
A small supernumerary marker chromosome (sSMC) is an abnormal extra chromosome. It contains copies of parts of one or more normal chromosomes and like normal chromosomes is located in the cell's nucleus, is replicated and distributed into each daughter cell during cell division, and typically has genes which may be expressed. However, it may also be active in causing birth defects and neoplasms. The sSMC's small size makes it virtually undetectable using classical cytogenetic methods: the far larger DNA and gene content of the cell's normal chromosomes obscures those of the sSMC. Newer molecular techniques such as fluorescence in situ hybridization, next generation sequencing, comparative genomic hybridization, and highly specialized cytogenetic G banding analyses are required to study it. Using these methods, the DNA sequences and genes in sSMCs are identified and help define as well as explain any effect(s) it may have on individuals.
Trisomy 8 causes Warkany syndrome 2, a human chromosomal disorder caused by having three copies (trisomy) of chromosome 8. It can appear with or without mosaicism.

The VACTERL association refers to a recognized group of birth defects which tend to co-occur. This pattern is a recognized association, as opposed to a syndrome, because there is no known pathogenetic cause to explain the grouped incidence.

Larsen syndrome (LS) is a congenital disorder discovered in 1950 by Larsen and associates when they observed dislocation of the large joints and face anomalies in six of their patients. Patients with Larsen syndrome normally present with a variety of symptoms, including congenital anterior dislocation of the knees, dislocation of the hips and elbows, flattened facial appearance, prominent foreheads, and depressed nasal bridges. Larsen syndrome can also cause a variety of cardiovascular and orthopedic abnormalities. This rare disorder is caused by a genetic defect in the gene encoding filamin B, a cytoplasmic protein that is important in regulating the structure and activity of the cytoskeleton. The gene that influences the emergence of Larsen syndrome is found in chromosome region, 3p21.1-14.1, a region containing human type VII collagen gene. Larsen syndrome has recently been described as a mesenchyme disorder that affects the connective tissue of an individual. Autosomal dominant and recessive forms of the disorder have been reported, although most cases are autosomal dominant. Reports have found that in Western societies, Larsen syndrome can be found in one in every 100,000 births, but this is most likely an underestimate because the disorder is frequently unrecognized or misdiagnosed.
The Pallister–Killian syndrome (PKS), also termed tetrasomy 12p mosaicism or the Pallister mosaic aneuploidy syndrome, is an extremely rare and severe genetic disorder. PKS is due to the presence of an extra and abnormal chromosome termed a small supernumerary marker chromosome (sSMC). sSMCs contain copies of genetic material from parts of virtually any other chromosome and, depending on the genetic material they carry, can cause various genetic disorders and neoplasms. The sSMC in PKS consists of multiple copies of the short arm of chromosome 12. Consequently, the multiple copies of the genetic material in the sSMC plus the two copies of this genetic material in the two normal chromosome 12's are overexpressed and thereby cause the syndrome. Due to a form of genetic mosaicism, however, individuals with PKS differ in the tissue distributions of their sSMC and therefore show different syndrome-related birth defects and disease severities. For example, individuals with the sSMC in their heart tissue are likely to have cardiac structural abnormalities while those without this sSMC localization have a structurally normal heart.

Axenfeld–Rieger syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder, which affects the development of the teeth, eyes, and abdominal region.
Emanuel syndrome, also known as derivative 22 syndrome, or der(22) syndrome, is a rare disorder associated with multiple congenital anomalies, including profound intellectual disability, preauricular skin tags or pits, and conotruncal heart defects. It can occur in offspring of carriers of the constitutional chromosomal translocation t(11;22)(q23;q11), owing to a 3:1 meiotic malsegregation event resulting in partial trisomy of chromosomes 11 and 22. An unbalanced translocation between chromosomes 11 and 22 is described as Emanuel syndrome. It was first described in 1980 by American medical researchers Beverly S. Emanuel and Elaine H. Zackai, and a consortium of European scientists the same year.

