
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States,running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race,its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely,ideally before the Soviet Union. Taken over from the US Air Force by the newly created civilian space agency NASA,it conducted 20 uncrewed developmental flights,and six successful flights by astronauts. The program,which took its name from Roman mythology,cost $2.27 billion. The astronauts were collectively known as the "Mercury Seven",and each spacecraft was given a name ending with a "7" by its pilot.

Titan was a family of United States expendable rockets used between 1959 and 2005. The Titan I and Titan II were part of the US Air Force's intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) fleet until 1987. The space launch vehicle versions contributed the majority of the 368 Titan launches,including all the Project Gemini crewed flights of the mid-1960s. Titan vehicles were also used to lift US military payloads as well as civilian agency reconnaissance satellites and to send interplanetary scientific probes throughout the Solar System.
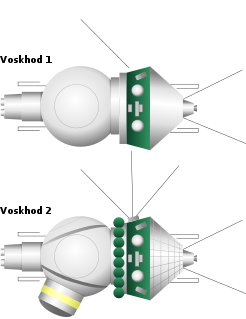
The Voskhod programme was the second Soviet human spaceflight project. Two one-day crewed missions were flown using the Voskhod spacecraft and rocket,one in 1964 and one in 1965,and two dogs flew on a 22-day mission in 1966.
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45,located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County,Florida.

Gemini 1 was the first mission in NASA's Gemini program. An uncrewed test flight of the Gemini spacecraft,its main objectives were to test the structural integrity of the new spacecraft and modified Titan II launch vehicle. It was also the first test of the new tracking and communication systems for the Gemini program and provided training for the ground support crews for the first crewed missions.

Gemini 2 was the second spaceflight of the American human spaceflight program Project Gemini,and was launched and recovered on January 19,1965. Gemini 2,like Gemini 1,was an uncrewed mission intended as a test flight of the Gemini spacecraft. Unlike Gemini 1,which was placed into orbit,Gemini 2 made a suborbital flight,primarily intended to test the spacecraft's heat shield. It was launched on a Titan II GLV rocket. The spacecraft used for the Gemini 2 mission was later refurbished into the Gemini B configuration,and was subsequently launched on another suborbital flight,along with OPS 0855,as a test for the US Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory. Gemini spacecraft no. 2 was the first craft to make more than one spaceflight since the X-15,and the only one until Space Shuttle Columbia flew its second mission in 1981;it would also be the only space capsule to be reused until Crew Dragon Endeavour was launched a second time in 2021.

The Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) was part of the United States Air Force (USAF) human spaceflight program in the 1960s. The project was developed from early USAF concepts of crewed space stations as reconnaissance satellites,and was a successor to the canceled Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar military reconnaissance space plane. Plans for the MOL evolved into a single-use laboratory,for which crews would be launched on 30-day missions,and return to Earth using a Gemini B spacecraft derived from NASA's Gemini spacecraft and launched with the laboratory.
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to 20,000-pound (9,100 kg) low Earth orbit payloads. The rocket's first stage was built as a cluster of propellant tanks engineered from older rocket tank designs,leading critics to jokingly refer to it as "Cluster's Last Stand". Its development was taken over from the Advanced Research Projects Agency in 1958 by the newly-formed civilian NASA. Its design proved sound and flexible. It was successful in initiating the development of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket propulsion,launching the Pegasus satellites,and flight verification of the Apollo command and service module launch phase aerodynamics. Ten Saturn I rockets were flown before it was replaced by the heavy lift derivative Saturn IB,which used a larger,higher total impulse second stage and an improved guidance and control system. It also led the way to development of the super-heavy lift Saturn V which carried the first men to landings on the Moon in the Apollo program.

Little Joe II was an American rocket used from 1963 to 1966 for five uncrewed tests of the Apollo spacecraft launch escape system (LES),and to verify the performance of the command module parachute recovery system in abort mode. It was named after a similar rocket designed for the same function in Project Mercury. Launched from White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico,it was the smallest of four launch rockets used in the Apollo program.

