
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek caeno- (recent), rhabditis (rod-like) and Latin elegans (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it Rhabditides elegans. Osche placed it in the subgenus Caenorhabditis in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised Caenorhabditis to the status of genus.

The spermatheca, also called receptaculum seminis, is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, oligochaeta worms and certain other invertebrates and vertebrates. Its purpose is to receive and store sperm from the male or, in the case of hermaphrodites, the male component of the body. Spermathecae can sometimes be the site of fertilization when the oocytes are sufficiently developed.

Hemerobiidae is a family of Neuropteran insects commonly known as brown lacewings, comprising about 500 species in 28 genera. Most are yellow to dark brown, but some species are green. They are small; most have forewings 4–10 mm long. These insects differ from the somewhat similar Chrysopidae not only by the usual coloring but also by the wing venation: hemerobiids differ from chrysopids in having numerous long veins and forked costal cross veins. Some genera are widespread, but most are restricted to a single biogeographical realm. Some species have reduced wings to the degree that they are flightless. Imagines (adults) of subfamily Drepanepteryginae mimic dead leaves. Hemerobiid larvae are usually less hairy than chrysopid larvae.

Ctenochasma is a genus of Late Jurassic ctenochasmatid pterosaur belonging to the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Three species are currently recognized: C. roemeri, C. taqueti, and C. elegans. Their fossilized remains have been found in the Solnhofen Limestone of Bavaria, Germany, the "Purbeck Group" of northeastern Germany, and the Calcaires tâchetés of eastern France.

Chlaenius is a large and diverse genus of ground beetle. It is native to the Palearctic realm, Afrotropical realm, and Nearctic realm. Worldwide, roughly 1,000 species are currently recognized with the majority of known species occurring in the Oriental and Afrotropical regions. The genus is divided into many subgenera.
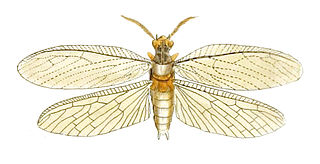
Chauliodes pectinicornis known as Summer fishfly. is a species of fishfly from North America.
In the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, Carl Linnaeus classified the arthropods, including insects, arachnids and crustaceans, among his class "Insecta". Insects with net-veined wings were brought together under the name Neuroptera.

Draconichthys elegans is a selenosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Frasnian Kellwasserkalk facies of the Anti-Atlas Mountains of what is now Morocco. During the Late Devonian, the region would have been a shallow, algae-dimmed sea.

Hemerobius is a genus of lacewings in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found throughout Europe and North America. Like most lacewings, both the larvae and adults are predatory, primarily eating acarines, scale insects, psyllids, aphids, thrips, and the eggs of lepidopterans and whiteflies.

Sympherobius is a genus of brown lacewings in the family Hemerobiidae. There are at least 50 described species in Sympherobius.
Sympherobius occidentalis is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in North America.

Hemerobius humulinus is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in Europe & Northern Asia, North America, and Southern Asia.
Sympherobius umbratus is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in North America.
Sympherobius amiculus is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in the Caribbean Sea and North America.
Sympherobius californicus is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in Central America, North America, and Oceania. The species was introduced to New Zealand to prey on aphids and mealybugs affecting crops, first noted in 1936, however was not able to be established.

Sympherobius barberi, or Barber's brown lacewing, is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in Europe & Northern Asia, Central America, North America, Oceania, and South America. The species was introduced to New Zealand to prey on aphids and mealybugs, first noted in 1936, however was not able to be established.
Sympherobius killingtoni is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Hemerobius stigma is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in Europe & Northern Asia and North America. The species was introduced to New Zealand to prey on adelgidae growing on pine plantations, and was first noted as being present in the country in 1935, however was not able to be established.
Hemerobius bistrigatus is a species of brown lacewing in the family Hemerobiidae. It is found in North America.












