Related Research Articles

Escherichia coli ( ESH-ə-RIK-ee-ə KOH-lye) is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes such as EPEC, and ETEC are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut and are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between E. coli and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship — where both the humans and the E. coli are benefitting each other. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for three days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.

Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no mutation event occurs, the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Hence, bacterial growth occurs. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. However, if the surviving number exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration by direct and individual, direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual, or indirect and bulk methods. Models reconcile theory with the measurements.

β-Galactosidase is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing β-D-galactose residues in β-D-galactosides.
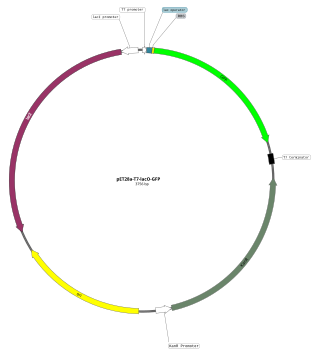
An expression vector, otherwise known as an expression construct, is usually a plasmid or virus designed for gene expression in cells. The vector is used to introduce a specific gene into a target cell, and can commandeer the cell's mechanism for protein synthesis to produce the protein encoded by the gene. Expression vectors are the basic tools in biotechnology for the production of proteins.

In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory.

A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells.

Lysogeny broth (LB) is a nutritionally rich medium primarily used for the growth of bacteria. Its creator, Giuseppe Bertani, intended LB to stand for lysogeny broth, but LB has also come to colloquially mean Luria broth, Lennox broth, life broth or Luria–Bertani medium. The formula of the LB medium was published in 1951 in the first paper of Bertani on lysogeny. In this article he described the modified single-burst experiment and the isolation of the phages P1, P2, and P3. He had developed the LB medium to optimize Shigella growth and plaque formation.
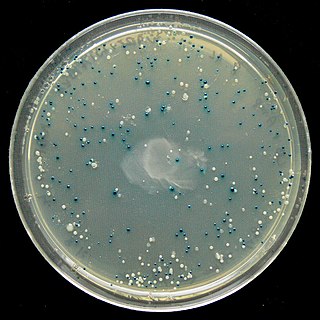
The blue–white screen is a screening technique that allows for the rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector-based molecular cloning experiments. This method of screening is usually performed using a suitable bacterial strain, but other organisms such as yeast may also be used. DNA of transformation is ligated into a vector. The vector is then inserted into a competent host cell viable for transformation, which are then grown in the presence of X-gal. Cells transformed with vectors containing recombinant DNA will produce white colonies; cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmids grow into blue colonies.
Fed-batch culture is, in the broadest sense, defined as an operational technique in biotechnological processes where one or more nutrients (substrates) are fed (supplied) to the bioreactor during cultivation and in which the product(s) remain in the bioreactor until the end of the run. An alternative description of the method is that of a culture in which "a base medium supports initial cell culture and a feed medium is added to prevent nutrient depletion". It is also a type of semi-batch culture. In some cases, all the nutrients are fed into the bioreactor. The advantage of the fed-batch culture is that one can control concentration of fed-substrate in the culture liquid at arbitrarily desired levels.
Transformation efficiency refers to the ability of a cell to take up and incorporate exogenous DNA, such as plasmids, during a process called transformation. The efficiency of transformation is typically measured as the number of transformants per microgram of DNA added to the cells. A higher transformation efficiency means that more cells are able to take up the DNA, and a lower efficiency means that fewer cells are able to do so.
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) transformation is a laboratory technique in prokaryotic (bacterial) cell biology. The addition of calcium chloride to a cell suspension promotes the binding of plasmid DNA to lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Positively charged calcium ions attract both the negatively charged DNA backbone and the negatively charged groups in the LPS inner core. The plasmid DNA can then pass into the cell upon heat shock, where chilled cells (+4 degrees Celsius) are heated to a higher temperature (+42 degrees Celsius) for a short time.
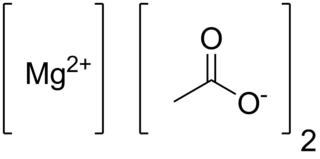
Anhydrous magnesium acetate has the chemical formula Mg(C2H3O2)2 and in its hydrated form, magnesium acetate tetrahydrate, it has the chemical formula Mg(CH3COO)2 • 4H2O. In this compound magnesium has an oxidation state of 2+. Magnesium acetate is the magnesium salt of acetic acid. It is deliquescent and upon heating, it decomposes to form magnesium oxide. Magnesium acetate is commonly used as a source of magnesium in biological reactions.
Herminiimonas glaciei is a species of ultramicrobacterium in the family Oxalobacteraceae. These small gram-negative cells have a variable number of long flagella at the ends and sides of their rod-shaped bodies. With dimensions of 0.5–0.9 by 0.3–0.4 μm, H. glaciei is roughly 10 to 50 times smaller than Escherichia coli. Discovered in 2009, the species was isolated from 120,000 years old glacial ice, 3,042 metres (1.9 mi) deep, from Greenland. It was revived after a long-term incubation—seven months of oxygen-free growth at 2 °C, followed by growth on agar plates at 5 °C for almost five months. DNA sequence analysis suggests that with a sequence similarity of 99.6%, H. glaciei is most closely related to H. saxobsidens, a species originally isolated from lichen-colonized rock. Loveland-Curtze, head of the team of scientists from Pennsylvania State University who found the species, speculates that it may offer insight into the existence of organisms in extraterrestrial habitats.
Tryptic soy broth or Trypticase soy broth is used in microbiology laboratories as a culture broth to grow aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. It is a general purpose medium that is routinely used to grow bacteria which tend to have high nutritional requirements.

