In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.

In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula CnH2n−2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood.

In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group. The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F). Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.
In organic chemistry, ozonolysis is an organic reaction where the unsaturated bonds are cleaved with ozone. Multiple carbon–carbon bond are replaced by carbonyl groups, such as aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. The reaction is predominantly applied to alkenes, but alkynes and azo compounds are also susceptible to cleavage. The outcome of the reaction depends on the type of multiple bond being oxidized and the work-up conditions.

Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide, discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.
In organic chemistry, neighbouring group participation has been defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) as the interaction of a reaction centre with a lone pair of electrons in an atom or the electrons present in a sigma or pi bond contained within the parent molecule but not conjugated with the reaction centre. When NGP is in operation it is normal for the reaction rate to be increased. It is also possible for the stereochemistry of the reaction to be abnormal when compared with a normal reaction. While it is possible for neighbouring groups to influence many reactions in organic chemistry this page is limited to neighbouring group effects seen with carbocations and SN2 reactions.
Pelargonic acid, also called nonanoic acid, is an organic compound with structural formula CH3(CH2)7CO2H. It is a nine-carbon fatty acid. Nonanoic acid is a colorless oily liquid with an unpleasant, rancid odor. It is nearly insoluble in water, but very soluble in organic solvents. The esters and salts of pelargonic acid are called pelargonates or nonanoates.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.
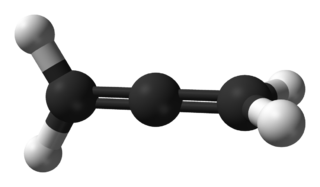
Propadiene or allene is the organic compound with the formula H2C=C=CH2. It is the simplest allene, i.e. a compound with two adjacent carbon double bonds. As a constituent of MAPP gas, it has been used as a fuel for specialized welding.
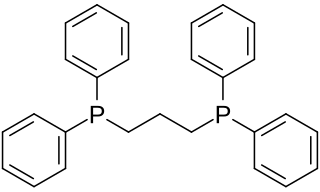
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph2P(CH2)3PPh2. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It is classified as a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
In chemistry, vinylidenes are compounds with the functional group C=CH2. An example is 1,1-dichloroethene (CCl2=CH2) commonly called vinylidene chloride. It and vinylidene fluoride are precursors to commercially useful polymers.
Borane, also known as borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula BH
3. The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated the likely existence of the borane molecule. However, the molecular species BH3 is a very strong Lewis acid. Consequently, it is highly reactive and can only be observed directly as a continuously produced, transitory, product in a flow system or from the reaction of laser ablated atomic boron with hydrogen. It normally dimerizes to diborane in the absence of other chemicals.

Methional is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCH2CH2CHO. It is a colorless liquid that is a degradation product of methionine. It is a notable flavor in potato-based snacks, namely potato chips, one of the most popular foods containing methional. Traces of the compound can also be found in black tea and green tea based products. Methional contains both aldehyde and thioether functional groups. It is readily soluble in alcohol solvents, including propylene glycol and dipropylene glycol.
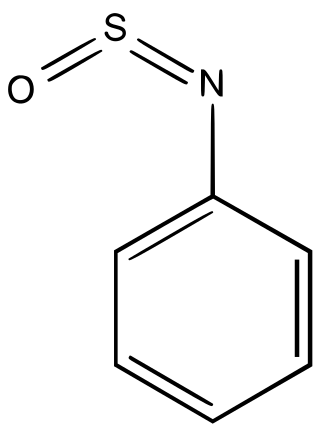
Sulfinylamines are organosulfur compounds with the formula RNSO where R = an organic substituent. These compounds are, formally speaking, derivatives of HN=S=O, i.e. analogues of sulfur dioxide and of sulfur diimide. A common example is N-sulfinylaniline. Sulfinyl amines are dienophile. They undergo [2+2] cycloaddition to ketenes.
In organic chemistry, methylenation is a chemical reaction that inserts a methylene group into a chemical compound:
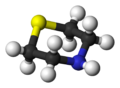
Diallylamine is the organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH=CH2)2. It is a colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. It is multifunctional, featuring a secondary amine and two alkene groups. Diallylamine is used in the production of N,N-diallyldichloroacetamide (dichlormid) and N,N-diallyldimethylammonium chloride.