
The country of Brazil occupies roughly half of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. Brazil covers a total area of 8,514,215 km2 (3,287,357 sq mi) which includes 8,456,510 km2 (3,265,080 sq mi) of land and 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. The highest point in Brazil is Pico da Neblina at 2,994 m (9,823 ft). Brazil is bordered by the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela, and French Guiana.

Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.

Mato Grosso do Sul is one of Brazil's 27 federal units, located in the southern part of the Central-West Region, bordering five Brazilian states: Mato Grosso, Goiás and Minas Gerais (northeast), São Paulo (east) and Paraná (southeast); and two South American countries: Paraguay and Bolivia (west). It is divided into 79 municipalities and covers an area of 357,145.532 square kilometers, which is about the same size as Germany. With a population of 2,839,188 inhabitants in 2021, Mato Grosso do Sul is the 21st most populous state in Brazil.

The Paraguay River is a major river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay and Argentina. It flows about 2,695 kilometres (1,675 mi) from its headwaters in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso to its confluence with the Paraná River north of Corrientes and Resistencia.

The Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay. It sprawls over an area estimated at between 140,000 and 195,000 km2. Various subregional ecosystems exist, each with distinct hydrological, geological, and ecological characteristics; up to 12 of them have been defined.
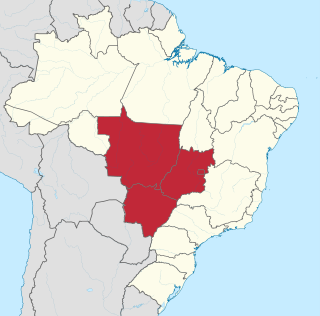
The Central-West or Center-West Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul; along with Distrito Federal, where Brazil's national capital, Brasília, is situated. The region comprises 18.86% of the national territory, and is the least populated in Brazil.

Corumbá is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, 425 km northwest of Campo Grande, the state's capital. It has a population of approximately 112,000 inhabitants, and its economy is based mainly on agriculture, animal husbandry, mineral extraction, and tourism, being the gateway to the biggest wetlands of the world, the Pantanal. Due to its border with Bolivia, Bolivians in Brazil constitute a significant portion of the city's population, forming a distinct cultural community. The city is served by Corumbá International Airport.

The Chapada dos Guimarães National Park is a national park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It is a region of rugged terrain with dramatic cliffs and waterfalls, and contains the geographical centre of the continent.

The Emas National Park is a national park and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the states of Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul in Brazil.
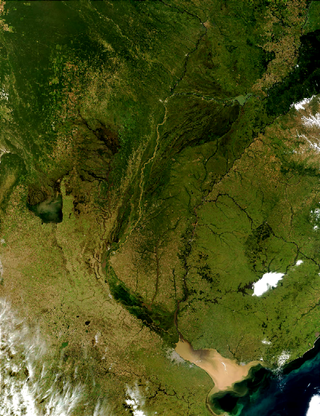
The Río de la Plata basin, more often called the River Plate basin in scholarly writings, sometimes called the Platine basin or Platine region, is the 3,170,000-square-kilometre (1,220,000 sq mi) hydrographical area in South America that drains to the Río de la Plata. It includes areas of southeastern Bolivia, southern and central Brazil, the entire country of Paraguay, most of Uruguay, and northern Argentina. Making up about one fourth of the continent's surface, it is the second largest drainage basin in South America and one of the largest in the world.
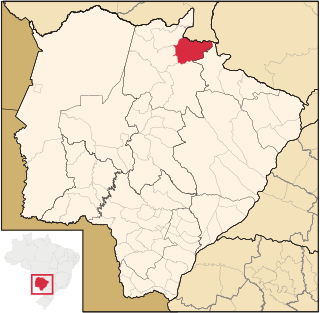
Alcinópolis is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. Its population was 5,417 (2020) and its area is 4,400 km².
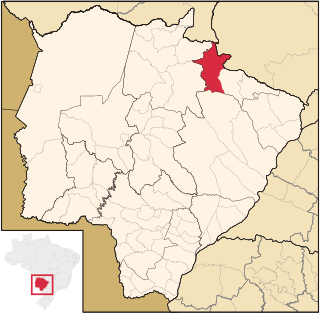
Costa Rica is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. Its population was 21,142 (2020) and its area is 5,723 km².

Coxim is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. Its population was 33,459 (2020) and its area is 6,412 km². It was founded in 1729.

The Pantanal Matogrossense National Park is a national park in the state of Mato Grosso at the border to Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil.

Serra da Bodoquena National Park is a national park in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil.

The Cuiabá River is a Brazilian river in the western state of Mato Grosso that flows in the Río de la Plata Basin. It is a tributary of the São Lourenço River.

The Rio Negro is a river of Mato Grosso do Sul state in southwestern Brazil.
An alluvial megafan is a large cone or fan-shaped deposit built up by complex deposition patterns of stream flows originating from a single source point known as an apex. Megafans differ from alluvial fans in their sheer size. Due to their larger size, they may be formed by different geomorphic processes. The criterion of what differentiates megafans from typical alluvial fans is an artificial one of scale. The scale divide varies in the literature, with the most common being a 100-km apex-to-toe length. Alternative values as little of 30-km apex-to-toe length have been proposed, as well as alternative metrics like coverage areas of greater than 10,000 square-km.
The Serra de Santa Bárbara State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It preserves a unique environment where the Amazon rainforest, pantanal and cerrado meet, and holds many endemic or endangered species.
The Nascentes do Rio Taquari State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. It protects the headwaters of the Taquari River in an area in the transition between the cerrado and pantanal biomes.


















