TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein is an adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the TYROBP gene. [5] [6]
TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein is an adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the TYROBP gene. [5] [6]
This gene encodes a transmembrane signaling polypeptide which contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) in its cytoplasmic domain. The encoded protein may associate with the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) family of membrane glycoproteins and may act as an activating signal transduction element. This protein may bind zeta-chain associated protein kinase 70 kDa (ZAP-70) and spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) and play a role in signal transduction, bone modeling, brain myelination, and inflammation. Mutations within this gene have been associated with polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy (PLOSL), also known as Nasu-Hakola disease. Its putative receptor, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), also causes PLOSL. Two alternative transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Other alternative splice variants have been described, but their full-length nature has not been determined. [7]
Pathological mutations of the TYROBP gene cause polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy 1, a condition presenting as early-onset dementia.
Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), are a family of type I transmembrane glycoproteins expressed on the plasma membrane of natural killer (NK) cells and a minority of T cells. At least 15 genes and 2 pseudogenes encoding KIR map in a 150-kb region of the leukocyte receptor complex (LRC) on human chromosome 19q13.4.
An immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) is a conserved sequence of four amino acids that is repeated twice in the cytoplasmic tails of non-catalytic tyrosine-phosphorylated receptors, cell-surface proteins found mainly on immune cells. Its major role is being an integral component for the initiation of a variety of signaling pathway and subsequently the activation of immune cells, although different functions have been described, for example an osteoclast maturation.

CD5 is a cluster of differentiation expressed on the surface of T cells and in a subset of murine B cells known as B-1a. The expression of this receptor in human B cells has been a controversial topic and to date there is no consensus regarding the role of this receptor as a marker of human B cells. B-1 cells have limited diversity of their B-cell receptor due to their lack of the enzyme terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and are potentially self-reactive. CD5 serves to mitigate activating signals from the BCR so that the B-1 cells can only be activated by very strong stimuli and not by normal tissue proteins. CD5 was used as a T-cell marker until monoclonal antibodies against CD3 were developed.
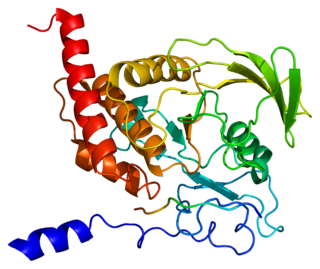
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6, also known as Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN6 gene.

Signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) is a regulatory membrane glycoprotein from SIRP family expressed mainly by myeloid cells and also by stem cells or neurons.

CD244 also known as 2B4 or SLAMF4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD244 gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR3DL1 gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DL1 gene.

Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAIR1 gene. LAIR1 has also been designated as CD305.

Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN7 gene.

Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIGLEC7 gene. SIGLEC7 has also been designated as CD328.

Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B, member 1, also known as KLRB1, NKR-P1A or CD161, is a human gene.
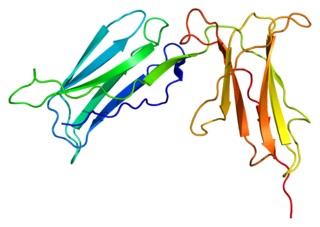
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DS4 gene.

Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCR2 gene. NCR2 has also been designated as CD336, NKp44, NKP44; NK-p44, LY95, and dJ149M18.1.

Hematopoietic cell signal transducer is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCST gene.

Signal-regulatory protein beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIRPB1 gene. SIRPB1 has also recently been designated CD172B.

Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily A member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LILRA2 gene.

Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2(TREM2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TREM2 gene. TREM2 is expressed on macrophages, immature monocyte-derived dendritic cells, osteoclasts, and microglia, which are immune cells in the central nervous system. In the liver, TREM2 is expressed by several cell types, including macrophages, that respond to injury. In the intestine, TREM2 is expressed by myeloid-derived dendritic cells and macrophage. TREM2 is overexpressed in many tumor types and has anti-inflammatory activities. It might therefore be a good therapeutic target.
CD94/NKG2 is a family of C-type lectin receptors which are expressed predominantly on the surface of NK cells and a subset of CD8+ T-lymphocyte. These receptors stimulate or inhibit cytotoxic activity of NK cells, therefore they are divided into activating and inhibitory receptors according to their function. CD94/NKG2 recognize nonclassical MHC glycoproteins class I (HLA-E in human and Qa-1 molecules in the mouse).
Nasu–Hakola disease also known as polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy is a rare disease characterised by early-onset dementia and multifocal bone cysts. It is caused by autosomal recessive loss of function mutations in either the TREM2 or TYROBP gene that are found most frequently in the Finnish and Japanese populations.