A toxin-antitoxin system consists of a "toxin" and a corresponding "antitoxin", usually encoded by closely linked genes. The toxin is usually a protein while the antitoxin can be a protein or an RNA. Toxin-antitoxin systems are widely distributed in prokaryotes, and organisms often have them in multiple copies. When these systems are contained on plasmids – transferable genetic elements – they ensure that only the daughter cells that inherit the plasmid survive after cell division. If the plasmid is absent in a daughter cell, the unstable antitoxin is degraded and the stable toxic protein kills the new cell; this is known as 'post-segregational killing' (PSK).

Douglas Hanahan is an American biologist, professor and director emeritus of the Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research at EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland. He is currently member of the Lausanne branch of the Ludwig Institute.
Glucose phosphate broth is used to perform methyl red (MR) test and Voges–Proskauer test (VP).
Virtual colony count (VCC) is a kinetic, 96-well microbiological assay originally developed to measure the activity of defensins. It has since been applied to other antimicrobial peptides including LL-37. It utilizes a method of enumerating bacteria called quantitative growth kinetics, which compares the time taken for a bacterial batch culture to reach a threshold optical density with that of a series of calibration curves. The name VCC has also been used to describe the application of quantitative growth kinetics to enumerate bacteria in cell culture infection models. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) can be done on 96-well plates by diluting the antimicrobial agent at varying concentrations in broth inoculated with bacteria and measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration that results in no growth. However, these methods cannot be used to study some membrane-active antimicrobial peptides, which are inhibited by the broth itself. The virtual colony count procedure takes advantage of this fact by first exposing bacterial cells to the active antimicrobial agent in a low-salt buffer for two hours, then simultaneously inhibiting antimicrobial activity and inducing exponential growth by adding broth. The growth kinetics of surviving cells can then be monitored using a temperature-controlled plate reader. The time taken for each growth curve to reach a threshold change in optical density is then converted into virtual survival values, which serve as a measure of antimicrobial activity.
This bacterial growth medium was developed in 1971 for Lactococcus species isolated from milk products. It was originally called M16 medium, but in 1975 Terzaghi and Sandine added disodium-β-glycerophosphate to the medium as a buffer, and named the new growth medium M17 medium. It was later found that the addition of disodium-β-glycerophosphate inhibits the growth of many Lactobacillus species.
No-SCAR genome editing is an editing method that is able to manipulate the Escherichia coli genome. The system relies on recombineering whereby DNA sequences are combined and manipulated through homologous recombination. No-SCAR is able to manipulate the E. coli genome without the use of the chromosomal markers detailed in previous recombineering methods. Instead, the λ-Red recombination system facilitates donor DNA integration while Cas9 cleaves double-stranded DNA to counter-select against wild-type cells. Although λ-Red and Cas9 genome editing are widely used technologies, the no-SCAR method is novel in combining the two functions; this technique is able to establish point mutations, gene deletions, and short sequence insertions in several genomic loci with increased efficiency and time sensitivity.
References
- ↑ Hanahan, D. (1983). "Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids". Journal of Molecular Biology. 166 (4): 557–580. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(83)80284-8. PMID 6345791.
- 1 2 SOC Medium
- 1 2 http://www.protocol-online.org/biology-forums/posts/10626more1.html [ dead link ]
- ↑ SOC medium