
Pulp is a fibrous lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically or mechanically producing cellulosic fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemicals or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products.

Paraná is one of the 26 states of Brazil, in the south of the country. It is bordered in the north by São Paulo state, in the east by the Atlantic Ocean, in the south by Santa Catarina state and the province of Misiones, Argentina, and in the west by Mato Grosso do Sul and Paraguay, with the Paraná River as its western boundary. It is subdivided into 399 municipalities, and its capital is the city of Curitiba. Other major cities are Londrina, Maringá, Ponta Grossa, Cascavel, São José dos Pinhais and Foz do Iguaçu. The state is home to 5.4% of the Brazilian population and generates 6.2% of the Brazilian GDP.

UPM-Kymmene Oyj is a Finnish forest industry company. UPM-Kymmene was formed by the merger of Kymmene Corporation with Repola Oy and its subsidiary United Paper Mills Ltd in 1996. UPM consists of six business areas: UPM Fibres, UPM Energy, UPM Raflatac, UPM Specialty Papers, UPM Communication Papers and UPM Plywood. The Group employs around 17,000 people and it has production plants in 11 countries. UPM shares are listed on the NASDAQ OMX Helsinki stock exchange. UPM is the only paper company which is listed in the global Dow Jones Sustainability Index and also a member of the United Nations Global Compact organization.

The Carnation Revolution, also known as the 25 April, was a military coup by military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo government on 25 April 1974 in Lisbon, producing major social, economic, territorial, demographic, and political changes in Portugal and its overseas colonies through the Processo Revolucionário Em Curso. It resulted in the Portuguese transition to democracy and the end of the Portuguese Colonial War.

Figueira da Foz, also known as Figueira for short, is a city and a municipality in the Coimbra District, in Portugal. Practically at the midpoint of the Iberian Peninsula's Atlantic coast, it is located at the mouth of the Mondego River, 40 km (25 mi) west of Coimbra and sheltered by hills, sharing about the same latitude with Philadelphia, Baku and Beijing. The population of the municipality in 2011 was 62,125, in an area of 379.05 km2 (146.35 sq mi). The city of Figueira da Foz proper has a population of 46,600. It is the second largest city in the district of Coimbra.

Klabin is a Brazilian paper producing, exporting and recycling company headquartered in São Paulo. It is the largest paper producer and exporter in the country, focusing on the production of pulp, packaging paper and board, corrugated cardboard packaging, and industrial sacks, besides selling timber in logs. It is controlled by Klabin Irmãos & Cia and NIBLAK Participações S/A, which jointly own 52.23% of the voting capital. It is organized into four business units certified by the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC).

The Central Region or Central Portugal is one of the statistical regions of Portugal. The cities with major administrative status inside this region are Coimbra, Aveiro, Viseu, Caldas da Rainha, Leiria, Castelo Branco, Torres Vedras, Tomar, and Guarda. It is one of the seven Regions of Portugal. It is also one of the regions of Europe, as given by the European Union for statistical and geographical purposes. Its area totals 28,462 km2 (10,989 sq mi). As of 2011, its population totalled 2,327,026 inhabitants, with a population density of 82 inhabitants per square kilometre.

Semapa - Sociedade de Investimento e Gestão is a Portuguese conglomerate holding company with interests in the cement, pulp and paper and environmental services sectors.
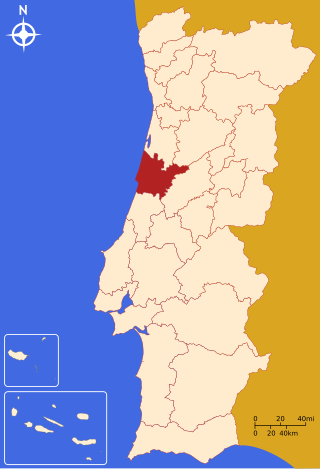
Baixo Mondego is a former Portuguese NUTS3 subregion that comprised the lower part of the Mondego River. It was abolished at the January 2015 NUTS 3 revision. It was a subregion of the Centro Region, centered on the historical city of Coimbra. With an area of 2,062 km² and a population of 336,376 inhabitants, the Baixo Mondego was a subregion with a mean density of 163/km². The subregion was named after the Mondego River and all this river area has been known as Baixo Mondego since ancient times, even before the creation of the NUTS3.