Cat-eye syndrome (CES) or Schmid–Fraccaro syndrome is a rare condition caused by an abnormal extra chromosome, i.e. a small supernumerary marker chromosome. This chromosome consists of the entire short arm and a small section of the long arm of chromosome 22. In consequence, individuals with the cat-eye syndrome have three (trisomic) or four (tetrasomic) copies of the genetic material contained in the abnormal chromosome instead of the normal two copies. The prognosis for patients with CES varies depending on the severity of the condition and their associated signs and symptoms, especially when heart or kidney abnormalities are seen.

18p- is a genetic condition caused by a deletion of all or part of the short arm of chromosome 18. It occurs in about 1 of every 50,000 births.
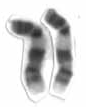
Tetrasomy 9p is a rare chromosomal disorder characterized by the presence of two extra copies of the short arm of chromosome 9, in addition to the usual two. Symptoms of tetrasomy 9p vary widely among affected individuals but typically include varying degrees of delayed growth, abnormal facial features and intellectual disability. Symptoms of the disorder are comparable to those of trisomy 9p.
FG syndrome (FGS) is a rare genetic syndrome caused by one or more recessive genes located on the X chromosome and causing physical anomalies and developmental delays. FG syndrome was named after the first letters of the surnames of the first patients noted with the disease. First reported by American geneticists John M. Opitz and Elisabeth G. Kaveggia in 1974, its major clinical features include intellectual disability, hyperactivity, hypotonia, and a characteristic facial appearance including macrocephaly.

Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.

Macrocephaly-capillary malformation (M-CM) is a multiple malformation syndrome causing abnormal body and head overgrowth and cutaneous, vascular, neurologic, and limb abnormalities. Though not every patient has all features, commonly found signs include macrocephaly, congenital macrosomia, extensive cutaneous capillary malformation, body asymmetry, polydactyly or syndactyly of the hands and feet, lax joints, doughy skin, variable developmental delay and other neurologic problems such as seizures and low muscle tone.
Malpuech facial clefting syndrome, also called Malpuech syndrome or Gypsy type facial clefting syndrome, is a rare congenital syndrome. It is characterized by facial clefting, a caudal appendage, growth deficiency, intellectual and developmental disability, and abnormalities of the renal system (kidneys) and the male genitalia. Abnormalities of the heart, and other skeletal malformations may also be present. The syndrome was initially described by Georges Malpuech and associates in 1983. It is thought to be genetically related to Juberg-Hayward syndrome. Malpuech syndrome has also been considered as part of a spectrum of congenital genetic disorders associated with similar facial, urogenital and skeletal anomalies. Termed "3MC syndrome", this proposed spectrum includes Malpuech, Michels and Mingarelli-Carnevale (OSA) syndromes. Mutations in the COLLEC11 and MASP1 genes are believed to be a cause of these syndromes. The incidence of Malpuech syndrome is unknown. The pattern of inheritance is autosomal recessive, which means a defective (mutated) gene associated with the syndrome is located on an autosome, and the syndrome occurs when two copies of this defective gene are inherited.

Distal 18q- is a genetic condition caused by a deletion of genetic material within one of the two copies of chromosome 18. The deletion involves the distal section of 18q and typically extends to the tip of the long arm of chromosome 18.

Ring chromosome 18 is a genetic condition caused by a deletion of the two ends of chromosome 18 followed by the formation of a ring-shaped chromosome. It was first reported in 1964.

13q deletion syndrome is a rare genetic disease caused by the deletion of some or all of the large arm of human chromosome 13. Depending upon the size and location of the deletion on chromosome 13, the physical and mental manifestations will vary. It has the potential to cause intellectual disability and congenital malformations that affect a variety of organ systems. Because of the rarity of the disease in addition to the variations in the disease, the specific genes that cause this disease are unknown. This disease is also known as:

Tetrasomy X, also known as 48,XXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has four, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. It is associated with intellectual disability of varying severity, characteristic "coarse" facial features, heart defects, and skeletal anomalies such as increased height, clinodactyly, and radioulnar synostosis. Tetrasomy X is a rare condition, with few medically recognized cases; it is estimated to occur in approximately 1 in 50,000 females.

Pentasomy X, also known as 49,XXXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has five, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. Pentasomy X is associated with short stature, intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, heart defects, skeletal anomalies, and pubertal and reproductive abnormalities. The condition is exceptionally rare, with an estimated prevalence between 1 in 85,000 and 1 in 250,000.















