
Pterygotus is a genus of giant predatory eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Pterygotus have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from Middle Silurian to Late Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from four continents; Australia, Europe, North America and South America, which indicates that Pterygotus might have had a nearly cosmopolitan (worldwide) distribution. The type species, P. anglicus, was described by Swiss naturalist Louis Agassiz in 1839, who gave it the name Pterygotus, meaning "winged one". Agassiz mistakenly believed the remains were of a giant fish; he would only realize the mistake five years later in 1844.

The crustacean order Tanaidacea make up a minor group within the class Malacostraca. There are about 940 species in this order.

Megalograptus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Megalograptus have been recovered in deposits of Katian age in North America. The genus contains five species: M. alveolatus, M. ohioensis, M. shideleri, M. welchi and M. williamsae, all based on fossil material found in the United States. Fossils unassigned to any particular species have also been found in Canada. The generic name translates to "great writing" and originates from the mistaken original belief that Megalograptus was a type of graptolite, often given names ending with -graptus.

Slimonia is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Slimonia have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in South America and Europe. Classified as part of the family Slimonidae alongside the related Salteropterus, the genus contains three valid species, S. acuminata from Lesmahagow, Scotland, S. boliviana from Cochabamba, Bolivia and S. dubia from the Pentland Hills of Scotland and one dubious species, S. stylops, from Herefordshire, England. The generic name is derived from and honors Robert Slimon, a fossil collector and surgeon from Lesmahagow.

Gigantometrus swammerdami, commonly called the giant forest scorpion, is a scorpion belonging to the family Scorpionidae. It is native to India. It is the world's largest scorpion species with 23 cm (9 in) in length, and weigh as much as 56 g (2.0 oz).

Carcinosoma is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Carcinosoma are restricted to deposits of late Silurian age. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, which the genus lends its name to, Carcinosoma contains seven species from North America and Great Britain.

Hughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Hughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of the Silurian age in China and the United States. Classified as part of the basal family Hughmilleriidae, the genus contains three species, H. shawangunk from the eastern United States, H. socialis from Pittsford, New York, and H. wangi from Hunan, China. The genus is named in honor of the Scottish geologist Hugh Miller.
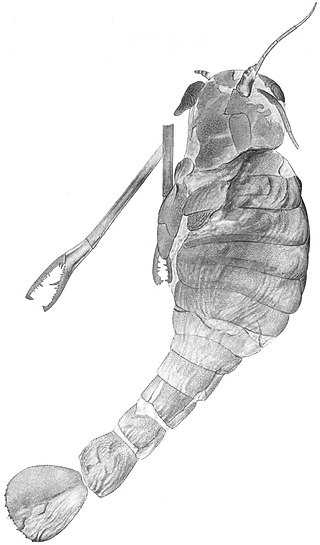
Acutiramus is a genus of giant predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Acutiramus have been discovered in deposits of Late Silurian to Early Devonian age. Seven species have been described, five from North America and two from the Czech Republic. The generic name derives from Latin acuto and Latin ramus ("branch"), referring to the acute angle of the final tooth of the claws relative to the rest of the claw.

Jaekelopterus is a genus of predatory eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Jaekelopterus have been discovered in deposits of Early Devonian age, from the Pragian and Emsian stages. There are two known species: the type species J. rhenaniae from brackish to fresh water strata in the Rhineland, and J. howelli from estuarine strata in Wyoming. The generic name combines the name of German paleontologist Otto Jaekel, who described the type species, and the Greek word πτερόν (pteron) meaning "wing".

Drepanopterus is an extinct genus of eurypterid and the only member of the family Drepanopteridae within the Mycteropoidea superfamily. There are currently three species assigned to the genus. The genus has historically included more species, with nine species having been associated with the genus Drepanopterus. Five of these have since been proven to be synonyms of pre-existing species, assigned to their own genera, or found to be based on insubstantial fossil data. The holotype of one species proved to be a lithic clast.

