Related Research Articles

Backgammon is a two-player board game played with counters and dice on tables boards. It is the most widespread Western member of the large family of tables games, whose ancestors date back nearly 5,000 years to the regions of Mesopotamia and Persia. The earliest record of backgammon itself dates to 17th-century England, being descended from the 16th-century game of Irish.

Ludo is a strategy board game for two to four players, in which the players race their four tokens from start to finish according to the rolls of a single die. Like other cross and circle games, Ludo is derived from the Indian game Pachisi. The game and its variations are popular in many countries and under various names.

Tables games are a class of board game that includes backgammon and which are played on a tables board, typically with two rows of 12 vertical markings called points. Players roll dice to determine the movement of pieces. Tables games are among the oldest known board games, and many different varieties are played throughout the world. They are called 'tables' games because the boards consist of four quadrants or 'tables'. The vast majority are race games, the tables board representing a linear race track with start and finish points, the aim being to be first to the finish line, but the characteristic features that distinguish tables games from other race games are that they are two-player games using a large number of pieces, usually fifteen per player.

Tabula, meaning a plank or board, was a Greco-Roman board game for two players that has given its name to the tables family of games of which backgammon is a member.

Pachisi is a cross and circle board game that originated in Ancient India. It is described in the ancient text Mahabharata under the name of "Pasha". It is played on a board shaped like a symmetrical cross. A player's pieces move around the board based upon a throw of six or seven cowrie shells, with the number of shells resting with the aperture upward indicating the number of spaces to move.

Nard is an historical Persian tables game for two players that is sometimes considered ancestral to backgammon. It is still played today, albeit in a different form. As in other tables games, the playing pieces are moved around a board according to rolls of dice. It uses a standard tables board, but has a different opening layout and rules of play from that of backgammon.

Acey-deucey is a tables game, a family of board games that includes backgammon. Since World War I, it has been a favorite game of the United States Navy, Marine Corps, and Merchant Marine. Some evidence shows that it was played in the early 1900s aboard U.S. Navy ships. The game is believed to be rooted in the Middle East, Greece, or Turkey, where there were variants in which the game started with pieces off the board.

Gul bara is a tables game, an ancient genre of board games that includes Backgammon, Trictrac and Nard. It is also called Rosespring Backgammon or Crazy Narde. The aim of the game is to move all of one's men around the board and bear them off. The first player who bears off all his or her men wins. The game is popular in Bulgaria, Azerbaijan, Greece, Turkey and North Macedonia.
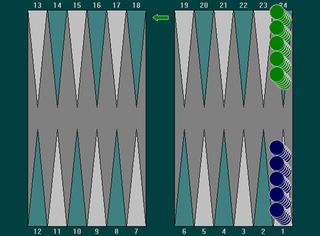
Plakoto (Πλακωτό) is a tables game for two players that is popular in Greece. The object is for the player to bring all 15 pieces around to his or her own home board and then bear them off. The player who bears off all 15 pieces first wins the game. This game is usually played along with two other variants, Févga and Pórtes. Together these three games are called Távli, and are played in sequence usually one after the other. Game is three, five or seven points. A Middle Eastern version of this game is Mahbusa, and the Bulgarian version of Plakoto is known as Tapa and also as Tsillitón (Τσιλλιτόν), in Cyprus. Parlett places Plakoto in the same group as the popular mediaeval game of English, as well as the French games of Tieste and Impérial, the Italian game of Testa and Spanish Emperador.
Tavli, sometimes called Greek backgammon in English, is the most popular way of playing tables games in Greece and Cyprus and is their national board game. Tavli is a compendium game for two players which comprises three different variants played in succession: Portes, Plakoto and Fevga. These are played in a cycle until one player reaches the target score - usually five or seven points.

Jacquet is a tables game played on a backgammon-like board and which was once very popular in France and several other parts of Europe. It probably emerged around 1800, but is attested by 1827. In the 20th century it replaced the classic French backgammon equivalent — the game of Trictrac — until Jacquet itself was superseded by Anglo-American games in the 1960s.
Robert Charles Bell (1917–2002) was the author of several books on board games, most importantly Board and Table Games 1 & 2. This work won the Premier Award of the Doctors' Hobbies Exhibition, London. He was instrumental in popularizing traditional games, and is acknowledged as one of 11 "principal sources" in David Parlett's The Oxford History of Board Games.
This glossary of board games explains commonly used terms in board games, in alphabetical order. For a list of board games, see List of board games; for terms specific to chess, see Glossary of chess; for terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems.

The following is a glossary of terms used in tables games, essentially games played on a Backgammon-type board. Terms in this glossary should not be game-specific, but applicable to a range of tables games.

Irish or the Irish Game was an Anglo-Scottish tables game for two players that was popular from the 16th to the mid-18th centuries before being superseded by its derivative, the "faster paced" backgammon. In its day, Irish was "esteemed among the best games at Tables." Its name notwithstanding, Irish was one of the most international forms of tables games, the equivalent of French toutes tables, Italian tavole reale and Spanish todas tablas, the latter name first being used in the 1283 El Libro de los Juegos, a translation of Arabic manuscripts by the Toledo School of Translators.

Ludus Anglicorum, also called the English Game, is an historical English tables game for two players using a board similar to that used today for Backgammon and other games. It is a "strategic game for serious game-players" and was well known in the Middle Ages. At one time it was considered the most popular tables game in England.
Verquere is an historical tables game. It was played by two players on a tables board of the same type as used in backgammon, but the direction and rules of play were quite different from that game.

Long Nardy, also just Nardy, is a Russian tables game for two players. It is also played in Armenia as Long Nardi or Nardi. It probably originated in the historical Persian game of Nard. It requires a tables board, 15 men apiece and two dice.

Fevga is a popular Greek tables game for two players. It is usually played as one of three different games in succession – the others being Portes and Plakoto – in social gatherings or coffee shops. When played in this way, it is known as Tavli. Very similar games, with slight variations, are Turkish Moultezim, Russian Narde and Egyptian and Lebanese Tawla 31 or Maghribiyyah.

Gioul is a tables game for two players that is common in the Levant and may have originated in Turkey. The set up and play are as in Greek Plakoto, blocking is as in Moultezim and doublets are very powerful as in the game of Gul Bara.