
Al-Qaeda is a pan-Islamist militant organization led by Sunni jihadists who self-identify as a vanguard spearheading a global Islamist revolution to unite the Muslim world under a supra-national Islamic caliphate. Its membership is mostly composed of Arabs but also includes people from other ethnic groups. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian, economic and military targets of the U.S. and its allies; such as the 1998 US embassy bombings, the USS Cole bombing, and the September 11 attacks.

A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concepts and experiences. All communication is achieved through the use of symbols: for example, a red octagon is a common symbol for "STOP"; on maps, blue lines often represent rivers; and a red rose often symbolizes love and compassion. Numerals are symbols for numbers; letters of an alphabet may be symbols for certain phonemes; and personal names are symbols representing individuals. The academic study of symbols is called semiotics.

The Great Eastern Islamic Raiders' Front is an Islamist militant organization. The group's self-proclaimed goal is to dismantle Turkey and form the State of Grandsublime, a Sunni Islamic federate state in the Middle East. They are notably hostile to Shia, Alevi, Christian and Jewish interests. IBDA-C carries on its pro-Islamic legacy with a newly born radicalism that wishes to restore religious rule to Turkey of whose government it finds illegal with an added willingness to commit acts of terrorism.
Islamic terrorism refers to terrorist acts carried out by fundamentalist militant Islamists and Islamic extremists.

Lashkar-e-Taiba is a Pakistani Islamist Salafi jihadist organisation. Described as one of Pakistan's "most powerful jihadi groups", it is most infamous outside Pakistan. The organisation's primary stated objective is to merge the whole of Kashmir with Pakistan. It was founded in 1985–1986 by Hafiz Saeed, Zafar Iqbal Shehbaz, Abdullah Azzam and several other Islamist mujahideen with funding from Osama bin Laden during the Soviet–Afghan War. It has been designated a terrorist group by numerous countries.
Abu Musab al-Suri, born Mustafa bin Abd al-Qadir Setmariam Nasar, is a suspected Al-Qaeda member and writer best known for his 1,600-page book The Global Islamic Resistance Call. He is considered by many as 'the most articulate exponent of the modern jihad and its most sophisticated strategist'.
Religious fanaticism is a pejorative designation used to indicate uncritical zeal or obsessive enthusiasm that is related to one's own, or one's group's, devotion to a religion – a form of human fanaticism that could otherwise be expressed in one's other involvements and participation, including employment, role, and partisan affinities. In psychiatry, the term hyperreligiosity is used. Historically, the term was applied in Christian antiquity to denigrate non-Christian religions, and subsequently acquired its current usage with the Age of Enlightenment.

The flag of the Shi'a political and military organization Hezbollah depicts a stylized representation of the Arabic words حزب الله in Kufic script. Written near the first letter of the word Allah, there is a hand that reaches up to grasp a stylized assault rifle. The flag incorporates several other symbols, namely a globe, a book, a sword, and a seven-leafed branch. The text above the logo reads فإن حزب الله هم الغالبون and means "Then surely the party of God are they that shall be triumphant", which is a reference to the name of the party. Underneath the logo are the words المقاومة الإسلامية في لبنان, meaning "The Islamic Resistance in Lebanon".

Jihadism is a neologism for modern militant Islamic movements that seek to base the state on Islamic principles. In a narrower sense, it refers to the belief that armed confrontation is a theologically legitimate method of socio-political change towards an Islamic system of governance.

Islamic extremism refers to extremist beliefs, behaviors and ideologies adhered to by some Muslims within Islam. The term 'Islamic extremism' is contentious, encompassing a spectrum of definitions, ranging from academic interpretations of Islamic supremacy to the notion that all ideologies other than Islam have failed and are inferior.
Rita Katz is a terrorism analyst and the co-founder of the Search International Terrorist Entities (SITE) Intelligence Group, a private intelligence firm based in Washington, D.C.
Globalization has been internalized in Arabic as awlaama (العولمة) and refers to the spread throughout the globe of ideas, customs, institutions, and attitudes originated in one part of the world which are usually Western in origin. For this reason it has often been perceived as largely equivalent to Westernization and is still widely regarded as an external threat rather than as an opportunity. In the Middle East the decade of globalization was marked by endless wars, intrusive US hegemony, renewed economic dependency and continuing insecurity. Globalization was ushered into the Middle East by a war which gave the Western victors excessive power over the region and created a violent anti-globalization struggle. As some authors argue, it has strengthened Islamic fundamentalism and, due to its ambiguity created a contradictory and tension filled situation. Globalization thus often acted as an obstacle rather than an impetus to democratization.

