
Streptococcus is a genus of gram-positive coccus or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales, in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single axis, thus when growing they tend to form pairs or chains, which may appear bent or twisted. This differs from staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes, thereby generating irregular, grape-like clusters of cells. Most streptococci are oxidase-negative and catalase-negative, and many are facultative anaerobes.

Streptococcus pyogenes is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus Streptococcus. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause Group A streptococcal infection. S. pyogenes is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A Streptococcus (GAS). However, both Streptococcus dysgalactiae and the Streptococcus anginosus group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) Streptococcus is thus also used.
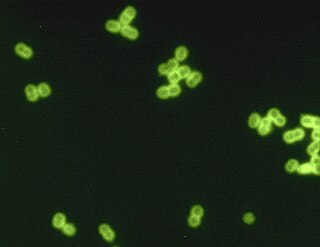
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic member of the genus Streptococcus. They are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form spores and are non motile. As a significant human pathogenic bacterium S. pneumoniae was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies.

Streptococcus salivarius is a species of spherical, gram-positive, facultative anaerobic lactic acid bacteria that is both catalase and oxidase negative. S. salivarius colonizes the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract of humans just a few hours after birth, making further exposure to the bacteria harmless in most circumstances. The bacterium is considered an opportunistic pathogen, rarely finding its way into the bloodstream, where it has been implicated in cases of sepsis in people with neutropenia,.

Streptococcus mutans is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. It is part of the "streptococci", an informal general name for all species in the genus Streptococcus. The microbe was first described by James Kilian Clarke in 1924.

Hemolysis is the breakdown of red blood cells. The ability of bacterial colonies to induce hemolysis when grown on blood agar is used to classify certain microorganisms. This is particularly useful in classifying streptococcal species. A substance that causes hemolysis is a hemolysin.
Gemella morbillorum is a species of bacteria within the genus Gemella. It is a facultative anaerobic Gram positive coccus usually preferring capnophilic or microaerophilic environments. From its discovery in 1917 until 1988, it was known as Streptococcus morbillorum. The name change followed closer examination with DNA filter hybridization which found it was very close to the species Gemella haemolysans.
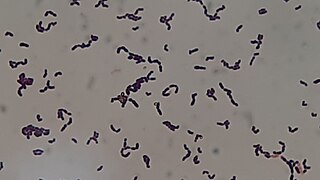
Streptococcus sanguinis, formerly known as Streptococcus sanguis, is a Gram-positive facultative anaerobic coccus species of bacteria and a member of the Viridans Streptococcus group. S. sanguinis is a normal inhabitant of the healthy human mouth where it is particularly found in dental plaque, where it modifies the environment to make it less hospitable for other strains of Streptococcus that cause cavities, such as Streptococcus mutans.
Streptococcus mitis is a mesophilic alpha-hemolytic species of Streptococcus that inhabits the oral cavity. It is coccus, gram-positive, catalase negative, and facultative anaerobe. It was previously classified as Streptococcus mitior. Streptococcus mitis is known to cause several medical conditions one of them being infective endocarditis.

Streptococcus oralis is a Gram positive viridans streptococcus of the Streptococcus mitis group. S. oralis is one of the pioneer species associated with eubiotic dental pellicle biofilms, and can be found in high numbers on most oral surfaces. It has been, however, found to be an opportunistic pathogen as well.
Streptococcus intermedius is an aerotolerant anaerobic commensal bacterium and a member of the Streptococcus anginosus group. The S. anginosus group, occasionally termed “Streptococcus milleri group” (SMG) display hemolytic and serologic diversity, yet share core physiological traits. Though the three members of the SMG are phenotypically diverse, one common trait they share is the mechanism of producing the metabolite diacetyl, which contributes to generating a signature caramel odor. Despite being commensal organisms, members of the S. anginosus group display wide pathogenic potential. S. intermedius has been isolated from patients with periodontitis and fatal purulent infections, especially brain and liver abscesses.
Streptococcus constellatus is a species of Streptococcus bacteria that is part of the normal flora in the oral cavity, urogenital region, and intestinal tract. However, it can frequently cause purulent infections in other parts of the body. DNA homology studies and 16S rRNA sequence analysis demonstrate S. constellatus belongs to the Streptococcus anginosus group along with Streptococcus intermedius and Streptococcus anginosus.

Streptococcus anginosus is a species of Streptococcus. This species, Streptococcus intermedius, and Streptococcus constellatus constitute the anginosus group, which is sometimes also referred to as the milleri group after the previously assumed but later refuted idea of a single species Streptococcus milleri. Phylogenetic relatedness of S. anginosus, S. constellatus, and S. intermedius has been confirmed by rRNA sequence analysis.

The Streptococcus anginosus group (SAG), also known as the anginosus group streptococci (AGS) or the milleri group streptococci (MGS), are a group of several species of streptococci with clinical similarities. The group is named after a principal member species, Streptococcus anginosus. The older name Streptococcus milleri is now pseudotaxonomic, as the idea that these streptococci constituted a single species was incorrect. The anginosus group streptococci are members of the viridans streptococci group. They have been implicated as etiologic agents in a variety of serious purulent infections, but because of their heterogeneous characteristics, these organisms may be unrecognized or misidentified by clinical laboratorians. The unique characteristic of them from other pathogenic streptococci, such as S. pyogenes and S. agalactiae, is their ability to cause abscesses.
Streptococcus vestibularis is a species of Streptococcus.
Streptococcus parasanguinis is a gram-positive bacterium of the genus Streptococcus that is classified as a member of the Streptococcus viridans group. S. parasanguinis is one of the major early colonizers of dental surfaces in the human oral cavity. Cell surface structures including pili and fimbriae allow the bacteria to adhere to oral surfaces. These adhesion molecules also play an important role in biofilm formation and promote aggregation with late tooth colonizers to form dental plaque. The presence of S. parasanguinis in the oral cavity is associated with a healthy microflora.

Streptococcus dysgalactiae is a gram positive, beta-haemolytic, coccal bacterium belonging to the family Streptococcaceae. It is capable of infecting both humans and animals, but is most frequently encountered as a commensal of the alimentary tract, genital tract, or less commonly, as a part of the skin flora. The clinical manifestations in human disease range from superficial skin-infections and tonsillitis, to severe necrotising fasciitis and bacteraemia. The incidence of invasive disease has been reported to be rising. Several different animal species are susceptible to infection by S. dysgalactiae, but bovine mastitis and infectious arthritis in lambs have been most frequently reported.
Rothia dentocariosa is a species of Gram-positive, round- to rod-shaped bacteria that is part of the normal community of microbes residing in the mouth and respiratory tract.

Streptococcus iniae is a species of Gram-positive, sphere-shaped bacterium belonging to the genus Streptococcus. Since its isolation from an Amazon freshwater dolphin in the 1970s, S. iniae has emerged as a leading fish pathogen in aquaculture operations worldwide, resulting in over US$100M in annual losses. Since its discovery, S. iniae infections have been reported in at least 27 species of cultured or wild fish from around the world. Freshwater and saltwater fish including tilapia, red drum, hybrid striped bass, and rainbow trout are among those susceptible to infection by S. iniae. Infections in fish manifest as meningoencephalitis, skin lesions, and septicemia.










