
Bengkulu is a province of Indonesia. It is located on the southwest coast of Sumatra. It was formed on 18 November 1968 by separating out the former Bencoolen Residency area from the province of South Sumatra under Law No. 9 of 1967 and was finalized by Government Regulation No. 20 of 1968. Spread over 19,813 km2, it is bordered by the provinces of West Sumatra to the north, Jambi to the northeast, Lampung to the southeast, and South Sumatra to the east, and by the Indian Ocean to the northwest, south, southwest, and west.

The Bangka Belitung Islands is a province of Indonesia. Situated off the southeastern coast of Sumatra, the province comprises two main landmasses—Bangka and Belitung—and numerous smaller islands. Bangka Belitung is bordered by the Bangka Strait to the west, the Natuna Sea to the north, the Java Sea is to the south and the Karimata Strait to the east. The province's capital and largest city is Pangkal Pinang. Bangka Belitung covers an area of 16,424.06 km2 (6,341.37 sq mi) and has a population of 1,455,678 according to the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 1,473,165.

Bangka is an island lying east of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is administered under the province of the Bangka Belitung Islands, being one of its namesakes alongside the smaller island of Belitung across the Gaspar Strait. The 9th largest island in Indonesia, it had a population of 1,146,581 at the 2020 census. It is the location of the provincial capital of Pangkal Pinang, and is administratively divided into four regencies and a city. The island itself and the surrounding sea suffers considerable environmental damage from its thriving tin mining industry which operates on- and offshore.
Belitung is an island on the east coast of Sumatra, Indonesia in the Java Sea. It covers 4,800.6 km2 (1,853.5 sq mi), and had a population of 309,097 at the 2020 Census. Administratively, it forms two regencies within the province of Bangka-Belitung Islands. The island is known for its pepper and for its tin. It was in the possession of the United Kingdom from 1812 until Britain ceded control of the island to the Netherlands in the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824. Its main town is Tanjung Pandan. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization has declared 17 tourist attractions in the Belitung Geopark as world geoparks.

Pangkal Pinang is the capital and largest city of the Bangka Belitung Islands Province in Indonesia. It is located on Bangka Island's east coast, the city is divided into seven districts (kecamatan) and has 42 wards (kelurahan).

Sungailiat is a city and district (kecamatan) of Bangka Regency, in the Bangka-Belitung province of Indonesia. It is also the regency seat.

Muntok or, more commonly, Mentok is a town in the Indonesian province of Bangka-Belitung on the island of Sumatra. The capital of West Bangka Regency, it is the site of the biggest tin smelter on the world. Mentok refers to the tip of the island.

Kisaran is a city in the North Sumatra province of Indonesia. Kisaran is the administrative capital of Asahan Regency. Kisaran is divided into two administrative districts (kecamatan) - West Kisaran District and East Kisaran District. Kisaran is situated on the Trans-Sumatra Highway, and is also located in the path of trains of northern Sumatra.

Manggar is a town in the Indonesian province of Bangka-Belitung, Indonesia which is a port on the east coast of Belitung Island, and is the seat of the East Belitung Regency. The town was founded as a tin mining town in the 19th century.

Tanjungpandan, is the largest town on the island Belitung in the Indonesian province of Bangka-Belitung, Indonesia. Tanjungpandan is the capital of the Belitung Regency comprising one of the five districts (kecamatan) within that Regency. It covers an area of 378.45 km2 and had a population of 86,487 at the 2010 Census and 103,062 at the 2020 Census.

West Bangka Regency is a regency (kabupaten) of Bangka Belitung Islands Province, Indonesia. It comprises the western part of Bangka Island, together with a number of small islands off its coast. The regency covers an area of 2,820.61 km2 and had a population of 175,110 at the 2010 Census, rising to 204,612 at the 2020 census. The town of Muntok is its regency seat.

Central Bangka Regency is a regency (kabupaten) of the Bangka Belitung Islands Province, Indonesia. It covers an area of 2,155.77 km2 and had a population of 161,075 at the 2010 Census, rising to 198,946 at the 2020 Census. The town of Koba is its regency seat.
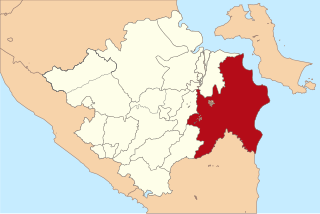
Ogan Komering Ilir Regency is a regency of South Sumatra Province, Indonesia. It takes its name from the Ogan River and the Komering River, which are the two main rivers that drain the area. The name Ilir means downstream. The administrative centre is the town of Kayu Agung. The regency borders Palembang, Ogan Ilir Regency and Banyuasin Regency to the north, Bangka Strait, and Java Sea to the east, Lampung Province to the south, and Ogan Ilir Regency, and East Ogan Komering Ulu Regency to the west.
Chinese Indonesians have lived in Bangka Belitung Islands, Indonesia for centuries. Bangka Belitung is one of the regions with the largest Chinese population in Indonesia besides Java, Riau, Eastern Sumatra and West Borneo.

Belinyu is a town and district (kecamatan) of Bangka Regency, in the Bangka-Belitung province of Indonesia. The district is located on the northern tip of Bangka Island.

Tukak Sadai is a district of South Bangka Regency, Bangka-Belitung Islands. The district is located in the southeastern section of Bangka Island, and contains the Sadai seaport.
Air Gegas is a district of South Bangka Regency, Bangka-Belitung Islands. It is the second largest and second most populated district in the regency after the regency seat of Toboali.
Payung is a district of South Bangka Regency, Bangka-Belitung Islands. It is located in the northern part of the regency, bordering the Central Bangka Regency.














