles.

The stratum basale is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the external covering of skin in mammals.
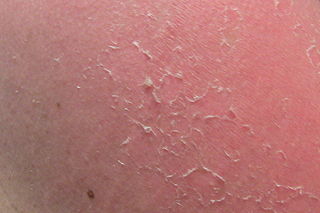
Desquamation, or peeling skin, is the shedding of dead cells from the outermost layer of skin.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and is usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.

The stratum granulosum is a thin layer of cells in the epidermis lying above the stratum spinosum and below the stratum corneum. Keratinocytes migrating from the underlying stratum spinosum become known as granular cells in this layer. These cells contain keratohyalin granules, which are filled with histidine- and cysteine-rich proteins that appear to bind the keratin filaments together. Therefore, the main function of keratohyalin granules is to bind intermediate keratin filaments together.

The stratum spinosum is a layer of the epidermis found between the stratum granulosum and stratum basale. This layer is composed of polyhedral keratinocytes. These are joined with desmosomes. Their spiny appearance is due to shrinking of the microfilaments between desmosomes that occurs when stained with H&E. Keratinization begins in the stratum spinosum, although the actual keratinocytes begin in the stratum basale. They have large pale-staining nuclei as they are active in synthesizing fibrillar proteins, known as cytokeratin, which build up within the cells aggregating together forming tonofibrils. The tonofibrils go on to form the desmosomes, which allow for strong connections to form between adjacent keratinocytes. The stratum spinosum also contains Langerhans cells, which functions as a macrophage by engulfing bacteria, foreign particles, and damaged cells that occur in this layer.
Spinous cells, or prickle cells, are keratin producing epidermal cells owing their prickly appearance to their numerous intracellular connections. They make up the stratum spinosum of the epidermis and provide a continuous net-like layer of protection for underlying tissue. They are susceptible to mutations caused by sunlight and can become malignant.

A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina.

In cell biology, lamellar bodies are secretory organelles found in type II alveolar cells in the lungs, and in keratinocytes in the skin. They are oblong structures, appearing about 300-400 nm in width and 100-150 nm in length in transmission electron microscopy images. Lamellar bodies in the alveoli of the lungs fuse with the cell membrane and release pulmonary surfactant into the extracellular space.

The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin".
Corneocytes are terminally differentiated keratinocytes and compose most of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis. They are regularly replaced through desquamation and renewal from lower epidermal layers and are essential for its function as a skin barrier.
Keratohyalin is a protein structure found in cytoplasmic granules of the keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis. Keratohyalin granules (KHG) mainly consist of keratin, profilaggrin, loricrin and trichohyalin proteins which contribute to cornification or keratinization, the process of the formation of epidermal cornified cell envelope. During the keratinocyte differentiation, these granules maturate and expand in size, which leads to the conversion of keratin tonofilaments into a homogenous keratin matrix, an important step in cornification.

Bullous impetigo is a bacterial skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus that results in the formation of large blisters called bullae, usually in areas with skin folds like the armpit, groin, between the fingers or toes, beneath the breast, and between the buttocks. It accounts for 30% of cases of impetigo, the other 70% being non-bullous impetigo.
Skin sloughing is the process of shedding dead surface cells from the skin. It is most associated with cosmetic skin maintenance via exfoliation, but can also occur biologically or for medical reasons.