Salafi jihadism, also known as Salafi-jihadism, jihadist Salafism and revolutionary Salafism, is a religiopolitical Sunni Islamist ideology that seeks to establish a global caliphate. In a narrower sense, jihadism refers to the belief that armed confrontation with political rivals is an efficient and theologically legitimate method of socio-political change. The Salafist interpretation of sacred Islamic texts is "in their most literal, traditional sense", which adherents claim will bring about the return to "true Islam".

Inspire is an English-language online magazine published by the organization al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP). The magazine is one of the many ways AQAP uses the Internet to reach its audience. Numerous international and domestic extremists motivated by radical interpretations of Islam have been influenced by the magazine and, in some cases, used its bomb-making instructions in their attempts to carry out attacks. The magazine is an important brand-building tool, not just of AQAP, but of all al-Qaeda branches, franchises and affiliates.
Islamic extremism in the United States comprises all forms of Islamic extremism occurring within the United States. Islamic extremism is an adherence to fundamentalist interpretations of Islam, potentially including the promotion of violence to achieve political goals. In the aftermath of the September 11, 2001 terror attacks, Islamic extremism became a prioritized national security concern of the U.S. government and a focus of many subsidiary security and law enforcement entities. Initially, the focus of concern was on foreign Islamic terrorist organizations, particularly al-Qaeda, but in the course of the years since the September 11 terror attacks, the focus has shifted more towards Islamic extremist radicalized individuals and jihadist networks within the United States.
Terrorism, fear, and media are interconnected. Terrorists use the media to advertise their attacks and or messages, and the media uses terrorism events to further aid their ratings. Both promote unwarranted propaganda that instills mass amounts of public fear. The leader of Al Qaeda, Osama Bin Laden, discussed weaponization of media in a letter written after his organization committed the terrorist attacks of 9/11. In that letter, Bin Laden stated that fear was the deadliest weapon. He noted that Western civilization has become obsessed with mass media, quickly consuming what will bring them fear. He further stated that societies are bringing this problem on their own people by giving media coverage an inherent power.
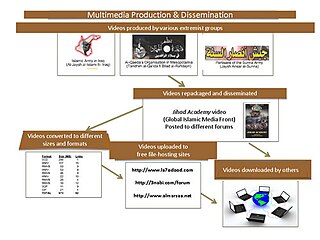
The Global Islamic Media Front (GIMF) is an Islamist propaganda organization that is associated with the terrorist group, al-Qaeda, and other jihadist groups. The GIMF is known by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) as an "underground media" organization. The GIMF specializes in production of jihadist material for distribution. It is one of several organizations that jihadists use to spread information via the Internet, including the well-known As-Sahab. Their slogan that is used on their materials is "Observing Mujahideen News and Inspiring the Believers." There is no indication who the leader of this organization is.
The ideology of the Islamic State, unoffically referred to as Islamic Statism, has been described as being a blend of Salafism, Salafi jihadism, Sunni Islamist fundamentalism, Wahhabism, and Qutbism. Through its official statement of beliefs originally released by its first leader Abu Omar al-Baghdadi in 2007 and subsequently updated since June 2014, the Islamic State defined its creed as "a middle way between the extremist Kharijites and the lax Murji'ites".

Starting in the mid-1970s and 1980s, Salafism and Wahhabism — along with other Sunni interpretations of Islam favored by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and other Gulf monarchies — achieved a "preeminent position of strength in the global expression of Islam."
Terrorism in Turkey is defined in Turkey's criminal law as crimes against the constitutional order and internal and external security of the state by the use of violence as incitement or systematic to create a general climate of fear and intimidation of the population and thereby effect political, religious, or ideological goals. Since the establishment of the Republic of Turkey, both organized groups, lone wolf, and international spy agencies have committed many acts of domestic terrorism against Turkish people.











