
Phycology is the scientific study of algae. Also known as algology, phycology is a branch of life science.

Prasiola is a genus of fresh water and marine green algae. Each individual plant is small but they usually grow side by side to form a green turf on rock surfaces. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution.

Nostoc, also known as star jelly, troll's butter, spit of moon, fallen star, witch's butter, and witch's jelly, is the most common genus of cyanobacteria found in a variety of both aquatic and terrestrial environments that may form colonies composed of filaments of moniliform cells in a gelatinous sheath of polysaccharides. It may also grow symbiotically within the tissues of plants, providing nitrogen to its host through the action of terminally differentiated cells known as heterocysts. Nostoc is a genus that includes many species that are diverse in morphology, habitat distribution, and ecological function. Nostoc can be found in soil, on moist rocks, at the bottom of lakes and springs, and rarely in marine habitats. It may also be found in terrestrial temperate, desert, tropical, or polar environments.

Felix Eugen Fritsch FRS was a British biologist.

Lemanea is a genus of freshwater red algae, in the order Batrachospermales. Both species are considered to be widespread in the northern hemisphere. Although placed in the Rhodophyta it in fact is green in colour.
The history of phycology is the history of the scientific study of algae. Human interest in plants as food goes back into the origins of the species, and knowledge of algae can be traced back more than two thousand years. However, only in the last three hundred years has that knowledge evolved into a rapidly developing science.
Thorea is a genus of fresh water algae in the division Rhodophyta. Thorea is a small alga with filaments up to 200 cm long, dark green in colour and not red as are marine Rhodophyta. The filaments have only as few secondary branches.
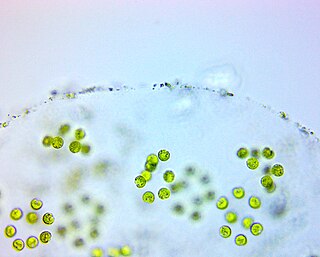
The Tetrasporaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. They are found in freshwater habitats.

Draparnaldia is a genus of freshwater green algae in the family Chaetophoraceae. Draparnaldia are uniseriate; each filament is composed of a chain of cells arranged in one row. Chloroplasts appear as a band within the center of each cell. The length of the main axis cells are generally the same, regardless of whether or not they bear branches. These side branches are divided extensively into terminal hairs. The entire plant is enveloped in loose, slippery mucilage. Draparnaldia is a cosmopolitan genus with wide distribution and it is usually found in cold aerated waters. They are either attached to sand or grow epiphytically on other aquatic plants. Draparnaldia can be seen growing in clear streams trailing on stones and boulders. Herman S. Forest of The Southern Appalachian Botanical Club has stated that while not common, it is present frequently enough to be recorded in almost all local flora lists of green algae that have been compiled. A multitude of species are present in Lake Baikal, Siberia and have been described by Meyer and Jasnitzky. A species of the genus had been placed and described in the Linnean Herbarium as Conferva mutabilis Roth in 1797. Nowadays Conferva is no longer used and the species is described as Draparnaldia mutabilis (Roth) Bory. Bory is added in honour of the researcher of the same name, based on whose description the genus was separated from similar appearing forms. Bory is accredited with the establishment of the genus.

Paulschulzia is a genus of green algae, specifically of the family Tetrasporaceae.
Planktosphaeria is a genus of Chlorophyceae of the green algae. It was first described by the phycologist Gilbert Morgan Smith in 1918, with Planktosphaeria gelatinosa as its type species. Species of Planktosphaeria are commonly found in freshwater plankton around the world.

Tetraspora is a genus of green algae in the family Tetrasporaceae of the order Chlamydomonadales, division Chlorophyta. Species of Tetraspora are unicellular green algae that exist in arrangements of four and consist of cells being packaged together in a gelatinous envelope that creates macroscopic colonies. These are primarily freshwater organisms, although there have been few cases where they have been found inhabiting marine environments and even contaminated water bodies. Tetraspora species can be found all around the globe, except in Antarctica. Despite the ubiquitous presence, the greatest growth of the genera's species is seen in the polar climatic zones.

Trentepohlia is a genus of filamentous chlorophyte green algae in the family Trentepohliaceae, living free on terrestrial supports such as tree trunks and wet rocks or symbiotically in lichens. The filaments of Trentepohlia have a strong orange colour caused by the presence of large quantities of carotenoid pigments which mask the green of the chlorophyll.

Bambusina is a genus of freshwater green algae in the family Desmidiaceae. Bambusina is a cosmopolitan genus, typically associated with acidic and oligotrophic waters. Species of this genus, particularly B. borreri, have been reported in all continents except Antarctica.
Korshikoviella is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae.

Vaucheria is a genus of Xanthophyceae or yellow-green algae known as water felt. It is one of only two genera in the family Vaucheriaceae. The type species of the genus is Vaucheria disperma.

Pediastrum duplex is a species of fresh water green algae in the genus Pediastrum. It is the type species of the genus Pediastrum.
Geminella minor is a species of filamentous freshwater green alga in the family Chlorellaceae. The species probably has a cosmopolitan distribution. The type specimen came from Switzerland and the species has been reported in the British Isles and elsewhere in the northern hemisphere, including Japan, Ukraine and North America. It occurs in freshwater aquatic habitats.

Thoreales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae. The order consists only one family, ThoreaceaeHassall, 1845. The family of Thoreaceae was circumscribed by Arthur Hill Hassall in A history of the British freshwater algae, including descriptions of the Desmideae and Diatomaceae in 1845.

Batrachospermum is a genus of red algae from the family Batrachospermaceae. Due to its complex biological life cycle, descriptions of the taxon typically focus on gametophytes, while sporophytes, i.e., carposporophytes, are filamentous structures growing on the gametophyte, on which they depend. Independently living sporophytes have sometimes been described as separate species within the genus Chantransia. Additionally, differences may occur in the descriptions of the genus due to variations in taxonomic approaches, as new taxonomic techniques, as with other algae, result in changes in the assignment of individual species to the genus Batrachospermum. The genus is cosmopolitan, and its representatives are found in freshwater environments, mainly rivers, and less frequently in standing waters. These plants have thalli in the form of gelatinous-coated filaments.















