Vichada Department is a department of the Republic of Colombia in South America. Vichada is located in the eastern plains of Colombia, in the Orinoquía Region within the Orinoco river basin bordering the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela to the north and east. To the north the department also borders with Arauca Department, to the northwest with Casanare Department, to the west with Meta Department, to the southwest narrowly bordering with Guaviare Department and to the south with Guainía Department. The department is the second largest in Colombia and scarcely populated in comparison to other departments.

Pasca is a town and municipality in the Cundinamarca department of Colombia located in the Andes. It belongs to the Sumapaz Province. Pasca is situated on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense at a distance of 71 kilometres (44 mi) from the capital Bogotá. It borders Fusagasugá, Sibaté and Soacha in the north, Bogotá D.C. in the north and east, Arbeláez in the south and Fusagasugá in the west. The urban center is located at an altitude of 2,180 metres (7,150 ft) and the altitude ranges from 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) to 3,500 metres (11,500 ft).

Melgar is a Colombian town in the Department of Tolima, 98 km (61 mi) southwest of Bogotá and 1 hour east of Ibagué, the capital city of Tolima.

The Cordillera Oriental is the widest of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Huila Department to Norte de Santander Department where it splits into the Serranía del Perijá and the Cordillera de Mérida in Venezuelan Andes. The highest peak is Ritacuba Blanco at 5,410 m (17,750 ft) in the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy.
Barrios Unidos is the 12th locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in the northwest of the city. This district is mostly inhabited by middle class residents. Barrios Unidos is completely urban, with some light industry and major commercial areas.

Antonio Nariño is the 15th locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in the south of the city. This district is mostly inhabited by lower middle and working class residents. The locality is named after an early Colombian leader, Antonio Nariño, who is often referred to as the precursor to the presidency.

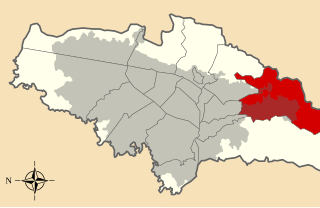
Chapinero is the 2nd locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in the north of the city and is one of the more affluent districts of the city. This district is mostly inhabited by upper class residents. The boundaries are Calle 39 in the south, Avenida Caracas in the west, Calle 100 in the north and the Eastern Hills in the east.

Kennedy, or Ciudad Kennedy, is the eighth locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in the southwest of the city and is the second most populous being home to 14% of the city's residents. This district is mostly inhabited by working and lower class residents.

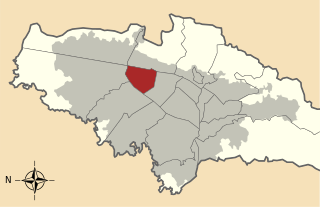
Teusaquillo is the 13th locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in the geographic center of the city, to the northwest of downtown Bogotá. This district is inhabited by middle class residents. It is an urbanized locality with several green zones as parks, avenues, and the campus of the National University of Colombia. It is located on the former site of an indigenous resguardo known as Pueblo Viejo, which existed until the main urbanization phase of the 20th century.

San Cristóbal, is the fourth locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in the southeast of Bogota. This district is mostly inhabited by lower class residents.

Tunjuelito is the 6th locality of the Capital District of the Colombian capital, Bogotá. Tunjuelito is located in the south of Bogotá, bordering to the north with the localities of Bosa, Kennedy and Puente Aranda, to the east with the localities of Rafael Uribe Uribe and Usme, to the south with Usme and to the west with Ciudad Bolívar. This district is mostly inhabited by working and lower class residents.
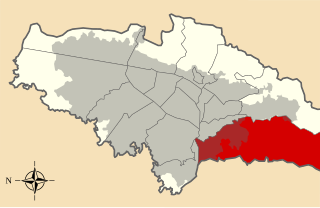
Ciudad Bolívar is the 19th locality in the Capital District of the Colombian capital city Bogotá. Ciudad Bolívar is located in the south of the city at the southern border of the Bogotá savanna. This district is mostly inhabited by underclass residents.

Chingaza National Natural Park is located in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, northeast of Bogotá, Colombia in the departments of Cundinamarca and Meta. The elevation in the park, to the east of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, ranges from 800 metres (2,600 ft) to 4,020 metres (13,190 ft), and the temperature ranges from 4 to 21.5 °C. The park extends over the Cundinamarca municipalities La Calera, Fómeque, Guasca and San Juanito (Meta).

The Eastern Hills are a chain of hills forming the eastern natural boundary of the Colombian capital Bogotá. They are part of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, the high plateau of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The Eastern Hills are bordered by the Chingaza National Natural Park to the east, the Bogotá savanna to the west and north, and the Sumapaz Páramo to the south. The north-northeast to south-southwest trending mountain chain is 52 kilometres (32 mi) long and its width varies from 0.4 to 8 kilometres. The highest hilltops rise to 3,550 metres (11,650 ft) over the western flatlands at 2,600 metres (8,500 ft). The Torca River at the border with Chía in the north, the boquerón Chipaque to the south and the valley of the Teusacá River to the east are the hydrographic limits of the Eastern Hills.

The Tunjuelo or Tunjuelito River is a river on the Bogotá savanna and a left tributary of the Bogotá River. The river, with a length of 73 kilometres (45 mi) originates in the Sumapaz Páramo and flows northward through the Usme Synclinal to enter the Colombian capital Bogotá. There, the river is mostly canalised flowing westward into the Bogotá River. It is one of the three main rivers of the city, together with the Fucha and Juan Amarillo Rivers.

The Usme Fault is a dextral oblique normal fault in the department of Cundinamarca in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of 64.9 kilometres (40.3 mi) and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 022.7 ± 6 in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes.