Related Research Articles
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 Ma to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Ma.

Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Asaphida is a large, morphologically diverse order of trilobites found in marine strata dated from the Middle Cambrian until their extinction during the Silurian. Asaphida contains six superfamilies, but no suborders. Asaphids comprise some 20% of described fossil trilobites.

Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
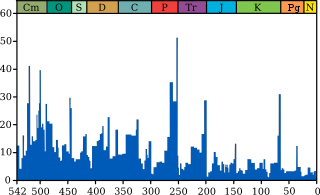
The Cambrian–Ordovician extinction event, also known as the Cambrian-Ordovician boundary event, was an extinction event that occurred approximately 485 million years ago (mya) in the Paleozoic era of the early Phanerozoic eon. It was preceded by the less-documented End-Botomian mass extinction around 517 million years ago, and the Dresbachian extinction event about 502 million years ago.
The Furongian is the fourth and final epoch and series of the Cambrian. It lasted from 497 to 485.4 million years ago. It succeeds the Miaolingian series of the Cambrian and precedes the Lower Ordovician Tremadocian Stage. It is subdivided into three stages: the Paibian, Jiangshanian and the unnamed 10th stage of the Cambrian.

Isotelus is a genus of asaphid trilobites from the Middle and Late Ordovician Period, fairly common in the northeastern United States, northwest Manitoba, southwestern Quebec and southeastern Ontario.

Ceraurus is a genus of cheirurid trilobite of the middle and, much more rarely, the upper Ordovician. They are commonly found in strata of the lower Great Lakes region. These trilobites have eleven thoracic segments, a very small pygidium and long genal and pygidial spines.
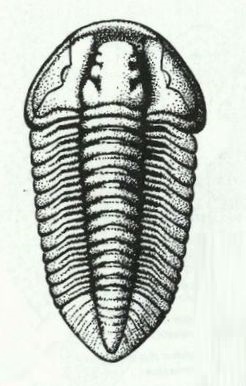
Flexicalymene Shirley, 1936. is a genus of trilobites belonging to the order Phacopida, suborder Calymenina and Family Calymenidae. Flexicalymene specimens can be mistaken for Calymene, Gravicalymene, Diacalymene and a few other Calymenina genera. They are used as an index fossil in the Ordovician. Ohio and North America are particularly known for being rich with Flexicalymene fossils.

Gravicalymene Shirley, 1936, is a genus of trilobites belonging to the order Phacopida, suborder Calymenina and family Calymenidae. Species included in this genus have previously been allocated to Calymene Brongniart 1822,Flexicalymene Shirley, 1936. and Sthenarocalymene Siveter 1977.

Diacalymene is a genus of trilobite from the order Phacopida, suborder Calymenina. It includes the species D. ouzregui, D. clavicula, D. diademata and D. gabrielsi. It lived in the Ordovician and Silurian periods.

Cheirurus is a genus of phacopid trilobites that lived from the Ordovician to the Devonian. Its remains have been found in Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America. Cheirurus is the type genus of Cheiruridae.

Asaphidae is a family of asaphid trilobites. Although the first genera originate in Upper Cambrian marine strata, the family becomes the most widely distributed and most species-rich trilobite family during the Ordovician. 754 species assigned to 146 genera are included in Asaphidae.

Illaenus is a genus of trilobites from Russia and Morocco, from the middle Ordovician.
Pliomerina is a genus of trilobites. A new species, P. tashanensis, was described from the late Ordovician of China by Dong-Chan Lee in 2012.
Raymondaspis is a genus of trilobites in the family Styginidae. It was described by Pribyl in 1949, and contains the species R. reticulatus and R. turgidus from the Whiterockian of Canada, R. vespertina from the Ordovician and Whiterockian of the United States and Norway, and a new species, R. grandigena, which existed during the Middle Ordovician of what is now Sweden. R. grandigena was described in 2012 by Martin Stein and Jan Bergström.
Annamitella Mansuy 1916 is a genus of trilobite, extinct marine arthropods. Annamitella lived from the Arenig to the Llandeilo age of the Ordovician Period from 478.6 to 460.9 million years ago.

Trinodus is a very small to small blind trilobite, a well known group of extinct marine arthropods, which lived during the Ordovician, in what are now the Yukon Territories, Virginia, Italy, Czech Republic, Poland, Denmark, Sweden, Svalbard, Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Iran, Kazakhstan and China. It is one of the last of the Agnostida order to survive.

Histiodella is an extinct genus of conodonts.

Librostoma is a subclass of trilobites defined by having a natant hypostome, which is a hypostome that is free from the anterior doublure and aligned with the anterior of the glabella, this is unlike a conterminant hypostome, which is attached to the exoskeleton.
References
- 1 2 Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera (Trilobita entry)". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 364: 560. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
- ↑ Fortey, R.A., "The Ordovician Trilobites of Spitsbergen"