Onychopterella is a genus of predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Onychopterella have been discovered in deposits from the Late Ordovician to the Late Silurian. The genus contains three species: O. kokomoensis, the type species, from the Early Pridoli epoch of Indiana; O. pumilus, from the Early Llandovery epoch of Illinois, both from the United States; and O. augusti, from the Late Hirnantian to Early Rhuddanian stages of South Africa.
Salteropterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Salteropterus have been discovered in deposits of Late Silurian age in Britain. Classified as part of the family Slimonidae, the genus contains one known valid species, S. abbreviatus, which is known from fossils discovered in Herefordshire, England, and a dubious species, S. longilabium, with fossils discovered in Leintwardine, also in Herefordshire. The generic name honours John William Salter, who originally described S. abbreviatus as a species of Eurypterus in 1859.

Holmipterus is a problematic genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. The type and only species of Holmipterus, H. suecicus, is known from deposits of Middle Silurian age in the Sweden. The generic name honours Gerhard Holm, a renowned Swedish palaeontologist specialising in arthropods and crustaceans, and the species name suecicus is Latin for 'Swedish'.

Erettopterus is a genus of large predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Erettopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from Early Silurian to the Early Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from two continents; Europe and North America. The genus name is composed by the Ancient Greek words ἐρέττω (eréttō), which means "rower", and πτερόν (pterón), which means "wing", and therefore, "rower wing".

Polydesmida is the largest order of millipedes, containing approximately 3,500 species, including all the millipedes reported to produce hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Polydesmids grow and develop through a series of moults, adding segments until they reach a fixed number in the adult stage, which is usually the same for a given sex in a given species, at which point the moulting and the addition of segments and legs stop. This mode of development, known as teloanamorphosis, distinguishes this order from most other orders of millipedes, which usually continue to moult as adults, developing through either euanamorphosis or hemianamorphosis.

Pterygotidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. They were members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea. Pterygotids were the largest known arthropods to have ever lived with some members of the family, such as Jaekelopterus and Acutiramus, exceeding 2 metres (6.6 ft) in length. Their fossilized remains have been recovered in deposits ranging in age from 428 to 372 million years old.

Hughmilleriidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. The hughmilleriids were the most basal members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea, in contrast with the more derived families Pterygotidae and Slimonidae. Despite their classification as pterygotioids, the hughmilleriids possessed several characteristics shared with other eurypterid groups, such as the lanceolate telson.

Slimonidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Slimonids were members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea and the family most closely related to the derived pterygotid eurypterids, which are famous for their cheliceral claws and great size. Many characteristics of the Slimonidae, such as their flattened and expanded telsons, support a close relationship between the two groups.
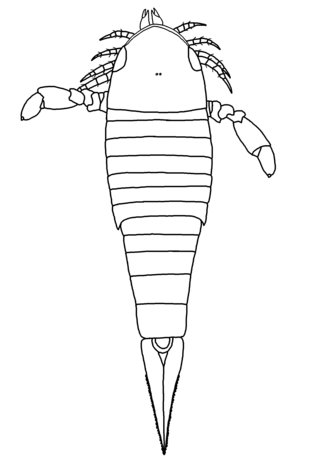
Herefordopterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Herefordopterus is classified as part of the family Hughmilleriidae, a basal family in the highly derived Pterygotioidea superfamily of eurypterids. Fossils of the single and type species, H. banksii, have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in Herefordshire and Shropshire, England. The genus is named after Herefordshire, where most of the Herefordopterus fossils have been found. The specific epithet honors Richard Banks, who found several well-preserved specimens, including the first Herefordopterus fossils.

Ciurcopterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Ciurcopterus have been discovered in deposits of Late Silurian age in North America. Classified as part of the family Pterygotidae, the genus contains two species, C. sarlei from Pittsford, New York and C. ventricosus from Kokomo, Indiana. The genus is named in honor of Samuel J. Ciurca, Jr., who has contributed significantly to eurypterid research by discovering a large amount of eurypterid specimens, including the four specimens used to describe Ciurcopterus itself.
















