The following is a timeline of the Brazilian economic stabilization plans in the "new Republic" (post-military dictatorship) era, a period characterized by intense inflation of the local currency, exceeding 2,700% in the period of 1989 to 1990.
This period was marked by intense economic experimentation (including many forms of economic heterodox shocks) and, as a whole, comprises a unique case study on macroeconomics.

The politics of Brazil take place in a framework of a federal presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. The political and administrative organization of Brazil comprises the federal government, the 26 states and a federal district, and the municipalities.

Fernando Affonso Collor de Mello is a Brazilian politician who served as the 32nd president of Brazil from 1990 to 1992, when he resigned in a failed attempt to stop his impeachment trial by the Brazilian Senate. Collor was the first president democratically elected after the end of the Brazilian military dictatorship. He became the youngest president in Brazilian history, taking office at the age of 40. After he resigned from the presidency, the impeachment trial on charges of corruption continued. Collor was found guilty by the Senate and disqualified from holding elected office for eight years (1992–2000). He was later acquitted of ordinary criminal charges in his judicial trial before Brazil's Supreme Federal Court, for lack of valid evidence.

José Sarney de Araújo Costa is a Brazilian politician, lawyer, and writer who served as 31st president of Brazil from 1985 to 1990. He briefly served as the 20th vice president of Brazil for a month between March and April 1985.

Itamar Augusto Cautiero Franco was a Brazilian politician who served as the 33rd president of Brazil from 29 December 1992 to 1 January 1995. Previously, he was the 21st vice president of Brazil from 1990 until the resignation of President Fernando Collor de Mello. During his long political career Franco also served as Senator, Mayor, Ambassador and Governor. At the time of his death he was a senator from Minas Gerais, having won the seat in the 2010 election.

Brazilian history from 1985 to the present, also known as the Sixth Brazilian Republic or New Republic, is the contemporary epoch in the history of Brazil, beginning when civilian government was restored after a 21-year-long military dictatorship established after the 1964 coup d'état. The negotiated transition to democracy reached its climax with the indirect election of Tancredo Neves by Congress. Neves belonged to the Brazilian Democratic Movement Party (MDB), the former controlled opposition to the military regime. He was the first civilian president to be elected since 1964.
The Collor Plan, is the name given to a collection of economic reforms and inflation-stabilization plans carried out in Brazil during the presidency of Fernando Collor de Mello, between 1990 and 1992. The plan was officially called New Brazil Plan, but it became closely associated with Collor himself, and "Plano Collor" became its de facto name.

Zélia Maria Cardoso de Mello served as Brazil's Minister of Economy from 1990 to 1991 under Fernando Collor de Mello. She was later married to Brazilian comedian Chico Anysio, with whom she has two children, Rodrigo and Victoria. The couple divorced in 1998.

The Cruzado Novo was the short-lived currency of Brazil between 15 January 1989 and 15 March 1990. It replaced the cruzado in the rate of 1000 cruzados = 1 cruzado novo. It had the symbol and the ISO 4217 code BRN. In 1990, the cruzado novo was renamed the (third) cruzeiro. This currency was subdivided in 100 centavos.

Presidential elections were held in Brazil in 1989, with the first round on November 15 and a second round on December 17. They were the first direct presidential elections since 1960, the first to be held using a two-round system and the first to take place under the 1988 constitution, which followed two decades of authoritarian rule after the 1964 Brazilian coup d'état.
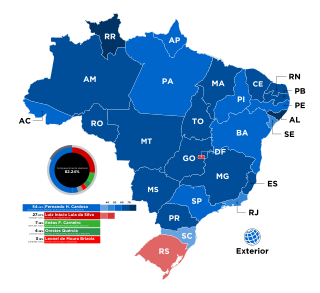
General elections were held in Brazil on October 3, 1994, the second to take place under the provisions of the 1988 constitution and the second direct presidential election since 1960.

Maílson Ferreira da Nóbrega is a Brazilian economist. He was Finance minister in José Sarney's administration during a period of hyperinflation in the late 1980s. He is married and has five children.

The following lists events that happened in the year 1989 in Brazil.

Maria da Conceição Tavares was a Portuguese naturalized Brazilian economist. She was a full professor at the State University of Campinas (Unicamp) and professor emeritus of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ). Her students included the former president of Brazil, Dilma Rousseff. Tavares was affiliated with the Workers' Party, and she was a Federal Deputy representing the state of Rio de Janeiro between 1995 and 1999. Left-wing focused, she was the author of several books on Brazil's economic development as well as numerous journal articles.

Luiz Carlos Bresser-Pereira is a Brazilian economist and social scientist. He teaches at the Getulio Vargas Foundation in São Paulo since 1959. In1981, he founded the Brazilian Journal of Political Economy and since then is its editor.
Dilson Domingos Funaro was a Brazilian businessman and politician, owner of the toy company Indústria de Brinquedos Trol. He was also CEO of the Brazilian Development Bank and later Finance Minister of Brazil during the term of President José Sarney, from August 1985 to April 1987. During his tenure as Finance Minister he was responsible for the creation of a plan for the stabilization of Brazil's monetary policy, the Plano Cruzado. He also was responsible for the unilateral suspension of payments on the Brazilian Republic's external debt to foreign financial institutions, which was implemented on February 20, 1987. With Brazil's financial crisis continuing with seemingly no solution on the horizon, Funaro was asked to resign from his post just a few months later.

In 1986 because of inflation banknotes of the cruzado were issued by Central Bank of Brazil in denominations of 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, 5000 and 10 000 cruzados. This bank had the sole authority to issue cruzado notes and Casa da Moeda do Brasil was the sole printer of these banknotes. Cruzado notes on the front/obverse featured prominent people while on the back/reverse depicted buildings and/or activities of those people mentioned before. Between 1989 and 1990 cruzado currency had also been replaced, this time by cruzado novo at a rate of 1 cruzado to 1000 cruzados novos.

The cruzeiro was the currency of Brazil between 1990 and 1993. It was the third iteration of a Brazilian currency named "cruzeiro", and replaced the cruzado novo at par. It was used until 1993, when it was replaced by the cruzeiro real at a rate of 1 cruzeiro real = 1000 cruzeiros.

The Collor government, also referred to as the Collor Era, was a period in Brazilian political history that began with the inauguration of President Fernando Collor de Mello on 15 March 1990, and ended with his resignation from the presidency on 29 December 1992. Fernando Collor was the first president elected by the people since 1960, when Jânio Quadros won the last direct election for president before the beginning of the Military Dictatorship. His removal from office on 2 October 1992, was a consequence of his impeachment proceedings the day before, followed by cassation.

The presidency of José Sarney, also called the José Sarney government was a period in Brazilian political history that corresponds to José Ribamar Ferreira Araújo da Costa Sarney's first mandate as President of the Republic until his succession by Fernando Collor. Sarney took over the position on an interim basis after Tancredo Neves was hospitalized, and definitively on 21 April 1985, with his death, when Sarney became the first civilian president after more than twenty years of military dictatorship in Brazil.

The Cruzado Plan was a set of economic measures launched by the Brazilian government on February 28, 1986, based on Decree-Law No. 2883 of February 27, 1986, with José Sarney as president and Dilson Funaro as Minister of Finance. The plan was approved in the Chamber of Deputies with 344 votes in favor and 13 against, while in the Federal Senate only 1 of the 49 parliamentarians voted against.