
Marchantiopsida is a class of liverworts within the phylum Marchantiophyta. The species in this class are known as complex thalloid liverworts. The species in this class are widely distributed and can be found worldwide.

Rhynchospora colorata, also known as starrush whitetop, white star sedge and white-topped sedge, is a perennial flowering plant in the sedge family. It has white bracts, giving it the appearance of white petals with long, green points. It is native to southeastern North America, from Virginia west to New Mexico in the United States, and south into the Caribbean islands.

Vernonia is a genus of about 350 species of forbs and shrubs in the family Asteraceae. Some species are known as ironweed. Some species are edible and of economic value. They are known for having intense purple flowers. There have been numerous distinct subgenera and subsections named in this genus, and some botanists have divided the genus into several distinct genera. For instance, the Flora of North America recognizes only about twenty species in Vernoniasensu stricto, seventeen of which are in North America north of Mexico, with the others being found in South America.

Takakia is a genus of two species of mosses known from western North America and central and eastern Asia. The genus is placed as a separate family, order and class among the mosses. It has had a history of uncertain placement, but the discovery of sporophytes clearly of the moss-type firmly supports placement with the mosses.

Pseudowintera colorata, also known as mountain horopito or pepper tree, is a species of woody evergreen flowering trees and shrubs, part of family Winteraceae. The species is endemic to New Zealand. All Winteraceae are magnoliids, associated with the humid Antarctic flora of the southern hemisphere.

Pallaviciniaceae is a widely distributed family of liverworts in the order Pallaviciniales. All species are thallose, typically organized as a thick central costa (midvein), each side with a broad wing of tissue one cell in thickness. All species are dioicous. The greatest diversity is in Australasia, with some species endemic to that region, though species belonging to the family may be found on every continent except Antarctica.
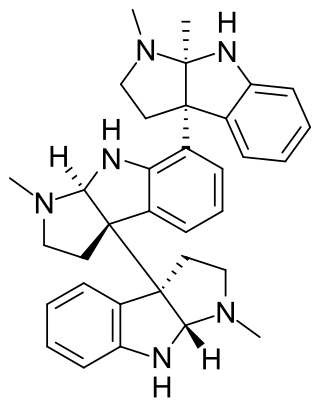
Hodgkinsine is an alkaloid found in plants of the genus Psychotria, particularly Psychotria colorata, although it is also found in Psychotria lyciiflora and probably other species in this family,
Crassula colorata, the dense pigmyweed or dense stonecrop, is an annual plant in the family Crassulaceae. The species is endemic to Australia, occurring in Western Australia, South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.

Jensenia spinosa is a dioicous bryophyte plant in the liverwort family Pallaviciniaceae. It is the only African member of the genus Jensenia, and generally occurs at high elevations. It is widespread but scarce, and has been found in South Africa, Malawi, Tanzania, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, as well as the islands of Mauritius, Réunion and Saint Helena.

Bathytoma is a genus of deep-water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Borsoniidae.

Merulempista is a genus of moths of the family Pyralidae described by Rolf-Ulrich Roesler in 1967.

Olearia rani, or heketara as it is known in Māori is a common small forest tree of New Zealand. It grows in lowland forest throughout the North Island and in the northern half of the South Island. Olearia rani var. rani has a more northern range than Olearia rani var. colorata which is found in forests from the Coromandel south to the Buller River. Its leaves have white undersides and prominent veins. During the spring the tree produces clusters of small white flowers.
Glyphipterix colorata is a species of sedge moth in the genus Glyphipterix. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1913. It is found in Guyana.
Thermoniphas colorata is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It is found along the coast of Kenya and in Ethiopia, eastern Tanzania, Malawi, Zambia, Mozambique and north-western Zimbabwe. The habitat consists of marshy areas in and on the edges of forests.
Crocomela colorata is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1865. It is found in Colombia and Peru.

Lygephila colorata is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by János Babics and László Aladár Ronkay in 2009. It is found in north-western Pakistan.

Bovista colorata is a species of puffball fungus in the family Agaricaceae. It is found in eastern North America and northwestern South America. The puffball was first described as Lycoperdon coloratum by Charles Horton Peck in 1878, from collections made in Sand Lake, New York. Hanns Kreisel transferred it to the genus Bovista by in 1964. The golden to orange-yellow fruitbodies are 13–30 cm (5.1–11.8 in) in diameter. Its spores are spherical, measuring 3.5–5 μm in diameter.

The Botany of Lord Auckland's Group and Campbell's Island is a description of the plants discovered in those islands during the Ross expedition written by Joseph Dalton Hooker and published by Reeve Brothers in London between 1844 and 1845. Hooker sailed on HMS Erebus as assistant surgeon. It was the first in a series of four Floras in the Flora Antarctica, the others being the Botany of Fuegia, the Falklands, Kerguelen's Land, Etc. (1845–1847), the Flora Novae-Zelandiae (1851–1853), and the Flora Tasmaniae (1853–1859). They were "splendidly" illustrated by Walter Hood Fitch.

Rhytidiadelphus is a genus of mosses belonging to the family Hylocomiaceae.














