
Mosquitoes are members of a group of about 3,500 species of small flies within the family Culicidae. The word "mosquito" is Spanish and Portuguese for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts.

N,N-Diethyl-meta-toluamide, also called DEET or diethyltoluamide, is the most common active ingredient in insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection against mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, chiggers, leeches and many biting insects.

Cinnamaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH=CHCHO. Occurring naturally as predominantly the trans (E) isomer, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. It is a phenylpropanoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway. This pale yellow, viscous liquid occurs in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus Cinnamomum. The essential oil of cinnamon bark is about 90% cinnamaldehyde.
Body odor is present in all animals, including humans, and its intensity can be influenced by many factors. Body odor has a strong genetic basis, but can also be strongly influenced by various diseases and physiological conditions. Though body odor has played an important role in early humankind, it is generally considered to be an unpleasant odor amongst many human cultures.

Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. This mosquito originated in Africa, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
Icaridin, also known as picaridin, is an insect repellent which can be used directly on skin or clothing. It has broad efficacy against various insects such as mosquitos, ticks, gnats, flies and fleas, and is almost colorless and odorless. A study performed in 2010 showed that Picaridin spray and cream at the 20% concentration provided 12 hours of protection against ticks. Icaridin does not dissolve plastics, synthetics or sealants.

Oct-1-en-3-one (CH2=CHC(=O)(CH2)4CH3), also known as 1-octen-3-one, is the odorant that is responsible for the typical "metallic" smell of metals and blood coming into contact with skin. Oct-1-en-3-one has a strong metallic mushroom-like odor with an odor detection threshold of 0.03–1.12 µg/m3 and it is the main compound responsible for the "smell of metal", followed by decanal (smell: orange skin, flowery) and nonanal (smell: tallowy, fruity). Oct-1-en-3-one is the degradative reduction product of the chemical reaction of skin lipid peroxides and Fe2+. Skin lipid peroxides are formed from skin lipid by oxidation, either enzymatically by lipoxygenases or by air oxygen. Oct-1-en-3-one is a ketone analog of the alkene 1-octene.

1-Octen-3-ol, octenol for short and also known as mushroom alcohol, is a chemical that attracts biting insects such as mosquitoes. It is contained in human breath and sweat, and it was once believed that insect repellent DEET worked by blocking the insects' octenol odorant receptors. Recent evidence in Anopheles gambiae and Culex quequinfasciatius mosquitoes suggest DEET reduces the volatility of 1-octen-3-ol which can result in a reduction in human attraction. 1-Octen-3-ol is a secondary alcohol derived from 1-octene. It exists in the form of two enantiomers, (R)-(–)-1-octen-3-ol and (S)-(+)-1-octen-3-ol.

Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIN2A gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II gamma chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK2G gene.

Glutamate receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIA1 gene.

Glutamate receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIA4 gene.

Olfactory receptor 51E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR51E1 gene.
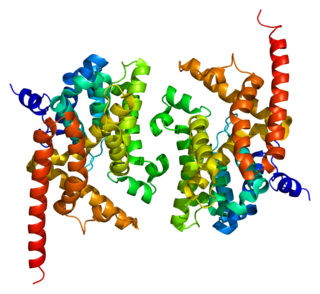
High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE9A gene.

Glutamate receptor, ionotropic kainate 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIK5 gene.

2-Heptanone, also known as methyl n-amyl ketone, or Heptan-2-one, is a ketone with the molecular formula C7H14O. It is a colorless, water-like liquid with a banana-like, fruity odor. 2-Heptanone has a neutral formal charge, and is only slightly soluble in water.
The molecular formula C8H14O (molar mass: 126.20 g/mol, exact mass: 126.1045 u) may refer to:

4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (MCHM, systematic name 4-methylcyclohexylmethanol) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H10CH2OH. Classified as a saturated higher alicyclic primary alcohol. Both cis and trans isomers exist, depending on the relative positions of the methyl (CH3) and hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring. Commercial samples of MCHM consists of a mixture of these isomers as well as other components that vary with the supplier.
Foot odor or bromodosis is a type of body odor that affects the feet of humans. It is sometimes considered to be an unpleasant smell, but can also be the target of foot fetishism, more specifically as a form of olfactophilia.

2-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one is an organic compound related to 1,2-cyclopentanedione. It is the enol tautomer of the diketone 3-methylcyclopentane-1,2-dione. Being an enol, the compound is often called methylcyclopentenolone. It is a colorless solid.















