
Copromorphidae, the "tropical fruitworm moths", is a family of insects in the lepidopteran order. These moths have broad, rounded forewings, and well-camouflaged scale patterns. Unlike Carposinidae the mouthparts include "labial palps" with the second rather than third segment the longest. With other unusual structural characteristics of the caterpillar and adult, it could represent the sister lineage of all other extant members of this superfamily. The genus Sisyroxena from Madagascar is also notable for its unusual venation and wing scale sockets.

Dichomeris is a genus of moths in the family Gelechiidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1818.

Hypatima is a genus of the twirler moth family (Gelechiidae). Among these, it belongs to a distinct lineage, which is variously treated as tribe Chelariini in subfamilies Dichomeridinae, Gelechiinae, or even Pexicopiinae, and historically was considered a subfamily in its own right, Chelariinae. Of this lineage, Hypatima – under its junior synonym Chelaria – is the type genus. This genus has numerous species, but its exact limits are not quite clear. This genus occurs mainly in the Southern Hemisphere, though one of the better-known species is the only member of this genus native to Europe, the lobster-clawed moth.

Lecithocera is a genus of moths in the lecithocerid subfamily Lecithocerinae. The genus was erected by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1853.

The Symmocinae are a subfamily of moths in the superfamily Gelechioidea. These small moths are found mainly in the Palearctic and Africa.

Antaeotricha is a genus of moths. It is the largest genus in the subfamily Stenomatinae, numbering over 400 species in the Western Hemisphere.

Acrocercops is a genus of moths in the family Gracillariidae.

Symmoca signatella is a moth of the family Autostichidae. It is known from most of western Europe, but also Lithuania, Croatia, Greece and southern Russia. It has also been recorded from California in North America.

Symmoca is a genus of moths in the family Autostichidae.

Gelechiinae is a subfamily of moths in the family Gelechiidae. It was described by Henry Tibbats Stainton in 1854.

Anomologinae is a subfamily of moths in the family Gelechiidae.
Symmoca alacris is a moth in the family Autostichidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1918. It is found in Kanara in Karnataka, India.
Symmoca crocodesma is a moth in the family Autostichidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1911. It is found in South Africa.
Symmoca pelospora is a moth in the family Autostichidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1927. It is found in Xinjiang, China.
Symmoca vetusta is a moth in the family Autostichidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1931. It is found in Brazil.
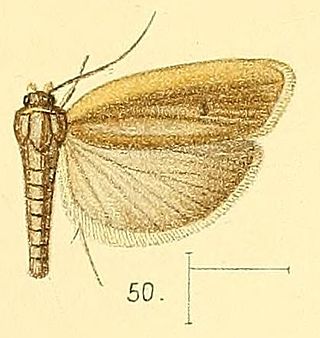
Stenoma is a genus of moths. The type species is Stenoma litura, which was described by Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1839.
Chlamydastis is a genus of moths in the subfamily Stenomatinae.

Tingena is a genus of the concealer moth family (Oecophoridae). This genus is endemic to New Zealand.











