
Photosynthesis is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their activities. Photosynthetic organisms use intracellular organic compounds to store the chemical energy they produce in photosynthesis within organic compounds like sugars, glycogen, cellulose and starches. Photosynthesis is usually used to refer to oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that produces oxygen. To use this stored chemical energy, the organisms' cells metabolize the organic compounds through another process called cellular respiration. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth.
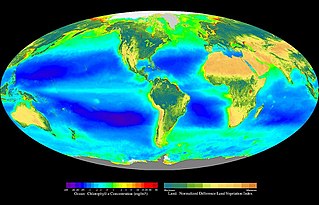
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as primary producers or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either net or gross, the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not.

Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. All living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. Each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level. In order to more efficiently show the quantity of organisms at each trophic level, these food chains are then organized into trophic pyramids. The arrows in the food chain show that the energy flow is unidirectional, with the head of an arrow indicating the direction of energy flow; energy is lost as heat at each step along the way.

Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite. This is in accordance with Justus von Liebig's law of the minimum. The total essential plant nutrients include seventeen different elements: carbon, oxygen and hydrogen which are absorbed from the air, whereas other nutrients including nitrogen are typically obtained from the soil.
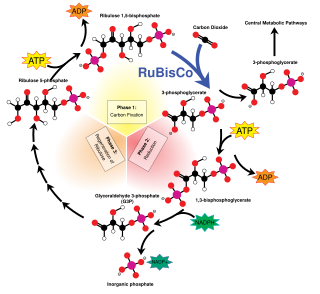
C3 carbon fixation is the most common of three metabolic pathways for carbon fixation in photosynthesis, the other two being C4 and CAM. This process converts carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP, a 5-carbon sugar) into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate through the following reaction:

Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants.

A seedling is a young sporophyte developing out of a plant embryo from a seed. Seedling development starts with germination of the seed. A typical young seedling consists of three main parts: the radicle, the hypocotyl, and the cotyledons. The two classes of flowering plants (angiosperms) are distinguished by their numbers of seed leaves: monocotyledons (monocots) have one blade-shaped cotyledon, whereas dicotyledons (dicots) possess two round cotyledons. Gymnosperms are more varied. For example, pine seedlings have up to eight cotyledons. The seedlings of some flowering plants have no cotyledons at all. These are said to be acotyledons.
The light compensation point (Ic) is the light intensity on the light curve where the rate of photosynthesis exactly matches the rate of cellular respiration. At this point, the uptake of CO2 through photosynthetic pathways is equal to the respiratory release of carbon dioxide, and the uptake of O2 by respiration is equal to the photosynthetic release of oxygen. The concept of compensation points in general may be applied to other photosynthetic variables, the most important being that of CO2 concentration – CO2 compensation point (Γ).Interval of time in day time when light intensity is low due to which net gaseous exchange is zero is called as compensation point.
The photosynthetic efficiency is the fraction of light energy converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis in green plants and algae. Photosynthesis can be described by the simplified chemical reaction
Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients it needs to live and reproduce. Microbes use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics. The specific metabolic properties of a microbe are the major factors in determining that microbe's ecological niche, and often allow for that microbe to be useful in industrial processes or responsible for biogeochemical cycles.

Algal nutrient solutions are made up of a mixture of chemical salts and seawater. Sometimes referred to as "Growth Media", nutrient solutions, provide the materials needed for algae to grow. Nutrient solutions, as opposed to fertilizers, are designed specifically for use in aquatic environments and their composition is much more precise. In a unified system, algal biomass can be collected by utilizing carbon dioxide emanating from power plants and wastewater discharged by both industrial and domestic sources. This approach allows for the concurrent exploitation of the microalgae's capabilities in both carbon dioxide fixation and wastewater treatment. Algae, macroalgae, and microalgae hold promise in addressing critical global challenges. Sustainable development goals can be advanced through algae-based solutions, to promote a healthy global ecosystem.
Ecophysiology, environmental physiology or physiological ecology is a biological discipline that studies the response of an organism's physiology to environmental conditions. It is closely related to comparative physiology and evolutionary physiology. Ernst Haeckel's coinage bionomy is sometimes employed as a synonym.

Soil respiration refers to the production of carbon dioxide when soil organisms respire. This includes respiration of plant roots, the rhizosphere, microbes and fauna.

Nutrient film technique (NFT) is a hydroponic technique where in a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth is re-circulated past the bare roots of plants in a watertight gully, also known as channels.

Plant stress measurement is the quantification of environmental effects on plant health. When plants are subjected to less than ideal growing conditions, they are considered to be under stress. Stress factors can affect growth, survival and crop yields. Plant stress research looks at the response of plants to limitations and excesses of the main abiotic factors, and of other stress factors that are important in particular situations. Plant stress measurement usually focuses on taking measurements from living plants. It can involve visual assessments of plant vitality, however, more recently the focus has moved to the use of instruments and protocols that reveal the response of particular processes within the plant
Biomass partitioning is the process by which plants divide their energy among their leaves, stems, roots, and reproductive parts. These four main components of the plant have important morphological roles: leaves take in CO2 and energy from the sun to create carbon compounds, stems grow above competitors to reach sunlight, roots absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil while anchoring the plant, and reproductive parts facilitate the continuation of species. Plants partition biomass in response to limits or excesses in resources like sunlight, carbon dioxide, mineral nutrients, and water and growth is regulated by a constant balance between the partitioning of biomass between plant parts. An equilibrium between root and shoot growth occurs because roots need carbon compounds from photosynthesis in the shoot and shoots need nitrogen absorbed from the soil by roots. Allocation of biomass is put towards the limit to growth; a limit below ground will focus biomass to the roots and a limit above ground will favor more growth in the shoot.

The CO2 fertilization effect or carbon fertilization effect causes an increased rate of photosynthesis while limiting leaf transpiration in plants. Both processes result from increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). The carbon fertilization effect varies depending on plant species, air and soil temperature, and availability of water and nutrients. Net primary productivity (NPP) might positively respond to the carbon fertilization effect. Although, evidence shows that enhanced rates of photosynthesis in plants due to CO2 fertilization do not directly enhance all plant growth, and thus carbon storage. The carbon fertilization effect has been reported to be the cause of 44% of gross primary productivity (GPP) increase since the 2000s. Earth System Models, Land System Models and Dynamic Global Vegetation Models are used to investigate and interpret vegetation trends related to increasing levels of atmospheric CO2. However, the ecosystem processes associated with the CO2 fertilization effect remain uncertain and therefore are challenging to model.

Lake metabolism represents a lake's balance between carbon fixation and biological carbon oxidation. Whole-lake metabolism includes the carbon fixation and oxidation from all organism within the lake, from bacteria to fishes, and is typically estimated by measuring changes in dissolved oxygen or carbon dioxide throughout the day.
Construction costs is a concept in biology that conveys how much glucose is required to construct a unit of plant biomass, given the biosynthetic pathways and starting from glucose and mineral constituents. It includes the sugars required to provide the carbon skeletons for the formation of e.g. lipids, lignin and proteins, but also the glucose required to produce energy (ATP) and reducing power to drive the metabolic pathways.
Biomass allocation is a concept in plant biology which indicates the relative proportion of plant biomass present in the different organs of a plant. It can also be used for whole plant communities.













