Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:

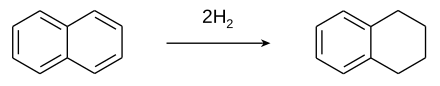
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula C
10H
8. It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs.

In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen (H−), a hydrogen atom with two electrons. The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. For inorganic chemists, hydrides refer to compounds and ions in which hydrogen is covalently attached to a less electronegative element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed.

Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.

Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula NaH. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in contrast to molecular hydrides such as borane, silane, germane, ammonia, and methane. It is an ionic material that is insoluble in all solvents (other than molten sodium metal), consistent with the fact that H− ions do not exist in solution.

Pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) consisting of four fused benzene rings, resulting in a flat aromatic system. The chemical formula is C16H10. This yellow-green solid is the smallest peri-fused PAH. Pyrene forms during incomplete combustion of organic compounds.

Decalin, a bicyclic organic compound, is an industrial solvent. A colorless liquid with an aromatic odor, it is used as a solvent for many resins or fuel additives.

In organic chemistry, a radical anion is a free radical species that carries a negative charge. Radical anions are encountered in organic chemistry as reduced derivatives of polycyclic aromatic compounds, e.g. sodium naphthenide. An example of a non-carbon radical anion is the superoxide anion, formed by transfer of one electron to an oxygen molecule. Radical anions are typically indicated by .

The Bergius process is a method of production of liquid hydrocarbons for use as synthetic fuel by hydrogenation of high-volatile bituminous coal at high temperature and pressure. It was first developed by Friedrich Bergius in 1913. In 1931 Bergius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his development of high-pressure chemistry.
In chemistry, transfer hydrogenation is a chemical reaction involving the addition of hydrogen to a compound from a source other than molecular H2. It is applied in laboratory and industrial organic synthesis to saturate organic compounds and reduce ketones to alcohols, and imines to amines. It avoids the need for high-pressure molecular H2 used in conventional hydrogenation. Transfer hydrogenation usually occurs at mild temperature and pressure conditions using organic or organometallic catalysts, many of which are chiral, allowing efficient asymmetric synthesis. It uses hydrogen donor compounds such as formic acid, isopropanol or dihydroanthracene, dehydrogenating them to CO2, acetone, or anthracene respectively. Often, the donor molecules also function as solvents for the reaction. A large scale application of transfer hydrogenation is coal liquefaction using "donor solvents" such as tetralin.

Basketane is a polycyclic alkane with the chemical formula C10H12. The name is taken from its structural similarity to a basket shape. Basketane was first synthesized in 1966, independently by Masamune and Dauben and Whalen. A patent application published in 1988 used basketane, which is a hydrocarbon, as a source material in doping thin diamond layers because of the molecule's high vapor pressure, carbon ring structure, and fewer hydrogen-to-carbon bond ratio.
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds.

The Sodium Reactor Experiment was a pioneering nuclear power plant built by Atomics International at the Santa Susana Field Laboratory near Simi Valley, California. The reactor operated from 1957 to 1964. On July 12, 1957 the Sodium Reactor Experiment became the first nuclear reactor in California to produce electrical power for a commercial power grid by powering the nearby city of Moorpark. In July 1959, the reactor experienced a partial meltdown when 13 of the reactor's 43 fuel elements partially melted, and a controlled release of radioactive gas into the atmosphere occurred. The reactor was repaired and restarted in September 1960. In February 1964, the Sodium Reactor Experiment was in operation for the last time. Removal of the deactivated reactor was completed in 1981. Technical analyses of the 1959 incident have produced contrasting conclusions regarding the types and quantities of radioactive materials released. Members of the neighboring communities have expressed concerns about the possible impacts on their health and environment from the incident. In August 2009, 50 years after the occurrence, the Department of Energy hosted a community workshop to discuss the 1959 incident.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.
In nitrile reduction a nitrile is reduced to either an amine or an aldehyde with a suitable chemical reagent.

FLiBe is the name of a molten salt made from a mixture of lithium fluoride (LiF) and beryllium fluoride. It is both a nuclear reactor coolant and solvent for fertile or fissile material. It served both purposes in the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment (MSRE) at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
A nuclear reactor coolant is a coolant in a nuclear reactor used to remove heat from the nuclear reactor core and transfer it to electrical generators and the environment. Frequently, a chain of two coolant loops are used because the primary coolant loop takes on short-term radioactivity from the reactor.
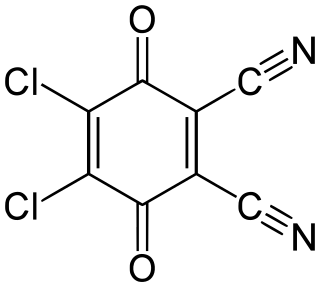
2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (or DDQ) is the chemical reagent with formula C6Cl2(CN)2O2. This oxidant is useful for the dehydrogenation of alcohols, phenols, and steroid ketones. DDQ decomposes in water, but is stable in aqueous mineral acid.
Exxon donor solvent process (EDS) is a coal liquefaction process developed by Exxon Research and Engineering Company, starting in 1966. The process converts solid coal directly to liquid synthetic fuels which could be used as a substitute for petroleum products. The process does not involve an intermediate step of coal gasification. Exxon operated a pilot plant in Texas from 1980 until 1982.
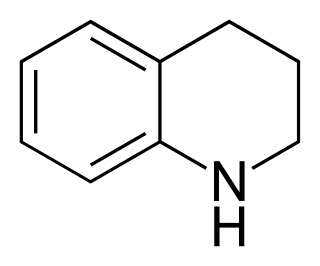
Tetrahydroquinoline is an organic compound that is the semi-hydrogenated derivative of quinoline. It is a colorless oil.