Grupo Desportivo Fabril is a Portuguese sports club established as Grupo Desportivo CUF do Barreiro, with CUF standing for the company Companhia União Fabril. A multisports club best known for its football section, it was founded as a works team in the city of Barreiro, District of Setúbal, on 27 January 1937. CUF Barreiro's greatest achievement was a third place in the 1964–65 Portuguese Liga season. The club's football home ground is the Complexo Desportivo Alfredo da Silva, which was inaugurated in June 1965 and named after Alfredo da Silva, an entrepreneur who was the founder of CUF.
Myllykoski Corporation was a family owned international paper group with central offices in Helsinki and Anjalankoski, manufacturing in Germany, Finland and North America, and sales offices around the world. The roots of the company date back to its founding by the Björnberg family in 1892. The company was acquired in 2011 by Finnish manufacturer UPM-Kymmene.

Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses, or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through a fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed on the surface, followed by pressing and drying. Although paper was originally made in single sheets by hand, almost all is now made on large machines—some making reels 10 metres wide, running at 2,000 metres per minute and up to 600,000 tonnes a year. It is a versatile material with many uses, including printing, painting, graphics, signage, design, packaging, decorating, writing, and cleaning. It may also be used as filter paper, wallpaper, book endpaper, conservation paper, laminated worktops, toilet tissue, currency, and security paper, or in a number of industrial and construction processes.

The environmental effects of paper are significant, which has led to changes in industry and behaviour at both business and personal levels. With the use of modern technology such as the printing press and the highly mechanized harvesting of wood, disposable paper became a relatively cheap commodity, which led to a high level of consumption and waste. The rise in global environmental issues such as air and water pollution, climate change, overflowing landfills and clearcutting have all lead to increased government regulations. There is now a trend towards sustainability in the pulp and paper industry as it moves to reduce clear cutting, water use, greenhouse gas emissions, fossil fuel consumption and clean up its influence on local water supplies and air pollution.
Suzano Papel e Celulose is a Brazilian producer of paper and pulp with a presence in over 80 countries. It is the largest paper and pulp company in Latin America. The company is headquartered in Salvador, administrative office in São Paulo and others offices in Buenos Aires, Fort Lauderdale, London, Shanghai and Signy-Avenex. It is one of the largest in its sector in the world.

The Companhia União Fabril (CUF) was one of the largest and oldest Portuguese conglomerates from the 1930s to 1974 and later a chemical corporation which was by then a part of Grupo José de Mello founded in 1988. After many acquisitions, mergers and divestitures, from the late 1970s to the 2010s, the company known as CUF and its brand was gradually restructured and morphed into a brand-new hospital in Lisbon. Now the brand cuf, whose major shareholders and founders are heirs of the old CUF conglomerate, is tied to one of the major healthcare providers of Portugal known as cuf saúde with several hospitals and clinics across the country and formerly known as José de Melo Saúde, a healthcare provider which is a division of Grupo José de Mello. The chemical industry businesses were consolidated in 2018 into a new brand and company called Bondalti which was established within the Grupo José de Mello.

Powell River Mill was a pulp mill and paper mill located in the Canadian town of Powell River, British Columbia. Part of Catalyst Paper, the mill has three paper machines which produce 469,000 tonnes of newsprint and uncoated fine paper. The mill had 441 employees as of 2014.
Pedro Queiroz Pereira was a Portuguese businessman and former competition driver.
Manuel Carvalheiro was a Portuguese filmmaker, documentary filmmaker, screenwriter, independent film producer, essayist, columnist and film critic. He was the first Portuguese film theorist.

Maria Judite Pinto Mendes de Abreu (1916–2007) was one of the first five Portuguese women to be elected as a mayor of a municipality. She served as mayor of Coimbra from 1976 to 1979 and as president of the municipal assembly of the same city from 1983 to 1986. An opponent of the Estado Novo dictatorship, she was a supporter of General Norton de Matos in the 1949 national election and a member of women's and other organizations that campaigned against the government. After the overthrow of the Estado Novo by the 1974 Carnation Revolution, she was active in the court that judged crimes committed by the dictatorship. Among other honours, she was awarded the Portuguese Order of Liberty.
















