
The Douglas fir is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir, Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir and Mexican Douglas-fir.
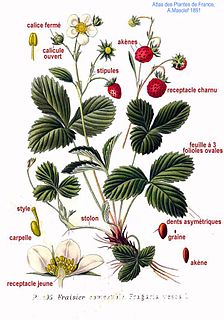
Fragaria is a genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, commonly known as strawberries for their edible fruits. There are more than 20 described species and many hybrids and cultivars. The most common strawberries grown commercially are cultivars of the garden strawberry, a hybrid known as Fragaria × ananassa. Strawberries have a taste that varies by cultivar, and ranges from quite sweet to rather tart. Strawberries are an important commercial fruit crop, widely grown in all temperate regions of the world.

Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than one pair of (homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, where each set contains one or more chromosomes and comes from each of two parents, resulting in pairs of homologous chromosomes between sets. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.

Acorus is a genus of monocot flowering plants. This genus was once placed within the family Araceae (aroids), but more recent classifications place it in its own family Acoraceae and order Acorales, of which it is the sole genus of the oldest surviving line of monocots. Some older studies indicated that it was placed in a lineage, that also includes aroids (Araceae), Tofieldiaceae, and several families of aquatic monocots. However, modern phylogenetic studies demonstrate that Acorus is sister to all other monocots. Common names include calamus and sweet flag.

Acorus calamus is a species of flowering plant with psychoactive chemicals. It is a tall wetland monocot of the family Acoraceae, in the genus Acorus. Although used in traditional medicine over centuries to treat digestive disorders and pain, there is no clinical evidence for its safety or efficacy – and ingested calamus may be toxic – leading to its commercial ban in the United States.

Arbutus menziesii or Pacific madrone, is a species of broadleaf evergreen tree in the family Ericaceae, native to the western coastal areas of North America, from British Columbia to California.

Nemophila menziesii, known commonly as baby blue eyes or baby's-blue-eyes, is an annual herb, native to western North America.

A clonal colony or genet is a group of genetically identical individuals, such as plants, fungi, or bacteria, that have grown in a given location, all originating vegetatively, not sexually, from a single ancestor. In plants, an individual in such a population is referred to as a ramet. In fungi, "individuals" typically refers to the visible fruiting bodies or mushrooms that develop from a common mycelium which, although spread over a large area, is otherwise hidden in the soil. Clonal colonies are common in many plant species. Although many plants reproduce sexually through the production of seed, reproduction occurs by underground stolons or rhizomes in some plants. Above ground, these plants most often appear to be distinct individuals, but underground they remain interconnected and are all clones of the same plant. However, it is not always easy to recognize a clonal colony especially if it spreads underground and is also sexually reproducing.

Cardamine pratensis, the cuckoo flower, lady's smock, mayflower, or milkmaids, is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae. It is a perennial herb native throughout most of Europe and Western Asia. The specific name pratensis is Latin for "meadow".

Exocarpos is a genus of flowering shrubs and small trees in the sandalwood family, Santalaceae. They are found throughout Southeast Asia, Australia and the Pacific Islands.

Banksia menziesii, commonly known as firewood banksia, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Banksia. It is a gnarled tree up to 10 m (33 ft) tall, or a lower spreading 1–3 m (3.3–9.8 ft) shrub in the more northern parts of its range. The serrated leaves are dull green with new growth a paler grey green. The prominent autumn and winter inflorescences are often two-coloured red or pink and yellow, and their colour has given rise to more unusual common names such as port wine banksia and strawberry banksia. Yellow blooms are rarely seen.

Tolmiea is a genus of flowering plants containing two species native to western North America. The genus was formerly considered to be monotypic until diploid populations were split off as T. diplomenziesii from the tetraploid populations of T. menziesii.

Tolmiea menziesii is a species of flowering plant in the family Saxifragaceae. It is known by the common names youth on age, pick-a-back-plant, piggyback plant, and thousand mothers. It is a perennial plant native to the West Coast of North America, occurring in northern California, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia and southern Alaska. It occurs as a naturalised plant or garden escape in Scotland, parts of Wales, Northern Ireland and northern and western parts of England.

Ribes menziesii, the canyon gooseberry, is a species of currant found only in California and Oregon. There are five to six varieties of the species found across the low elevation mountains of California, especially the Coast Ranges, and the coastal canyons and foothills, into southern Oregon. It can be found in the chaparral plant community.

The Rocky Mountain Floristic Region, also known as the Rocky Mountain Floristic Province, is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in western North America delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. The region extends from Kodiak Island in Alaska to the San Francisco Bay Area and Sierra Nevada in California. The Vancouverian Province comprises the coastal part of the region for its entire length, including the Pacific Coast Ranges, and the Rocky Mountain Province includes the Rocky Mountains and associated ranges. There are no endemic plant families in the region but many endemic genera and species.

Amsinckia menziesii is a species of plant in the family Boraginaceae, the borage or forget-me-not family.

Isocoma menziesii is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, known by the common name Menzies' goldenbush.

Drosera menziesii, the pink rainbow, is an erect or scrambling perennial tuberous species in the carnivorous plant genus Drosera. It is endemic to Western Australia and grows in a variety of habitats, including winter-wet depressions, swamps, and granite outcrops in clay or peat sand soils or loam. D. menziesii produces small, circular carnivorous leaves along an undulating erect stem that can be .05–1.1 m (0.2–3.6 ft) high. Its pink flowers emerge from July to November.

Ribes thacherianum, with the common name Santa Cruz gooseberry, or Santa Cruz Island gooseberry, is a rare North American species of currant found only on one island off the coast of California.


















