
A dental implant is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biological process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to the bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery/facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.
Osseointegration is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing artificial implant. A more recent definition defines osseointegration as "functional ankylosis ", where new bone is laid down directly on the implant surface and the implant exhibits mechanical stability. Osseointegration has enhanced the science of medical bone and joint replacement techniques as well as dental implants and improving prosthetics for amputees.
Chin augmentation using surgical implants alter the underlying structure of the face, intended to balance the facial features. The specific medical terms mentoplasty and genioplasty are used to refer to the reduction and addition of material to a patient's chin. This can take the form of chin height reduction or chin rounding by osteotomy, or chin augmentation using implants. Altering the facial balance is commonly performed by modifying the chin using an implant inserted through the mouth. The intent is to provide a suitable projection of the chin as well as the correct height of the chin which is in balance with the other facial features.

Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems primarily arising from skeletal disharmonies, and other orthodontic dental bite problems that cannot be treated easily with braces, as well as the broad range of facial imbalances, disharmonies, asymmetries, and malproportions where correction may be considered to improve facial aesthetics and self-esteem.

An Er:YAG laser (erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser, erbium YAG laser) is a solid-state laser whose active laser medium is erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Er:Y3Al5O12). Er:YAG lasers typically emit light with a wavelength of 2940 nm, which is infrared light.
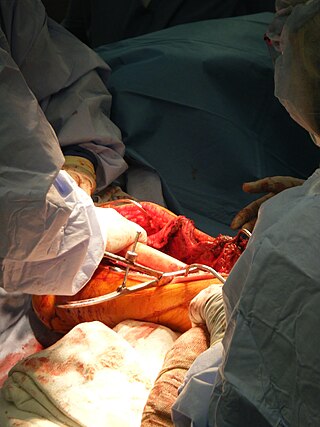
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured without bone grafting, but the risk is greater for large fractures like compound fractures.
Median palatal cysts are uncommon hard palate fissural cysts that are not odontogenic. These lesions are located behind the incisive canal in the midline of the hard palate. The majority of the time, median palatine cysts are asymptomatic and are discovered by coincidence while a patient is being evaluated for a different ailment.
Simon Hullihen MD, DDS was a dental surgeon born in Point Township, Pennsylvania. He completed his medical degree and then was inspired to seek a career in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Regarded as the first oral surgeon in the United States, he helped to develop many modern techniques of maxillofacial surgery and contributed to the establishment of oral and maxillofacial surgery as a surgical specialty.
Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis (NICO) is a diagnosis whereby a putative jawbone cavitation causes chronic facial neuralgia; this is different from osteonecrosis of the jaw. In NICO the pain is said to result from the degenerating nerve ("neuralagia"). The condition is probably rare, if it does exist.

Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a serious complication of radiation therapy in cancer treatment where radiated bone becomes necrotic and exposed. ORN occurs most commonly in the mouth during the treatment of head and neck cancer, and can arise over 5 years after radiation. Common signs and symptoms include pain, difficulty chewing, trismus, mouth-to-skin fistulas and non-healing ulcers.

Bicon Dental Implants is a privately owned company located in Boston, MA. The company specializes in short dental implants that use a locking taper or cold welding connection to secure the abutment to the implant. Bicon is notable and worthy of mention for the following three reasons: First, Bicon implants are extremely short in length. The size of Bicon implants allow them to be placed in regions that are crowded with natural teeth and/or implants, or in regions that would otherwise require bone grafting. Second, the implants do not have the screw-form design typical of other available implants. Third, the abutments are connected to the implant via a locking taper. This is notable from both a medical and engineering standpoint as no other implant company offers an implant with a biological seal at the implant/abutment interface; almost all other implants possess an internal screw to connect their abutments.
Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion (SARPE), also known as surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion(SARME), is a technique in the field of orthodontics which is used to expand the maxillary arch. This technique is a combination of both Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Orthodontics. This procedure is primarily done in adult patients whose maxillary sutures are fused and cannot be expanded via other techniques.
Alveoloplasty is a surgical pre-prosthetic procedure performed to facilitate removal of teeth, and smoothen or reshape the jawbone for prosthetic and cosmetic purposes. In this procedure, the bony edges of the alveolar ridge and its surrounding structures is made smooth, redesigned or recontoured so that a well-fitting, comfortable, and esthetic prosthesis may be fabricated or implants may be surgically inserted. This pre-prosthetic surgery which may include bone grafting prepares the mouth to receive a prosthesis or implants by improving the condition and quality of the supporting structures so they can provide support, better retention and stability to the prosthesis.
The foramen tympanicum, or also known as the foramen of Huschke, is an anatomical variation of the tympanic part of the temporal bone in humans resulting from a defect in normal ossification during the first five years of life. The structure was found in 4.6% to as high as 23% of the population.
Alloplasty is a surgical procedure performed to substitute and repair defects within the body with the use of synthetic material. It can also be performed in order to bridge wounds. The process of undergoing alloplasty involves the construction of an alloplastic graft through the use of computed tomography (CT), rapid prototyping and "the use of computer-assisted virtual model surgery." Each alloplastic graft is individually constructed and customised according to the patient's defect to address their personal health issue. Alloplasty can be applied in the form of reconstructive surgery. An example where alloplasty is applied in reconstructive surgery is in aiding cranial defects. The insertion and fixation of alloplastic implants can also be applied in cosmetic enhancement and augmentation. Since the inception of alloplasty, it has been proposed that it could be a viable alternative to other forms of transplants. The biocompatibility and customisation of alloplastic implants and grafts provides a method that may be suitable for both minor and major medical cases that may have more limitations in surgical approach. Although there has been evidence that alloplasty is a viable method for repairing and substituting defects, there are disadvantages including suitability of patient bone quality and quantity for long term implant stability, possibility of rejection of the alloplastic implant, injuring surrounding nerves, cost of procedure and long recovery times. Complications can also occur from inadequate engineering of alloplastic implants and grafts, and poor implant fixation to bone. These include infection, inflammatory reactions, the fracture of alloplastic implants and prostheses, loosening of implants or reduced or complete loss of osseointegration.

Shan K. Bagby is a United States Army brigadier general and the 28th Chief of the Army Dental Corps. Bagby also serves as the Commanding General, Regional Health Command-Central. Bagby, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, was the Army’s first African-American dental officer promoted to brigadier general.
A root-analogue dental implant (RAI) – also known as a truly anatomic dental implant, or an anatomical/custom implant – is a medical device to replace one or more roots of a single tooth immediately after extraction. In contrast to common titanium screw type implants, these implants are custom-made to exactly match the extraction socket of the specific patient. Thus there is usually no need for surgery.
The ameloblastic fibro-odontoma (AFO) is essentially a benign tumor with the features characteristic of ameloblastic fibroma along with enamel and dentin. Though it is generally regarded as benign, there have been cases of its malignant transformation into ameloblastic fibrosarcoma and odontogenic sarcoma. Cahn LR and Blum T, believed in "maturation theory", which suggested that AFO was an intermediate stage and eventually developed during the period of tooth formation to a complex odontoma thus, being a hamartoma.

Mewing is a form of oral posture training purported to improve jaw and facial structure. It was named after Mike and John Mew, the controversial British orthodontists who created the technique as a part of a practice called "orthotropics". It involves placing one's tongue at the roof of the mouth and applying pressure, with the aim of changing the structure of the jaws. No credible scientific research has ever proven the efficacy of orthotropics.






