Susanna B. Hecht is an American geographer, professor of Urban Planning at UCLA and professor of international history at the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies in Geneva.
Her early work on the deforestation of the Amazon led to the founding of the subfield of political ecology. This subfield of geography embraces sociology, economics, history, literature, ecology, environmental studies and a wide variety of other fields in an effort to paint a more intricate picture of a particular geographic region and the influence it has on the world around it as well as how the world impacts the region. [1] The Amazon rainforest is her primary subject of inquiry and she is the co-author of the book, Fate of the Forest: Destroyers, Developers and Defenders of the Amazon with Alexander Cockburn, originally published in 1990, but which has been updated and reissued by the University of Chicago Press in 2010. In 2004, Fate of the Forest was named one of the most influential books in cultural geography by the American Association of Geography. The book has become a classic text in environmental studies, and has won numerous awards. She is widely considered a preeminent authority on forest transition and sustainable agriculture. In addition to her academic work, she has also written popular articles for the Nation, [2] New Left Review and Fortune magazine. [3]
Hecht received her A.B. from the University of Chicago and her Ph.D. in Geography from the University of California, Berkeley. [4] She was awarded the prestigious John Simon Guggenheim fellowship in 2008 and has received fellowships and grants from NASA, the National Science Foundation, The Pew Charitable Trust, the MacArthur Foundation, The Ford Foundation, and many others. She has also been a resident fellow at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton and the Center for the Advanced Study of the Behavioral Sciences at Stanford University.
In 2018, she was awarded the David Livingstone Centenary Medal of the American Geographical Society. [5]
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
The Amazon River in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the longest or second-longest river system in the world, a title which is disputed with the Nile.

Political ecology is the study of the relationships between political, economic and social factors with environmental issues and changes. Political ecology differs from apolitical ecological studies by politicizing environmental issues and phenomena.

The Amazon rainforest, also called Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), of which 6,000,000 km2 (2,300,000 sq mi) are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations and 3,344 indigenous territories.

Francisco Alves Mendes Filho, better known as Chico Mendes, was a Brazilian rubber tapper, trade union leader, and environmentalist. He fought to preserve the Amazon rainforest, and advocated for the human rights of Brazilian peasants and Indigenous people. He was assassinated by a rancher on December 22, 1988. The Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation, a body under the jurisdiction of the Brazilian Ministry of the Environment, is named in his honor.

Euclides da Cunha was a Brazilian journalist, sociologist and engineer. His most important work is Os Sertões, a non-fictional account of the military expeditions promoted by the Brazilian government against the rebellious village of Canudos, known as the War of Canudos.

Terra preta is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil (anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its full name is terra preta do índio or terra preta de índio. Terra mulata is lighter or brownish in color.

Ellen Churchill Semple was an American geographer and the first female president of the Association of American Geographers. She contributed significantly to the early development of the discipline of geography in the United States, particularly studies of human geography. She is most closely associated with work in anthropogeography and environmentalism, and the debate about "environmental determinism".

The Kayapo people are the indigenous people in Brazil who inhabit a vast area spreading across the states of Pará and Mato Grosso, south of the Amazon River and along the Xingu River and its tributaries. This pattern has given rise to the nickname "the Xingu tribe". They are one of the various subgroups of the great Mebêngôkre nation. The term "Kayapo" is used by neighbouring groups rather than the Kayapo themselves. They refer to outsiders as "Poanjos".

Os Sertões, translated as Rebellion in the Backlands, is a book written by the Brazilian author Euclides da Cunha. Mixing science and literature, the author narrates the true story of a war that happened at the end of the 19th century in Canudos, a settlement of Bahia's Sertão ("backland"), an extremely arid region where, even now, struggles against poverty, drought and political corruption continue. During the war (1893–1897) against the republican army, the sertanejos were commanded by a messianic leader called Antônio Conselheiro.
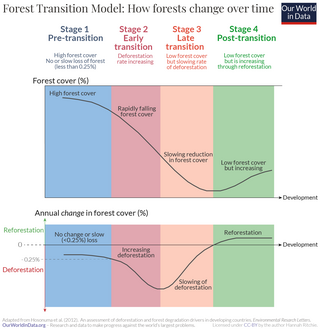
Forest transition refers to a geographic theory describing a reversal or turnaround in land-use trends for a given territory from a period of net forest area loss to a period of net forest area gain. The term "landscape turnaround" has also been used to represent a more general recovery of natural areas that is independent of biome type.
Darrell Addison Posey was an American anthropologist and biologist who vitalized the study of traditional knowledge of indigenous and folk populations in Brazil and other countries. He called his approach ethnobiology and combined research with respect for other cultures, especially indigenous intellectual property rights.
The Nomole or Cujareño people, also known as the Mashco Piro, are an indigenous tribe of nomadic hunter-gatherers who inhabit the remote regions of the Amazon rainforest. They live in Manú National Park in the Madre de Dios Region in Peru. They have actively avoided contact with non-native peoples.

Brazil once had the highest deforestation rate in the world and in 2005 still had the largest area of forest removed annually. Since 1970, over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the Amazon rainforest have been destroyed. In 2001, the Amazon was approximately 5,400,000 square kilometres (2,100,000 sq mi), which is only 87% of the Amazon's original size. According to official data, about 729,000 km² have already been deforested in the Amazon biome, which corresponds to 17% of the total. 300,000 km² have been deforested in the last 20 years.

The Treaty of Badajoz is a peace treaty of the XIX-th century signed by Spain and Portugal on 6 June 1801. Portugal ceded the border town of Olivenza to Spain and closed its ports to British military and commercial shipping.

The 1801 Treaty of Madrid was signed on 29 September 1801 by Portugal and France. Portugal made territorial concessions to France in Northern Brazil, closed its ports to British shipping and paid an indemnity of 20 million francs.
William Maxfield Denevan is an American geographer. He is professor emeritus of Geography at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and is a prominent member of the Berkeley School of cultural-historical geography. He also worked in the Latin American Center and the Institute for Environmental Studies at Wisconsin. His research interests are in the historical ecology of the Americas, especially Amazonia and the Andes.
Paulinho Paiakan was a leader of the Kayapo people, an indigenous tribe of Brazil. He led the Kayapo in their protests against the destruction of the Amazon rainforest.
A várzea forest is a seasonal floodplain forest inundated by whitewater rivers that occurs in the Amazon biome. Until the late 1970s, the definition was less clear and várzea was often used for all periodically flooded Amazonian forests.

Ana Maria Duran Calisto is an Ecuadorean architect, urbanist, environmental planner, and cofounder of architectural firm Estudio A0.

Carlos Scharff was a Peruvian rubber baron of German descent who was active along the Upper Purus and Las Piedras rivers during the Amazon rubber boom in Peru. He also served for many years during his youth as an agent for the Belgian consulate in Brazil.