The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) and space launcher developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM,but was later adapted as a medium-lift space launch vehicle to carry payloads to Earth orbit for the United States Air Force (USAF),National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Those payloads included the USAF Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP),NOAA weather satellites,and NASA's Gemini crewed space capsules. The modified Titan II SLVs were launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base,California,up until 2003.

Titan IV was a family of heavy-lift space launch vehicles developed by Martin Marietta and operated by the United States Air Force from 1989 to 2005. Launches were conducted from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station,Florida and Vandenberg Air Force Base,California.

Titan IIIB was the collective name for a number of derivatives of the Titan II ICBM and Titan III launch vehicle,modified by the addition of an Agena upper stage. It consisted of four separate rockets. The Titan 23B was a basic Titan II with an Agena upper stage,and the Titan 24B was the same concept,but using the slightly enlarged Titan IIIM rocket as the base. The Titan 33B was a Titan 23B with the Agena enclosed in an enlarged fairing,in order to allow larger payloads to be launched. The final member of the Titan IIIB family was the Titan 34B which was a Titan 24B with the larger fairing used on the Titan 33B.

The Titan IIIC was an expendable launch system used by the United States Air Force from 1965 until 1982. It was the first Titan booster to feature large solid rocket motors and was planned to be used as a launcher for the Dyna-Soar,though the spaceplane was cancelled before it could fly. The majority of the launcher's payloads were DoD satellites,for military communications and early warning,though one flight (ATS-6) was performed by NASA. The Titan IIIC was launched exclusively from Cape Canaveral while its sibling,the Titan IIID,was launched only from Vandenberg AFB.

Project Gemini was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo,Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966.

A space capsule is an often-crewed spacecraft that uses a blunt-body reentry capsule to reenter the Earth's atmosphere without wings. Capsules are distinguished from satellites primarily by the ability to survive reentry and return a payload to the Earth's surface from orbit. Capsule-based crewed spacecraft such as Soyuz or Orion are often supported by a service or adapter module,and sometimes augmented with an extra module for extended space operations. Capsules make up the majority of crewed spacecraft designs,although one crewed spaceplane,the Space Shuttle,has flown in orbit.

A launch escape system (LES) or launch abort system (LAS) is a crew-safety system connected to a space capsule that can be used to quickly separate the capsule from its launch vehicle in case of an emergency requiring the abort of the launch,such as an impending explosion. The LES is typically controlled by a combination of automatic rocket failure detection,and a manual activation for the crew commander's use. The LES may be used while the launch vehicle is still on the launch pad,or during its ascent. Such systems are usually of two types:

The Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets,and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first five Mariner uncrewed probes to the planets Venus and Mars,and the Ranger and Lunar Orbiter uncrewed probes to the Moon. The upper stage was also used as an uncrewed orbital target vehicle for the Gemini crewed spacecraft to practice rendezvous and docking. However,the launch vehicle family was originally developed for the Air Force and most of its launches were classified DoD payloads.

The Titan II GLV or Gemini-Titan II was an American expendable launch system derived from the Titan II missile,which was used to launch twelve Gemini missions for NASA between 1964 and 1966. Two uncrewed launches followed by ten crewed ones were conducted from Launch Complex 19 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station,starting with Gemini 1 on April 8,1964.
Advanced Gemini is a number of proposals that would have extended the Gemini program by the addition of various missions,including manned low Earth orbit,circumlunar and lunar landing missions. Gemini was the second manned spaceflight program operated by NASA,and consisted of a two-seat spacecraft capable of maneuvering in orbit,docking with unmanned spacecraft such as Agena Target Vehicles,and allowing the crew to perform tethered extra-vehicular activities.

The 6555th Aerospace Test Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Eastern Space and Missile Center and stationed at Patrick Air Force Base,Florida. It was inactivated on 1 October 1990.



















