
Theodoxus fluviatilis, common name the river nerite, is a species of small freshwater and brackish water snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Neritidae, the nerites.
Fluvidona anodonta or more commonly known as the North Pine River freshwater snail is a species of minute freshwater snail that is endemic to Australia. Originally discovered in 1892 by Hedley & Musson, the snail is highly elusive and only has been sighted four times since its discovery. The snail is 2 mm long and 1 mm wide with the shell colouring being of a yellow-whiteish shade. Fluvidona anodonta resides within the Moreton Bay Region, specifically in four river systems within the D'Aguilar National Park, Queensland. The four river systems are the South Pine River headwaters, the North Pine River headwaters, Kobble Creek and Low Branch Creek. The snail is found under deeply submerged rocks within permanent freshwater systems.
Beddomeia camensis is a species of very small freshwater snail that is endemic to Australia. The invertebrate is 2-4 mm in size, it is a gastropod mollusk and belongs to the Hydrobiidae family, a large family of freshwater snails recognised by their small size and cosmopolitan distribution. Beddomeia camensis is one of the least populated species within its family distributed across only 5 small to medium-sized streams that flow into the Cam River catchment in North-West Tasmania.

Beddomeia fultoni(B. fultoni) is a species of small freshwater snail belonging to the family Tateidae.

Beddomeia hallae, also known as Buttons Rivulet hydrobiid snail, is a species of small freshwater snail that is endemic to Australia. The species is an aquatic operculate gastropod mollusk in the family Hydrobiidae. Beddomeia hallae belongs to the genus Beddomeia, which is the largest group in the family Hydrobiidae, consisting of 47 species. In the Threatened Species Protection Act 1995, this species is one of the 37 Beddomeia species listed as endangered, however, on the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List, the species is listed as vulnerable. Found in Tasmania, in the streams of Buttons Rivulet and Castra Rivulet, Beddomeia hallae is sighted in its natural habitat amongst wood, leaves and under stones. Nonetheless, the Beddomeia species including Beddomeia hallae are geographically isolated, existing within restricted ranges.
Beddomeia launcestonensis is a species of very small freshwater snail that has a gill and an operculum, an aquatic operculate gastropod mollusk in the family Hydrobiidae. This species is endemic to Australia.
The Beddomeia minima is a population of freshwater snails that are endemic to Australia. It is commonly called a hydrobiid snail. This population was listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List in 2011 due to its distribution being restricted to a single location and range of possible threats present in Tasmania. The Beddomeia minima is one of a few fresh water snail species belonging to the same genus Beddomeia that survive in Tasmania, Australia, specifically a single location in the Scottsdale area.
Beddomeia waterhouseae, also known as Claytons Rivulet freshwater snail, is a species of freshwater snail in the family Tateidae. This species is endemic to northern Tasmania in Australia. The holotype specimen was found in a very small tributary of Little Clayton's Rivulet and is held at the Australian Museum. B. waterhouseae is small and as an adult has a shell measuring between 1.7 to 3.7 mm in length. The shell shape is ovate-conic to broadly conic and has a thin inner lip and no columellar bulge. This species feeds on algae and detritus on rocks. The female of the species lay single eggs in capsules made of sand grains and attached to the underside of rocks or wood. B. waterhouseae is considered vulnerable by the IUCN as it has a very small range and is sensitive to water quality and so may be threatened by disturbances of its habitat. Other threats include habitat loss. Conservation activities such as assessment of the aquatic ecosystem and vegetal surveys are being undertaken in an attempt to preserve this species.

Cumberlandia monodonta is a freshwater mussel endemic to the United States. Currently, C. monodonta is listed as an endangered species by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
The lacy elimia also known as the lacey elimia, scientific name Elimia crenatella, is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Pleuroceridae.

Newcomb's snail is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, a gastropod mollusk in the family Lymnaeidae. This species is endemic to Hawaii, in the United States. Its natural habitat is rivers. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Leptoxis ampla, common name the round rocksnail, is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusc in the family Pleuroceridae.

The plicate rocksnail, scientific name Leptoxis plicata, is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Pleuroceridae.

Theodoxus is a genus of nerites, small water snails with an operculum, some of which live in freshwater, and some in both freshwater and brackish water, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family Neritidae, the nerites.
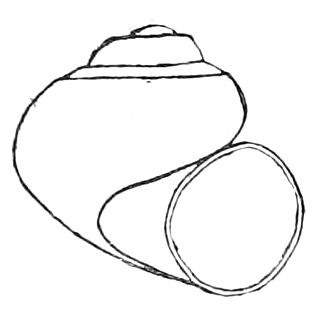
The Utah roundmouth snail, also known as the Utah valvata or desert valvata, scientific name Valvata utahensis, is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusc in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails.
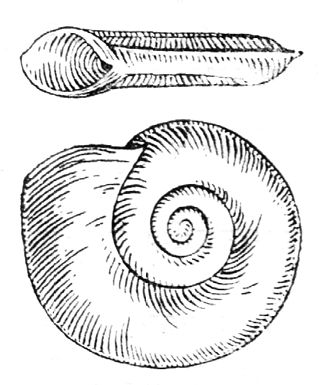
Planorbis carinatus is species of air-breathing freshwater snail, a pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ramshorn snails.

Bathyomphalus contortus is a species of small air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails and their allies.

Gillia altilis, common name the Buffalo pebblesnail, is a species of freshwater snail, an aquatic gastropod mollusk with an operculum in the family Lithoglyphidae.

Theodoxus altenai is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Neritidae, the nerites.

Squalius valentinus, commonly known as the Valencia chub and the Levantine bagra, is a species of freshwater fish in the carp family Cyprinidae. It was first isolated from the Turia River in Valencia, hence its name. It is considered endangered. This species is differentiated from its cogenerates by having eight branched rays in its dorsal fin; eight branched rays in its anal fin; two rows of pharyngeal teeth on both sides possessing 2 and 5 teeth ; a wide caudal peduncle; its number of gill rakers; the number of scales in its lateral line; the number of scale rows above the latter; by possessing three scale rows below it; by having thirty-nine vertebrae ; showing large 4th and 5th infraorbital bones; a maxilla with a very distinct marked anterior process; exhibiting a frontal bone expanded at the middle; a wide neurocranium bone; the lower branch of the pharyngeal bone being robust; a large and narrow urohyal; as well as genetic differences (allozymes).













