 1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene | |
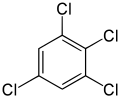 1,2,3,5-Tetrachlorobenzene | |
 1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.390 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H2Cl4 | |
| Molar mass | 215.88 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Tetrachlorobenzene is any of three isomeric chlorobenzenes with the molecular formula C6H2Cl4. They differ by the positions of the chlorine atoms around the ring. Tetrachlorobenzenes are colorless crystalline compounds. [1]